Method for recovering lithium from lithium iron phosphate waste and application thereof
A lithium iron phosphate and recycling method technology, applied in recycling technology, waste collector recycling, battery recycling, etc., can solve the problem that the recovery rate of lithium carbonate is difficult to guarantee, the performance of lithium iron phosphate material is affected, and phosphorus resource recycling is not considered. Consumption and other problems, to achieve the effect of low energy consumption cost, considerable economic benefits, and low equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
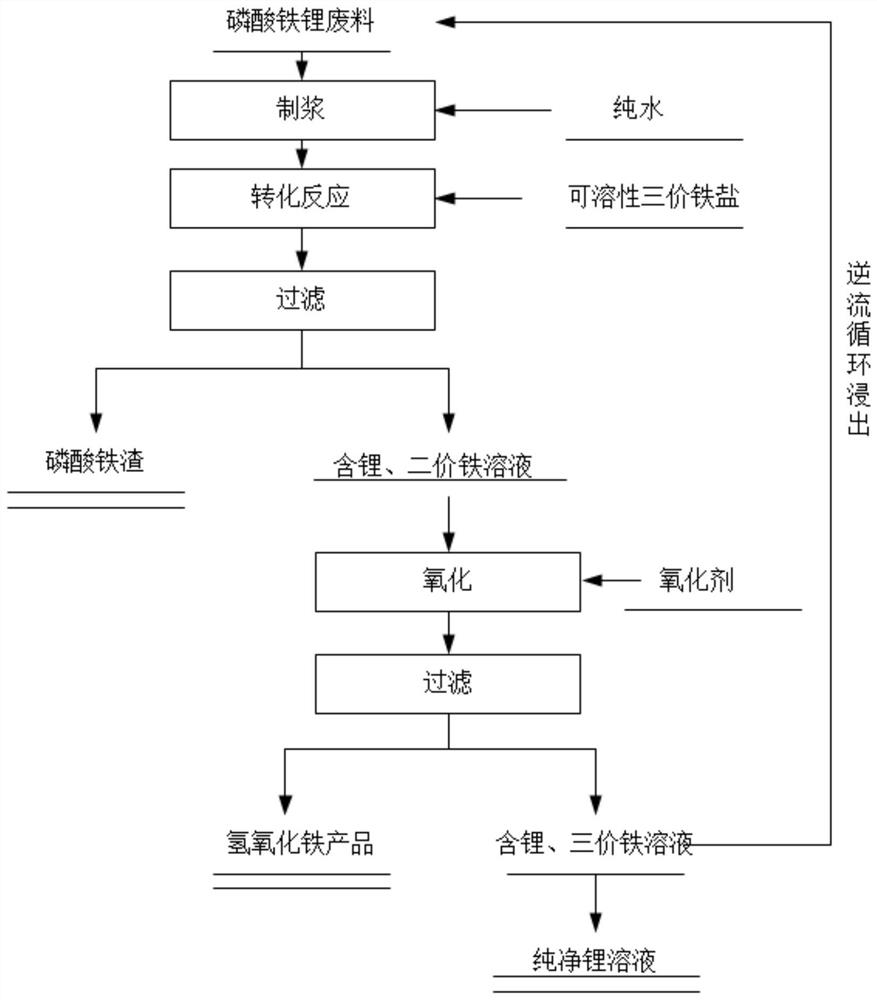
[0033] The recovery method of lithium in the lithium iron phosphate waste material of the present embodiment may further comprise the steps:
[0034] (1) 100g mass fraction of 96.8% lithium iron phosphate waste and 600ml pure water are mixed and pulped to obtain lithium iron phosphate slurry;
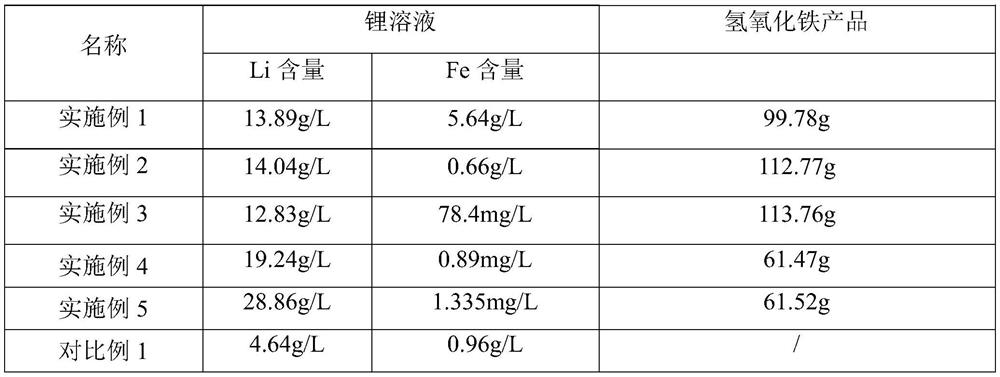
[0035] (2) Add 173 grams of ferric chloride to the slurry obtained in step (1), heat up to 50° C., react for 45 minutes, filter to obtain 700 ml of lithium chloride and ferrous chloride solution, and obtain 95.7 grams of ferric phosphate slag ;
[0036] (3) Feed oxygen into the solution containing lithium chloride and ferrous chloride obtained in step (2), react at 50° C. for 50 minutes, filter to obtain lithium chloride, ferric chloride solution and ferric hydroxide products;
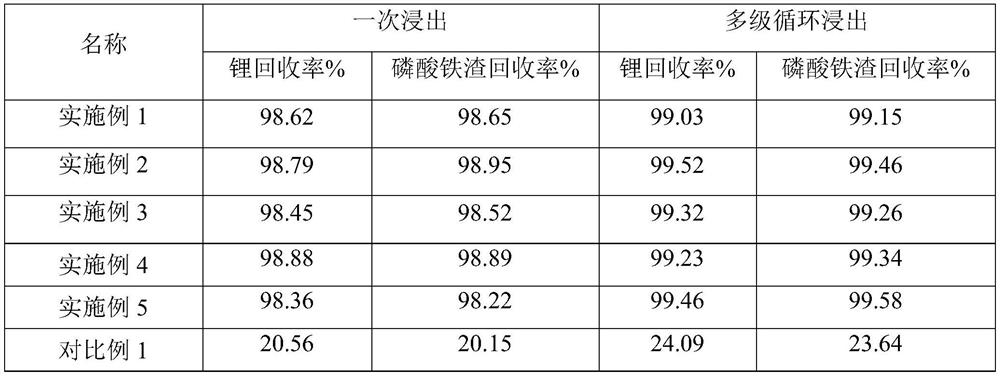
