C-EPS control strategy hardware-in-loop simulation development platform based on active fault tolerance
A C-EPS and control strategy technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, geometric CAD, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as low precision, lack of precise loading and steering resistance, and poor simulation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
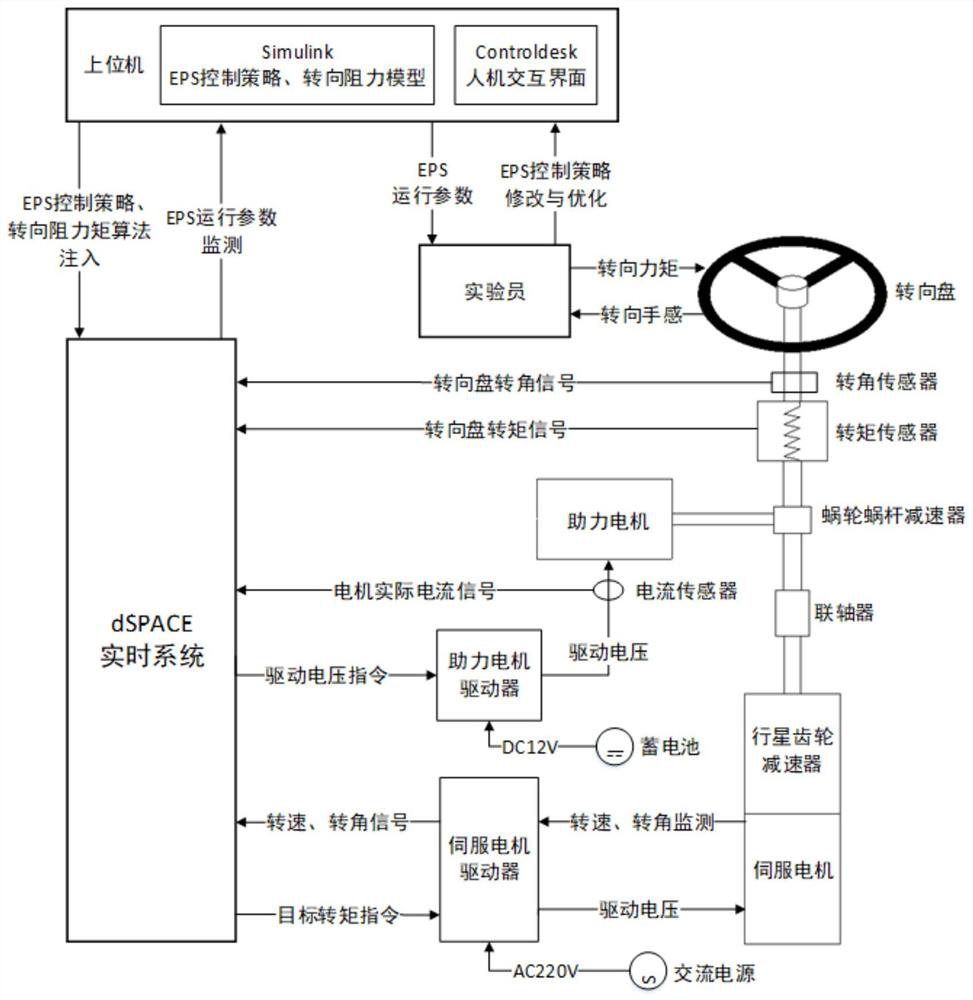
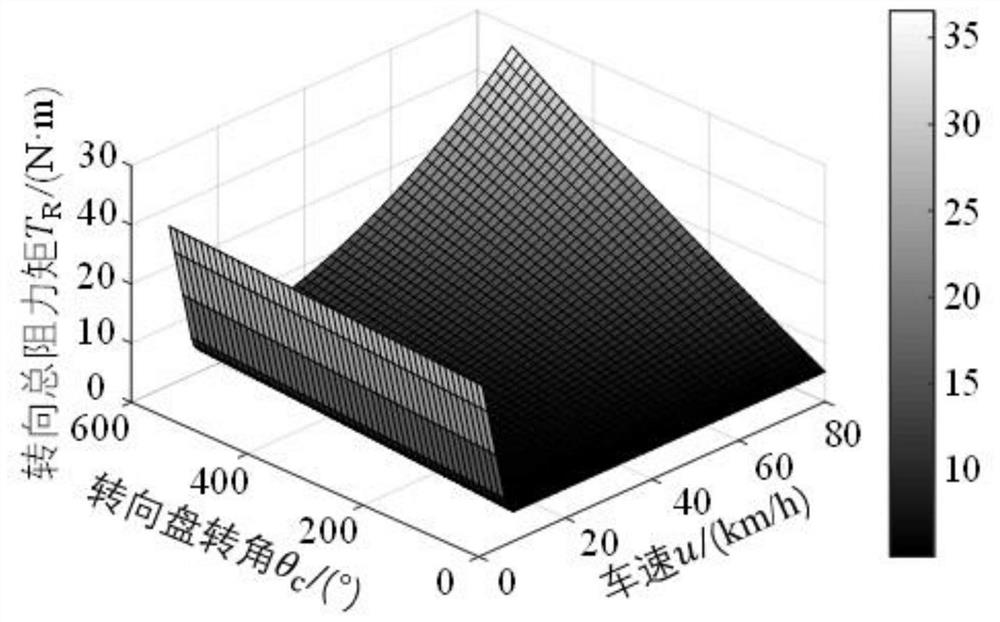
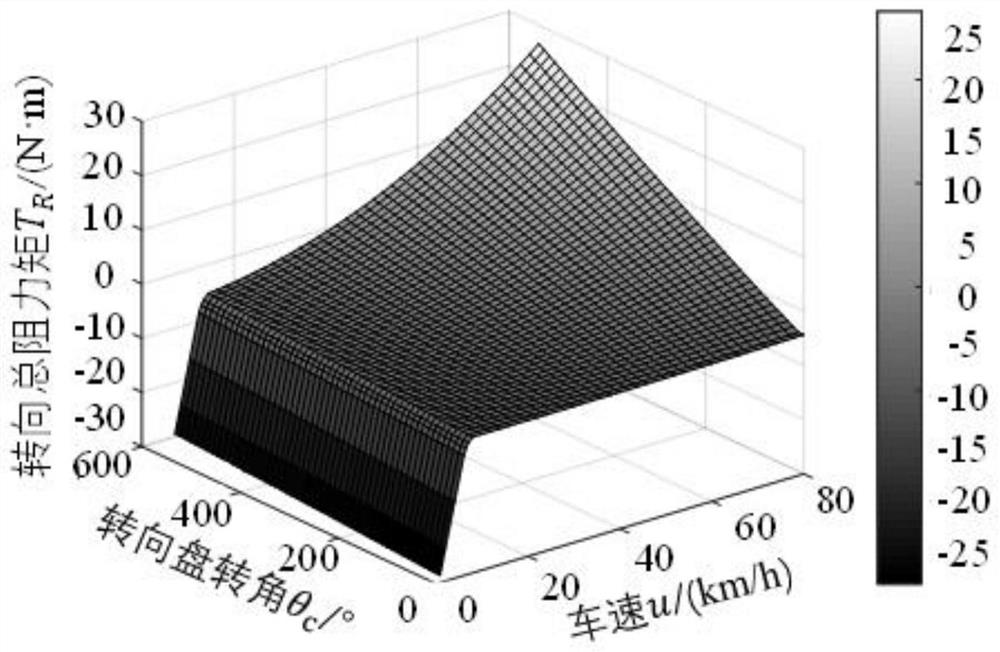
[0087] Embodiment 1: A hardware-in-the-loop simulation development platform based on active fault-tolerant C-EPS control strategy, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes hardware device, dSPACE real-time simulation system and host computer; dSPACE real-time simulation system is composed of DS1006 processor board and DS2202 HILI / O interface board. The required signals are generated, and the two are connected through the PHS++ bus; the DS1006 processor board is equipped with a 64-bit AMDOpteron as the main processor, which integrates a 256MB local memory for running the real-time model, and a 128MB global memory for communicating with the host computer For data exchange, it can be applied to rapid control prototyping (RCP) and hardware-in-the-loop (HIL), and can handle complex, large models that require extremely high processing performance, such as power systems and virtual vehicles. The DS2202 HIL I / O interface board provides 16 differential A / D acquisition channels, 24 PWM me...
Embodiment 2
[0142] Embodiment 2: The first half steps of this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1, but the control mode switching module is switched to the failure mode in the C-EPS system control strategy.
[0143] In the fault mode, the faults of the rotation angle sensor, current sensor and torque sensor are described as follows:
[0144] the y if =y i +(Δ mi -1)y i +α;
[0145] Where: y if is the actual output value of the sensor; y i is the real value; α is the sensor stuck value; Δ m is the sensor fault gain, when Δ m is 1, when α is 0, the sensor has no fault;
[0146]
[0147] the y f =y+f s ;
[0148] In the formula: when i=1,2,3, represent angle sensor, current sensor and torque sensor respectively; y f is the sensor signal with fault; y is the system status output of the sensor with fault; f s is the error deviation value of the sensor;
[0149] Taking the mandrel of the steering column, the booster motor and the booster motor circuit as reference ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com