Infrared antibacterial coating and preparation method
An antibacterial coating and infrared technology, applied in the field of antibacterial, can solve the problems of low antibacterial performance and insufficient antibacterial timeliness, and achieve the effect of improving antibacterial performance and timeliness, increasing product forms and application scenarios, and single material components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
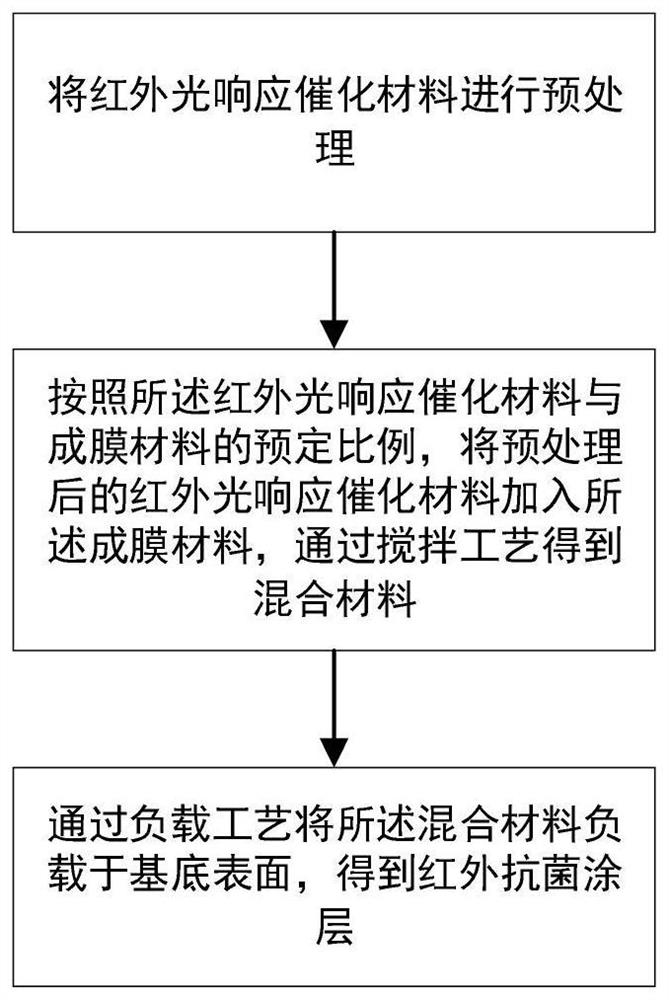
[0048] Embodiment 1 is a spraying embodiment, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0049] 1. Material pretreatment: use ball mill to grind C 3 N 4 Quantum dots are ultrasonically dispersed to form a homogeneous material solution;
[0050] 2. Multi-component blending: the film-forming material is water-based polyacrylic acid emulsion, C 3 N 4 The quantum dot solution and the aqueous polyacrylic acid emulsion are blended according to a mass ratio of 1:60, and stirred together to obtain a mixed material;
[0051] 3. Mixed solution loading: Use a spray gun to load the mixed solution on the surface of plastics, walls, etc. to form an infrared antibacterial coating on the surface.
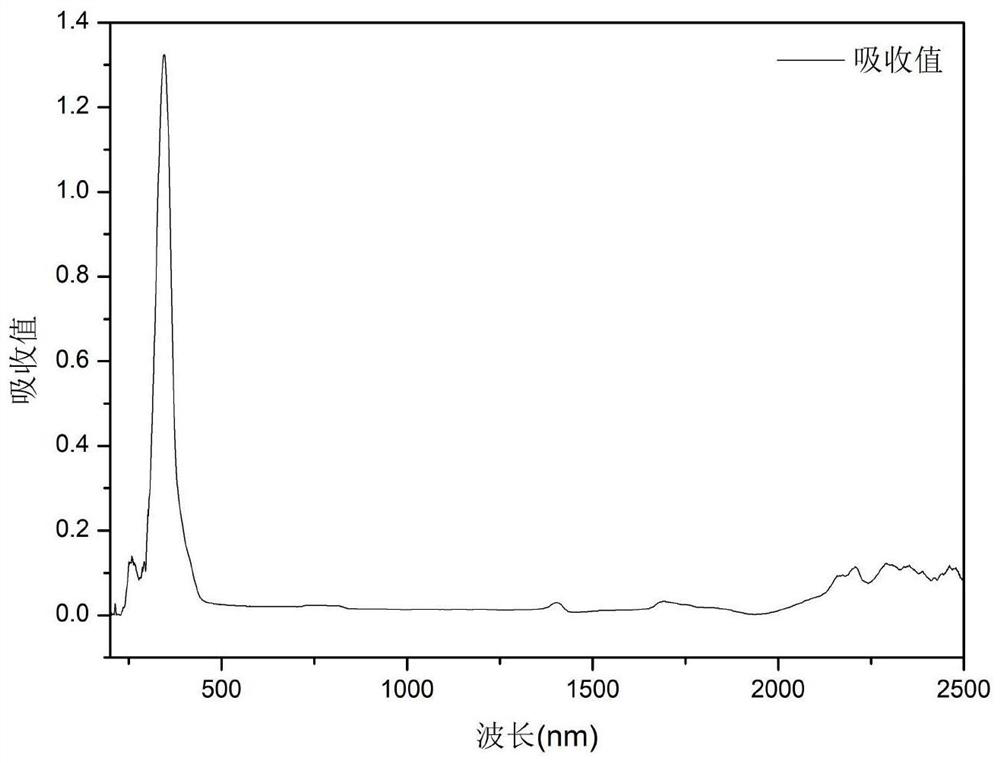
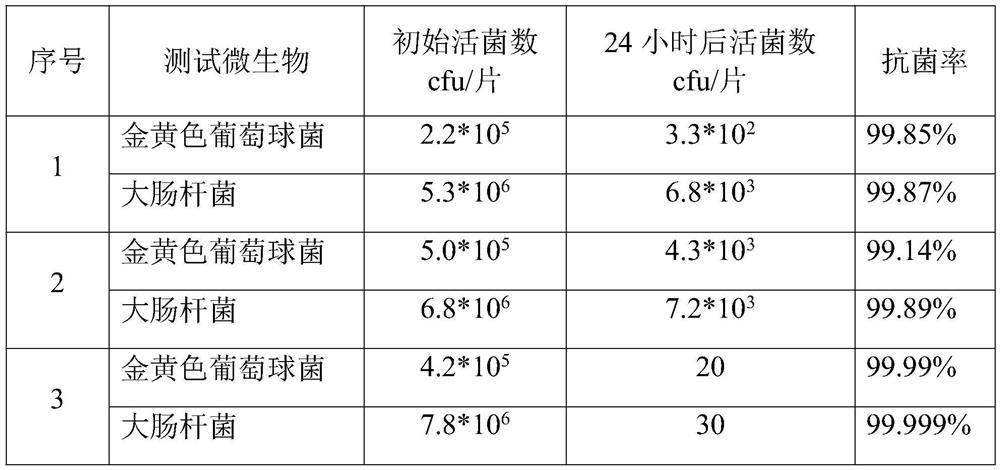
[0052] The infrared antibacterial coating material prepared in the embodiment of the present invention has infrared antibacterial performance and has the potential of wide application. The preparation process of the embodiment of the present invention is short and the conditions are mild, wh...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2 is soaking embodiment, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0055] 1. Material pretreatment: use ultrasonic machine to dope Na with C 3 N 4 Perform ultrasound to achieve uniform dispersion and obtain a homogeneous material solution with a size below 1 μm;
