Method for removing PPCPs in water by catalyzing H2O2 with MIL-100 (Fe/Mn) derivative
A technology of H2O2 and derivatives, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of iron sludge precipitation, activated carbon failure, narrow applicable pH range, etc., and achieve the effect of low preparation cost and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
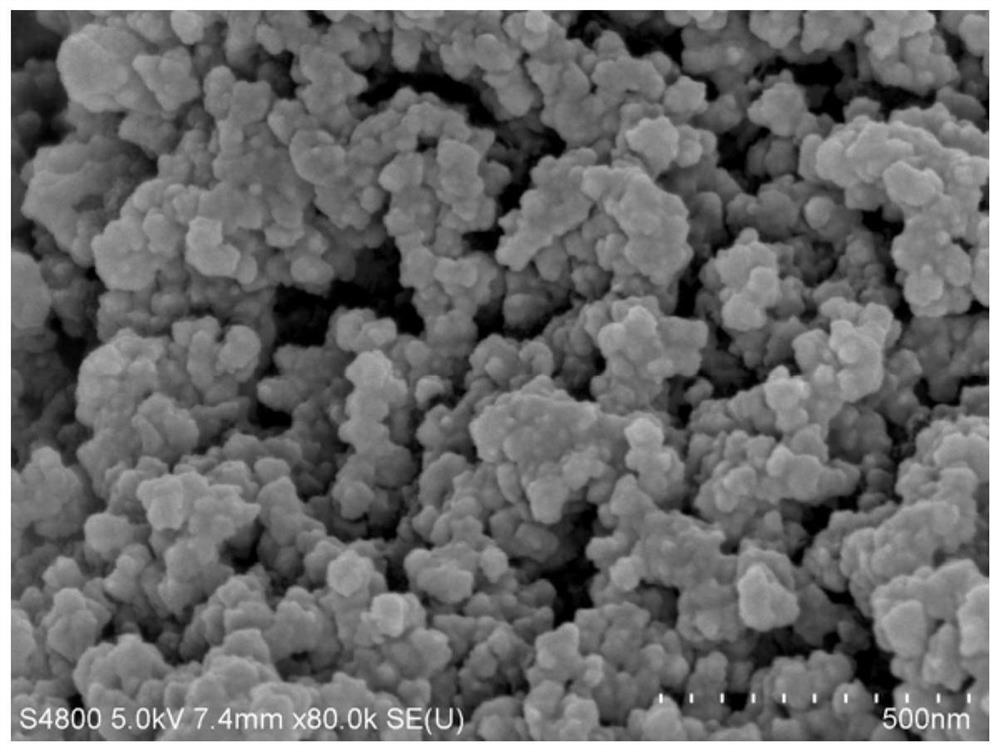
[0033] Embodiment 1: Explore the preparation and characterization of MIL-100 (Fe / Mn) derivative catalyst material, the steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) Add 2.50 g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, 0.50 g of manganese sulfate monohydrate and 2.52 g of trimesic acid into 35 ml of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), and magnetically stir and mix for 24 hours;
[0035] (2) Put the mixed solution of step (1) into a 50ml polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel autoclave, place in a muffle furnace, heat at 180°C for 12h, and cool to room temperature after the reaction is complete;
[0036] (3) The product obtained in step (2) was first washed with DMF for 3 times, then washed with ethanol for 3 times, and dried at 60° C. for 12 hours to obtain a brown powder;
[0037] (4) The brown powder prepared in (3) was calcined at 350° C. for 3 h in an air atmosphere in a muffle furnace to prepare a MIL-100 (Fe / Mn) derivative catalyst.
[0038] (5) Field emission scanning electron microscopy (...
Embodiment 2
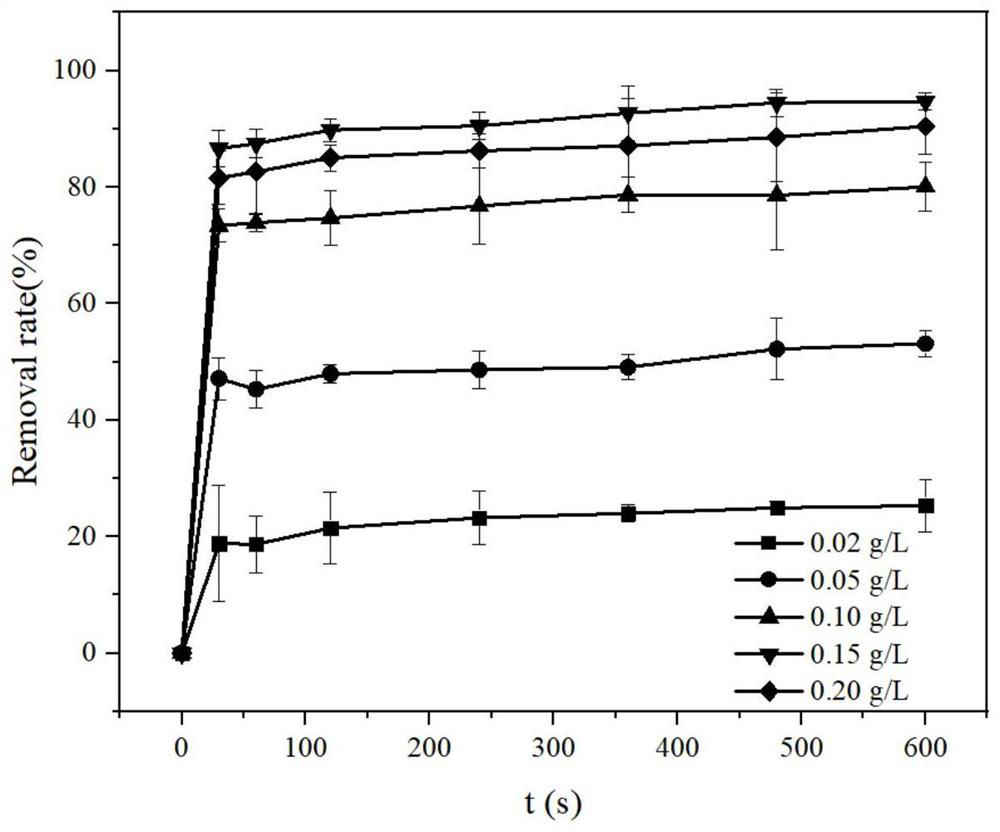
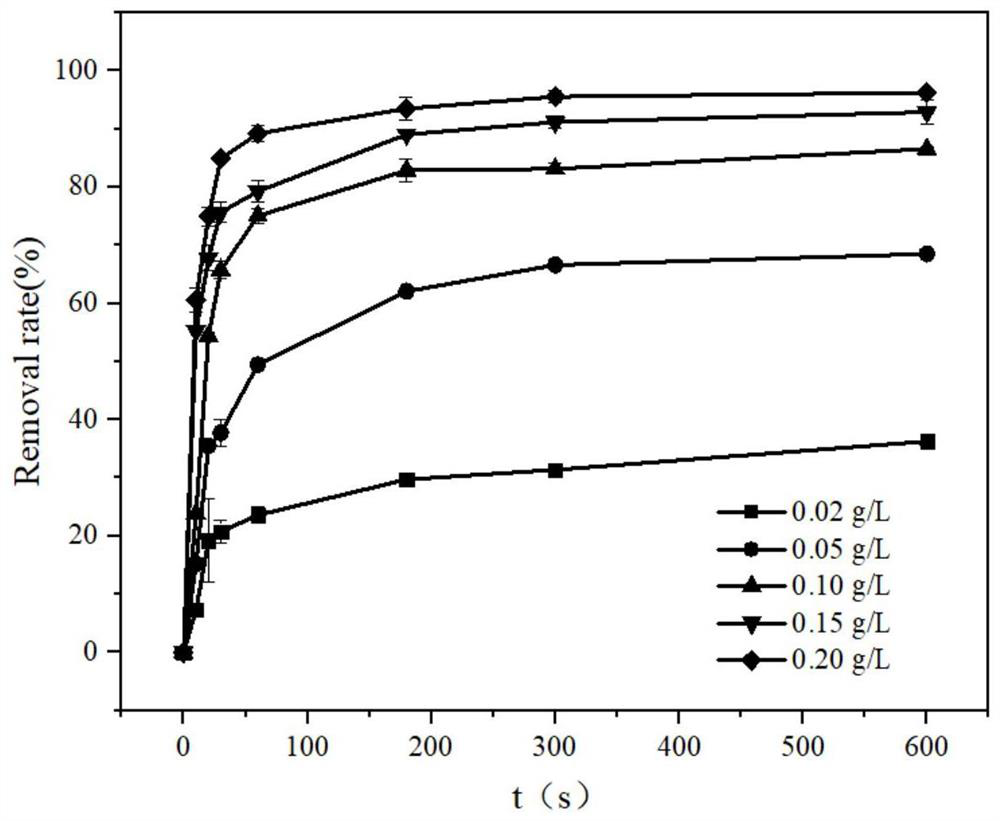
[0039] Embodiment 2: explore catalyst material dosage to MIL-100 (Fe / Mn) derivative catalytic H 2 o 2 The impact of degrading PPCPs, the details are as follows:
