Method for analyzing heterocyclic amine formation mechanism by using dry and hot soy protein isolate as model
A technology of soybean protein isolate and analysis method, which is applied in the direction of material separation, material analysis, material stimulation analysis, etc., and can solve the problems of heterocyclic amine formation mechanism limitation, complex composition, incompatible protein decomposition and supplementary amino acid content, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
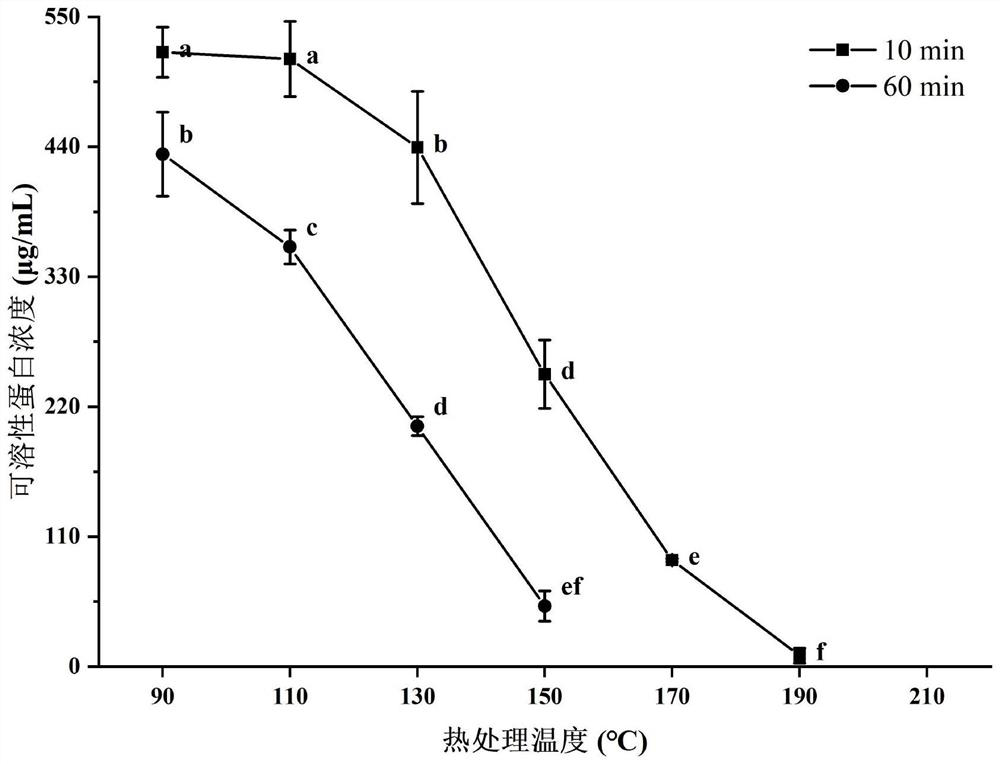
[0047] In order to determine the best conditions for simultaneous analysis of protein physicochemical properties and heterocyclic amine production content, the dry heat treatment conditions of soybean protein isolate were designed. Weigh 5g of DuPont 603 soybean protein isolate, place it in a glass petri dish with a diameter of 10cm, and place it in a blast drying oven with a constant temperature for 30min, heat it at 90-230°C for 10min and 60min respectively, and then culture it Take out the dish, put it in a sealed bag after it cools down naturally, and store it in a -20°C refrigerator for later use.
[0048] Because of the obvious color change of dry heat soybean protein isolate (soybean protein isolate after the above dry heat treatment), the L, a, and b values of soybean protein isolate after dry heat were determined.
[0049]L value represents lightness (black and white), a represents red-green, b represents yellow-blue, among them, L: if it is a positive value, it mea...
