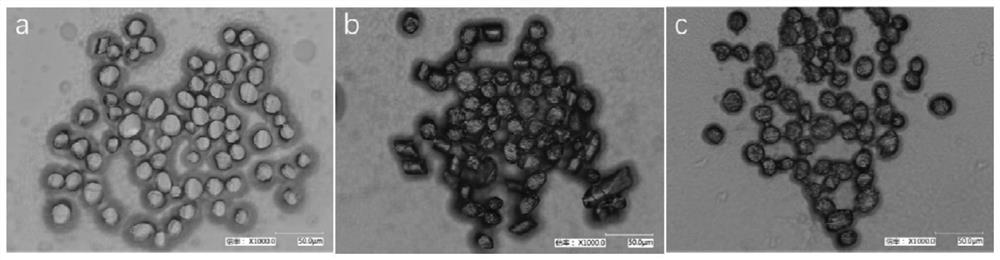
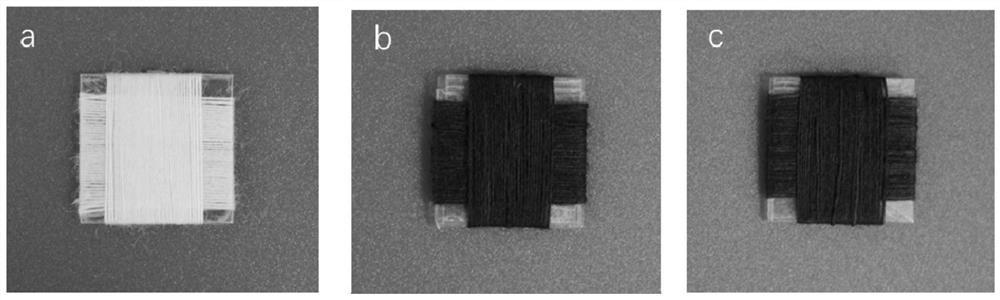
Biological enzymatic dyeing method for improving wool fiber strength
A wool fiber and biological enzyme technology, applied in the direction of dyeing, textile and paper making, etc., can solve the problems of single use, environmental user health threat, etc., and achieve the effects of improved alkali resistance, good dyeing performance and broad development prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Preprocessing:
[0033] The treatment process prescription and conditions: Weigh 1g of wool yarn and sodium carbonate, dissolve sodium carbonate in deionized water to prepare a 1g / L sodium carbonate solution with a bath ratio of 1:30. Soak the wool fibers in sodium carbonate solution at 40°C for 15 minutes, then wash them with absolute ethanol at 40°C for 10 minutes, rinse with deionized water, and dry the washed wool fibers at 40°C.
[0034] (2) Enzyme catalyzes the reaction between phenolic compounds and wool:
[0035] Prepare solution: prepare 0.2mol / L acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, adjust the pH to 5.0, add 0.04mol / L catechol and 75U / mL laccase in sequence, bath ratio 1:30, place in the reactor for shaking Evenly, put the pretreated wool yarn into the prepared buffer solution, and shake it at 40°C for 5 hours.
[0036] (3) Post-processing:
[0037] After the wool yarn obtained in step (3) is taken out, it is frozen at -50° C. for 12 hours to inac...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Preprocessing:
[0040] The treatment process prescription and conditions: put 1g of wool yarn in the low-temperature plasma treatment machine, turn on the vacuum pump, feed all the oxygen, click on the automatic mode, and perform low-temperature plasma treatment on the protein fiber, the treatment power is 100W, and the treatment time is 5 minutes .
[0041] (2) Enzyme catalyzes the reaction between phenolic compounds and wool:
[0042] Prepare solution: Prepare 0.2mol / L acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, adjust the pH to 5.5, add 0.04mol / L catechol and 75U / mL laccase in sequence, bath ratio 1:50, place in the reactor for shaking Evenly, put the pretreated wool yarn into the prepared buffer solution, and shake it at 40°C for 5 hours.
[0043] (3) Post-processing:
[0044] After the wool yarn obtained in step (3) is taken out, it is frozen at -40° C. for 12 hours to inactivate the enzyme, then washed with deionized water, and dried naturally.
[0045] T...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3 explores the impact of laccase dosage on wool fiber dyeing
[0053] Referring to Example 1, the amount of laccase in step (2) is replaced by 25U / mL, 50U / mL, 100U / mL, 125U / mL respectively, and other conditions remain unchanged:
[0054] (1) Preprocessing:
[0055] The treatment process prescription and conditions: Weigh 1g of wool yarn and sodium carbonate, dissolve sodium carbonate in deionized water to prepare a 1g / L sodium carbonate solution with a bath ratio of 1:30. Soak the wool fibers in sodium carbonate solution at 40°C for 15 minutes, then wash them with absolute ethanol at 40°C for 10 minutes, rinse with deionized water, and dry the washed wool fibers at 40°C.
[0056] (2) Enzyme catalyzes the reaction between phenolic compounds and wool:
[0057] Prepare solution: prepare 0.2mol / L acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, adjust the pH to 5.0, add 0.04mol / L catechol and 25U / mL, 50U / mL, 75U / mL, 100U / mL, 125U / mL in sequence mL laccase, bath rat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com