[0040] (1) In this implementation case, under normal temperature and pressure, the typical representatives of PPCPs MNZ and BPB aqueous solutions with a concentration of 5 mg / L were prepared respectively, and H was added with a concentration of 30 mM and 1 mM 2 o 2The mixed solution in two groups of reactors, each group is added with 0.02g / L, 0.05g / L, 0.1g / L, 0.15g / L, 0.20g / L MIL-100 (Fe / Mn) derivative catalyst, use 0.2 mol / L phosphate buffer to adjust the pH of the mixture to 7.0, and react for 10 min. The liquid samples were taken out from the reactor periodically, and the remaining MNZ and BPB concentrations of the samples were determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Please refer to the sampling time figure 2 and image 3 . Among them, the dosage concentration of MIL-100(Fe / Mn) deriva...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: Exploring initial pH to MIL-100 (Fe / Mn) derivative catalytic H 2 o 2 The impact of degrading typical PPCPs (MNZ and BPB), the details are as follows:
[0043] (1) In this implementation case, under normal temperature and pressure, MNZ and BPB, the typical representatives of PPCPs with a concentration of 5mg / L, were prepared respectively, and the concentrations of 30mM and 1mM H 2 o 2 The mixed solution of the mixed solution is placed in two groups of reactors, and each group is added the MIL-100 (Fe / Mn) derivative catalyst prepared by 0.15mg / L embodiment, and the pH of each group mixed solution is adjusted with 0.2mol / L phosphate buffer The values are 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, and the reaction takes 10 minutes. The liquid samples were taken out from the reactor periodically, and the remaining MNZ and BPB concentrations of the samples were determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Among them, the dosage concentration of MIL-100(Fe / Mn) derivat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com