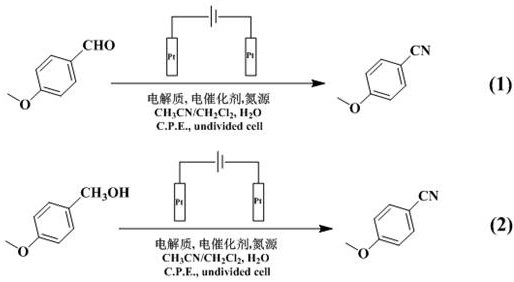
A kind of method of indirect electrocatalytic synthesis of anisonitrile
An anise nitrile and electrocatalysis technology, applied in the directions of organic chemistry, electrolysis components, electrolysis process, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of organic solvent, difficult purification treatment, large amount of waste, etc., and achieve environmental friendliness, strong atom economy, The effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
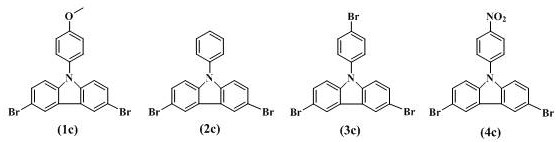
[0047] Add 0.0272 g p-methoxybenzaldehyde, 0.0040 g electrocatalyst 2c, 0.0492 g hydroxylamine sulfate, 0.3419 g tetrabutylammonium perchlorate, 8 mL solvent (volume ratio CH 3 CN:CH 2 Cl 2 =4:1), 2 mL distilled water, 50 ℃, Pt as anode, Pt as cathode, Ag / AgNO 3 (0.01 M AgNO 3 Acetonitrile solution) electrode was used as a reference electrode, and the target product anisonitrile was obtained by electrolysis at a constant potential of 1.5 V for 9 h. The yield of electrolysis products was analyzed by gas chromatography GC, and the analysis method was the area normalization method. The product yield is 95% as shown in Table 1. The reaction solution was extracted with anhydrous ether (5 mL×3), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, purified by column chromatography (petroleum ether / ethyl acetate=15:1), and then characterized.
[0048] The product structure is characterized by: 1 HNMR (500 MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 3.86 (s, 3H), 6.96 (d, J=8.5Hz, 2H), 7.59 (d, J=8.0 Hz, 2H)GC-MS (EI, ...
Embodiment 2-4、 comparative example 1
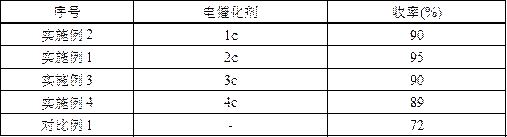
[0050] The reaction steps and reaction process are the same as in Example 1, except that the electrocatalyst is replaced by equimolar 0.0033 g 1c (Example 2), 0.0048 g 3c (Example 3), 0.0045 g 4c (Example 4) and The above constant potential electrolysis experiment was carried out without adding electrocatalyst (comparative example 1), and the results are listed in Table 1.
[0051] Table 1 Electrolysis of p-methoxybenzaldehyde to generate anisonitrile under the action of different electrocatalysts.
[0052]
[0053] It can be seen from Table 1 that all electrocatalysts 1c-4c can be used as electrocatalysts in the field of aromatic aldehyde electrooxidation to synthesize aromatic nitriles. When 2c was used as the electrocatalyst, the yield of the target product was up to 95%, so the electrocatalyst was preferably 2c (Example 1).
Embodiment 5-10
[0055] The reaction steps and reaction process are the same as in Example 1, except that the reaction temperature is 5°C (Example 5), 20°C (Example 6), 25°C (Example 7), 30°C (Example 8), 40°C °C (Example 9) and 60 °C (Example 10), the above constant potential electrolysis experiments were carried out, and the results are listed in Table 2.
[0056] Table 2 Electrolysis results at different reaction temperatures
[0057]
[0058] From the above reaction results, it can be known that the reaction temperature is preferably 50° C. (Example 1).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com