Electronic waste recycling method
An electronic waste, step three technology, applied in the direction of photography technology, equipment, photography auxiliary technology, etc., can solve the problem of untreated residue, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
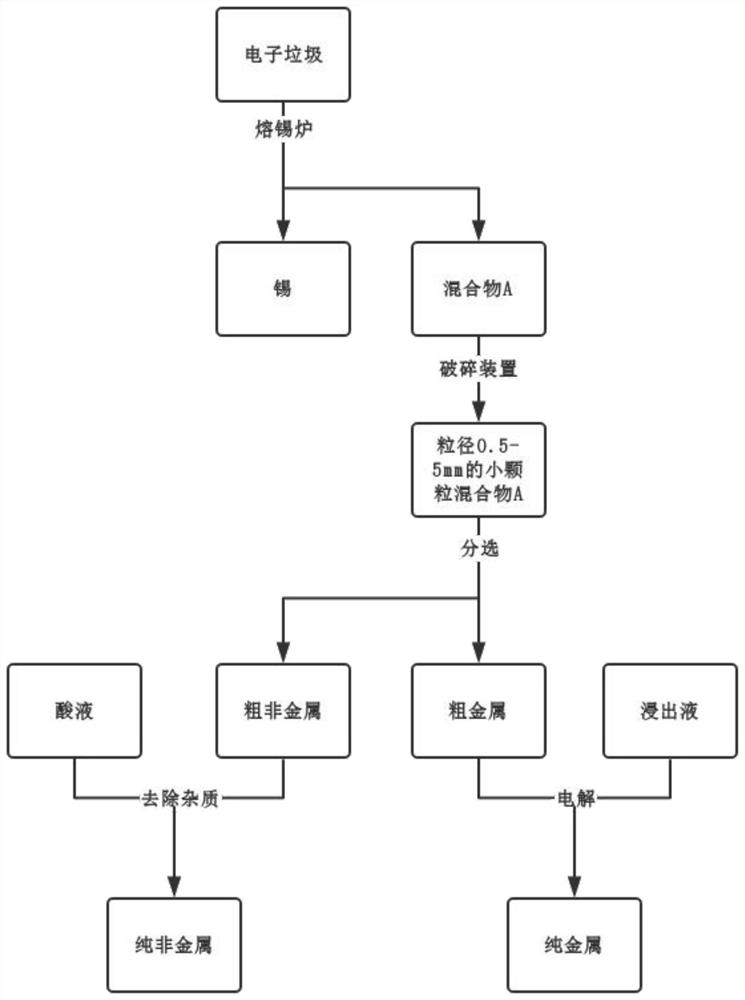
[0033] A method for recycling electronic waste comprises the following steps:
[0034] Step 1: dismantling the electronic waste with large components, dissolving the tin on the surface of the electronic waste with large components after dismantling through a tin melting furnace, recycling metal tin, and obtaining mixture A;
[0035] Step 2: The mixture A is crushed into small particles with a particle diameter of 3 mm by a shredding type crushing device;
[0036] Step 3: Buoyancy sorting the small particles crushed in Step 2 into coarse metals and coarse non-metals, and the sorting time is 15 minutes;
[0037] Step 4: immerse the crude nonmetal metal obtained in step 3 in sulfuric acid to obtain pure nonmetal, and the recovery rate of pure nonmetal is 96.1%;
[0038] Step 5: soak the crude metal obtained in step 3 in the leaching solution (ferric chloride and hydrochloric acid, wherein the ratio of the amount of ferric chloride to the amount of hydrochloric acid is 3:5), and ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A method for recycling electronic waste comprises the following steps:
[0041] Step 1: dismantling the electronic waste with large components, dissolving the tin on the surface of the electronic waste with large components after dismantling through a tin melting furnace, recycling metal tin, and obtaining mixture A;
[0042] Step 2: Using a hammer crushing device to crush the mixture A into small particles with a particle size of 0.25mm;
[0043] Step 3: The small particles crushed in Step 2 are subjected to current sorting into coarse metals and coarse non-metals, and the sorting time is 20 minutes;
[0044] Step 4: soak the crude non-metallic metal obtained in step 3 in hydrochloric acid to obtain pure non-metal, and the recovery rate of pure non-metal is 92.5%;
[0045] Step 5: soak the crude metal obtained in step 3 in the leaching solution (ferric chloride and hydrochloric acid, wherein the ratio of the amount of ferric chloride to the amount of hydrochloric acid...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A method for recycling electronic waste comprises the following steps:
[0048] Step 1: dismantling the electronic waste with large components, dissolving the tin on the surface of the electronic waste with large components after dismantling through a tin melting furnace, recycling metal tin, and obtaining mixture A;
[0049] Step 2: using a crushing device to crush the mixture A into small particles with a particle size of 0.5mm;
[0050] Step 3: Gravity sort the small particles crushed in Step 2 into coarse metals and coarse non-metals, and the sorting time is 10 minutes;
[0051] Step 4: Soak the crude nonmetallic metal obtained in step 3 in nitric acid to obtain pure nonmetallic, and the recovery rate of pure nonmetallic is 96%;
[0052] Step 5: soak the crude metal obtained in step 3 in the leach solution (ferric chloride and hydrochloric acid, wherein the ratio of the amount of ferric chloride to the amount of hydrochloric acid is 3:4), and then collect the pure me...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com