Embodiment 2
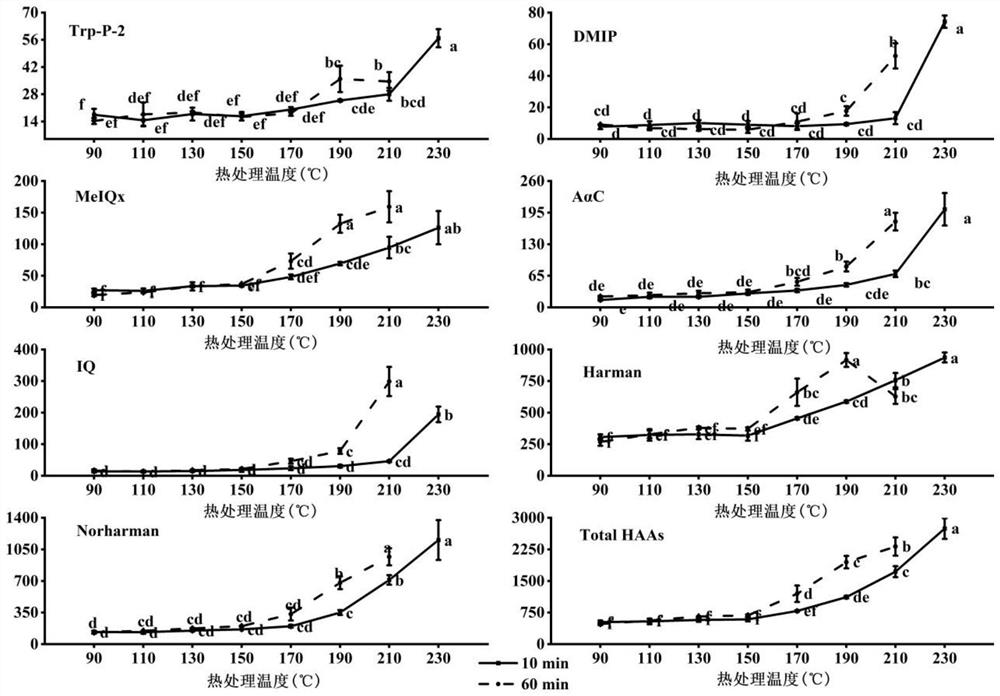
[0063] The dry-heated soybean protein isolate obtained in Example 1 was acid-hydrolyzed to obtain heterocyclic amines, and the heterocyclic amines were purified and concentrated in combination with solid-phase extraction; The content of each heterocyclic amine, the experimental results are as follows image 3 shown, where image 3 The vertical axis of all represents the heterocyclic amine content, and the unit is ng / g.
[0064] Accurately weigh 1 g of each dry-heated soybean protein isolate sample that has been heat-treated at 90-230°C in Example 1, mix them with 10mL6mol / L hydrochloric acid in a 10mL hydrolysis tube, and hydrolyze in a blast drying oven at 110°C for 24 hours. Water was added to the solution to nearly 100mL, and the hydrolyzed solution was adjusted to 100mL after suction filtration with an organic filter membrane.
[0065] Take 10mL of the above diluted hydrolyzate for solid phase extraction. The solid-phase extraction column was pre-activated with 10 mL of...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Analysis of changes in dry heat soy protein isolate using SDS-PAGE:
[0074] A gel rapid preparation kit from Biosharp was used to prepare a 4% stacking gel and a 15% separating gel for SDS-PAGE gel. The soybean protein isolate after the heat treatment in Example 1 was dissolved in PBS, and the supernatant was collected by centrifugation for gel electrophoresis experiment.
[0075] Fluorescein-5-thiosemicarbazide (FTC) can bind to carbonyl compounds in proteins, so FTC can be used to label carbonyl proteins to visualize the degree of protein oxidation and oxidation sites.
[0076] The specific operation is: mix 0.4 mL of the protein (0.5 mg / mL) in Example 1 with 0.1 mL of 5 mmol / L FTC solution, and incubate at 37° C. for 150 min in the dark, stirring gently every 30 min. Proteins were then precipitated with 20% pre-cooled trichloroacetic acid. The mixture was then incubated at 4°C for 10 min in the dark and centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. The precipitate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com