Composite bacterial cellulose dressing and preparation method based on controllable nanofiber spatial structure
A technology of fiber spatial structure and bacterial cellulose, applied in bacteria, bandages, drug delivery, etc., can solve the problems of fast water loss rate and high water vapor transmission rate, so as to enhance the intermolecular force and control the microenvironment of the wound , Low endotoxin effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
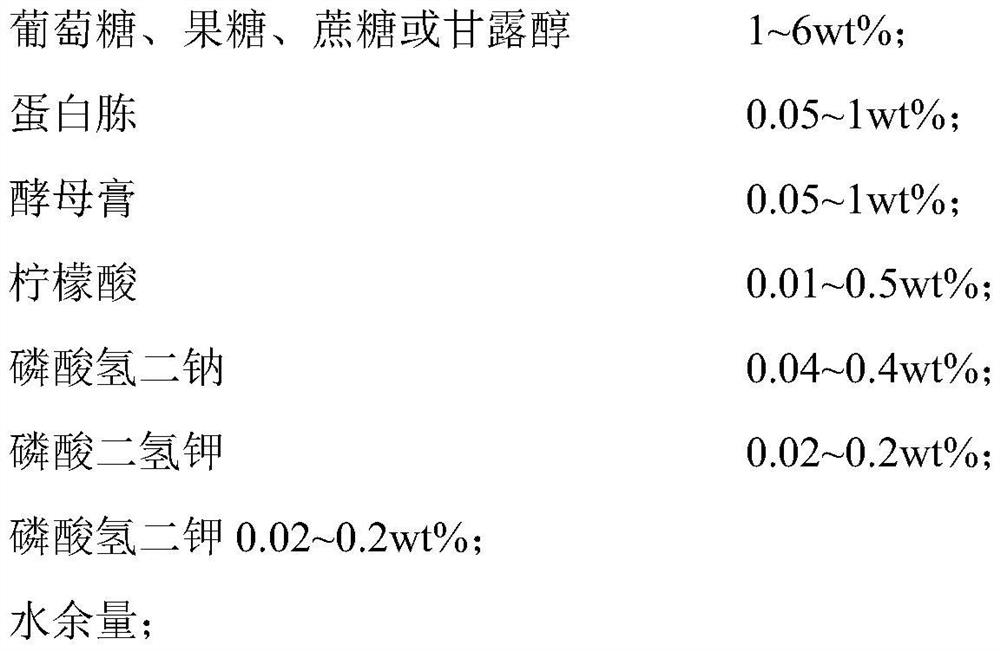
[0049] A preparation method of a composite bacterial cellulose dressing based on a controllable nanofiber spatial structure, the steps are as follows:
[0050] (1) Dissolve gelatin particles (content 1 wt%) and bovine serum albumin (content 0.2 wt%) in deionized water, stir at 35° C. for 1 h, add citric acid to adjust the pH to 5, and obtain Gelatin-based aqueous solutions;
[0051] (2) adding the gelatin-based aqueous solution dropwise to the non-woven material containing the protein component, and naturally drying, to obtain a composite non-woven material with a gelatin-based component content of 0.1 wt%; wherein the natural drying is drying at room temperature for 12 hours; containing The gram weight of the non-woven material of the protein ingredient is 40g / m2 2 , is obtained by spunlace non-woven processing of medical staple fibers with an average diameter of 5 μm containing protein components (content 0.1wt%); medical staple fibers containing protein components In the ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] A preparation method of a composite bacterial cellulose dressing based on a controllable nanofiber spatial structure, the steps are as follows:
[0072] (1) Dissolve gelatin granules (content 1.3 wt%) and bovine serum albumin (content 0.4 wt%) in deionized water, stir at 37°C for 2 h, add citric acid to adjust pH to 5, to obtain a gelatin-based aqueous solution;
[0073] (2) adding the gelatin-based aqueous solution dropwise to the non-woven material containing the protein component, and naturally drying, to obtain a composite non-woven material with a gelatin-based component content of 0.5 wt%; wherein the natural drying is drying at room temperature for 48h; containing The gram weight of the non-woven material of the protein ingredient is 70g / m2 2 , is obtained by spunlace non-woven processing of medical staple fibers with an average diameter of 10 μm containing protein components (content 3wt%); medical staple fibers containing protein components Fiber (Lyocell fib...
Embodiment 3
[0093] A preparation method of a composite bacterial cellulose dressing based on a controllable nanofiber spatial structure, the steps are as follows:
[0094] (1) Dissolve gelatin particles (content 1.5 wt%) and bovine serum albumin (content 0.6 wt%) in deionized water, stir at 40° C. for 3 h, add acetic acid to adjust the pH to 5, and obtain Gelatin-based aqueous solutions;
[0095] (2) The gelatin-based aqueous solution was added dropwise to the non-woven material containing the protein component, and dried in an oven to obtain a composite non-woven material with a gelatin-based component content of 1 wt%; the oven drying temperature was 35 ° C, and the time was 1 h ;The gram weight of non-woven materials containing protein ingredients is 100g / m2 2 , is obtained by spunlace non-woven processing of medical staple fibers with an average diameter of 20 μm containing protein components (content is 5wt%); medical staple fibers containing protein components are reduced keratin s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com