[0056] 2. Multi-component blending: the film-forming material is sodium silicate solution, Na doped with C 3 N 4 Blend with sodium silicate solution according to the mass ratio of 1:80, and mechanically stir together to obtain a mixed solution;
[0057] 3. Mixed solution loading: use the soaking loading method to load the mixed solution on the bulk phase of materials such as ceramic modules, porous products, metal modules, filter module products, etc., to form a bulk infrared antibacterial coating.
[0058] The infrared antibacterial coating material prepared in the embodiment of the present invention has infrared antibacterial properties and has the potential for wide application. The prepa...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3 is auxiliary agent embodiment, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0061] 1. Material pretreatment: use an ultrasonic machine to convert MoS 2 / C 3 N 4 Perform ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a homogeneous material solution;
[0062] 2. Multi-component blending: the film-forming material is chitosan, MoS 2 / C 3 N 4 Carry out blending with chitosan according to mass ratio 1:10, stir together to obtain mixed material;
[0063] 3. Mixed materials are added as additives: the mixed solution is added to plastic molding, coating preparation and other preparation processes to form infrared antibacterial products.
[0064] The infrared antibacterial auxiliary agent prepared in the embodiment of the present invention has infrared antibacterial properties and has the potential for wide application. The preparation process of the embodiment of the present invention is short and mild, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production. The method of s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com