Optical filter based on nanopore array structure
A nanohole array and optical filter technology, which is applied in the field of optical filters, can solve the problems of different, low stability, and difficult processing of optical filters.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
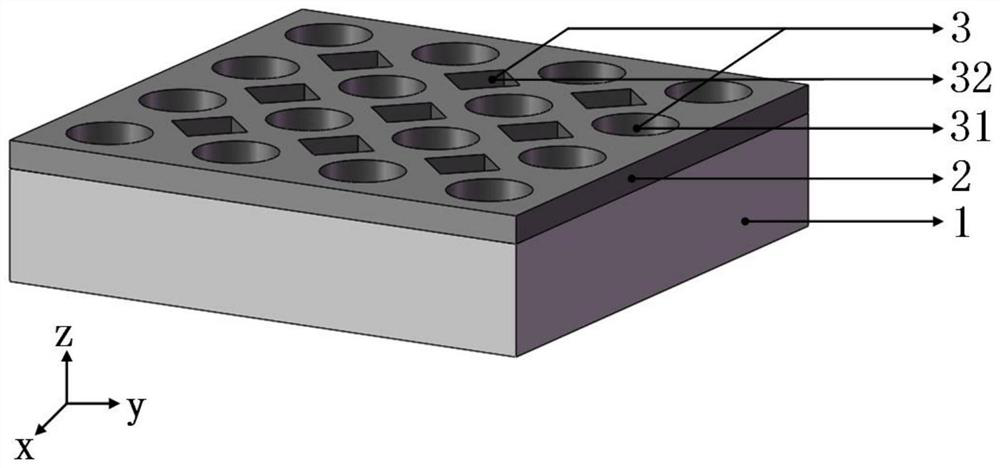
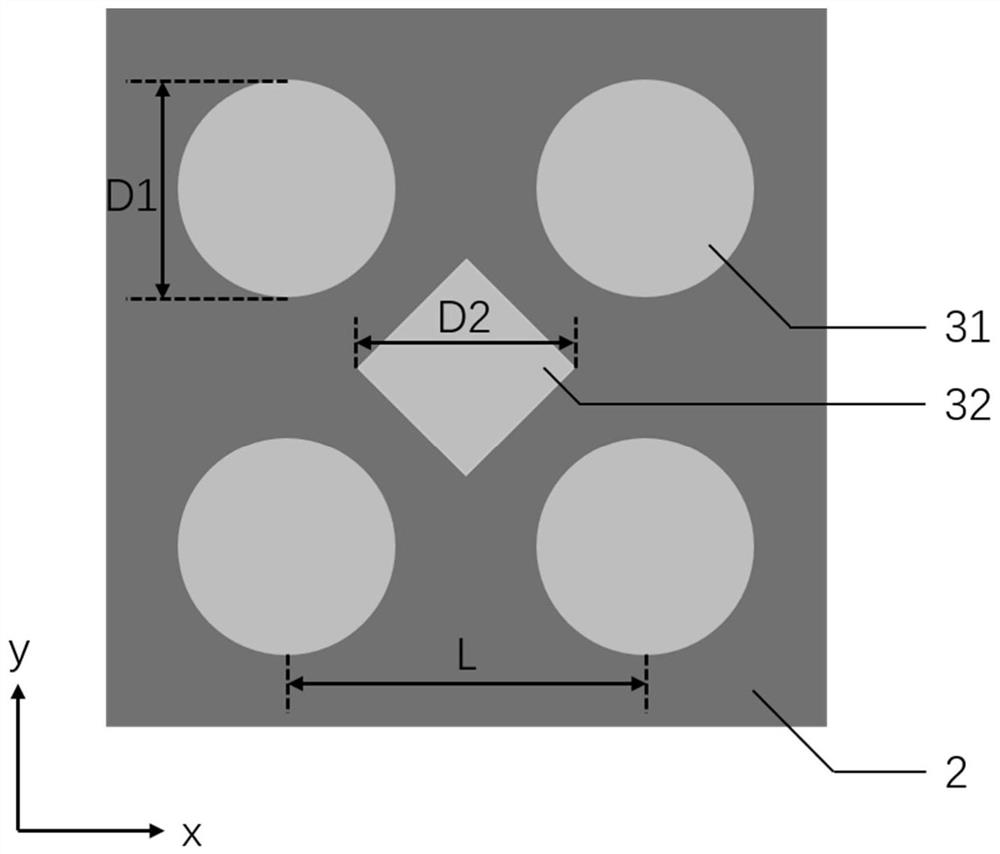
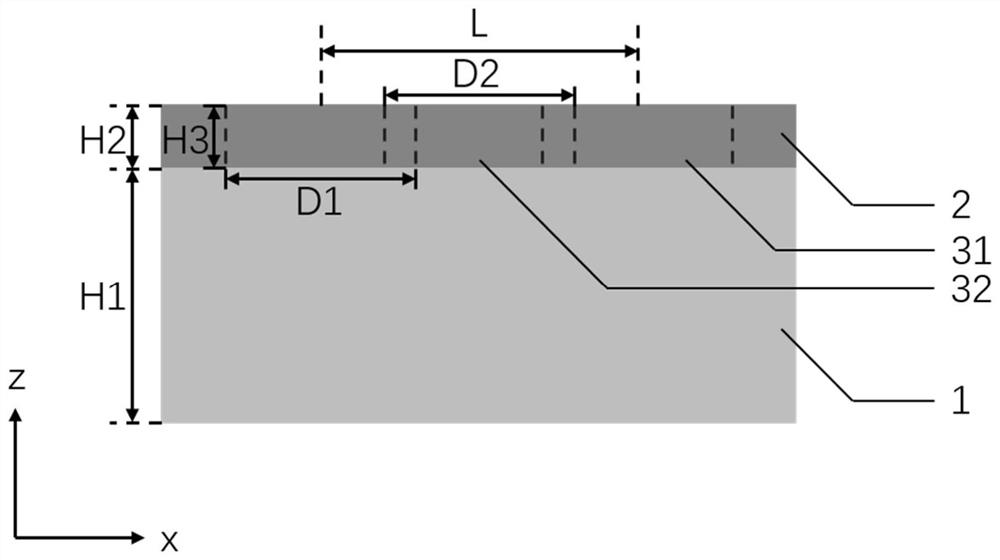
[0030] If the thickness H1 of the substrate 1 is 200nm, the thickness H2 of the metal film 2 is 50nm, and the period P is 300nm, according to the relationship of D1=D2=0.6*P, the diameter D1 of the circular hole 31 is 180nm, and the pair of rhombus holes 32 Diagonal line length D2 is 180nm, circular hole 31 is arranged according to square, and it has the same period P in row direction and column direction, and rhombus hole 32 is arranged according to square, and it has same period P in row direction and column direction, and positive The positions of the diamond-shaped holes 32 are arranged according to the circular holes 31 shifted along the row direction by a half-period P / 2 length and then along the column direction by a half-period P / 2 length, so as to obtain circular holes 31 staggered in rows or columns with a period P As with the regular rhombus hole 32 array, the distance from the center of any hole to the center of four adjacent holes around it is the same, forming a f...
Embodiment 2
[0032]Its structure is the same as that of Example 1, and the thickness of substrate 1 and metal film 2 is also the same as that of Example 1, the period P is changed to 360nm, and the circular hole is set according to the relationship of D1=D2=0.6*P=216nm The diameter D1 of 31 and the length D2 of the diagonal line of the rhombus hole 32 constitute a filter with a base thickness of 200nm, a metal film thickness of 50nm, and a nanohole array period of 360nm.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Its structure is the same as that of Example 1, and the thickness of substrate 1 and metal film 2 is also the same as that of Example 1, the period P is changed to 420nm, and the circular hole is set according to the relationship of D1=D2=0.6*P=252nm The diameter D1 of 31 and the length D2 of the diagonal line of the rhombus hole 32 constitute a filter with a base thickness of 200nm, a metal film thickness of 50nm, and a nanohole array period of 420nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com