[0037] (4) Lithium chloride, ferric chloride solution in step (3) and lithium iron phosphate battery powder in step (1) are subjected to 5 times of countercurrent cycle leaching, enriching lithium content while...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The recovery method of lithium in the lithium iron phosphate waste material of the present embodiment may further comprise the steps:
[0042] (1) 100g mass fraction of 96.8% lithium iron phosphate waste and 700ml pure water are mixed and pulped to obtain lithium iron phosphate slurry;
[0043] (2) Add 173 grams of ferric chloride to the slurry obtained in step (1), heat up to 40° C., react for 30 minutes, filter to obtain 800 ml of lithium chloride and ferrous chloride solution, and obtain 95.0 grams of ferric phosphate slag ;
[0044] (3) Pass into ozone to step (2) to obtain containing lithium chloride and ferrous chloride solution, at 50 ℃, reaction time 40min, filter and obtain lithium chloride, ferric chloride solution and ferric hydroxide product;
[0045] (4) Lithium chloride, ferric chloride solution in step (3) and lithium iron phosphate battery powder in step (1) are subjected to 10 countercurrent cycle leaching, enriching lithium content while reducing iron...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The recovery method of lithium in the lithium iron phosphate waste material of the present embodiment may further comprise the steps:
[0048] (1) 100g mass fraction of 96.8% lithium iron phosphate waste and 800ml pure water are mixed and pulped to obtain lithium iron phosphate slurry;
[0049] (2) Add 173 grams of ferric chloride to the slurry obtained in step (1), heat up to 60° C., react for 30 minutes, filter to obtain 900 ml of lithium chloride and ferrous chloride solution, and obtain 93.9 grams of ferric phosphate slag ;
[0050] (3) Pass through hydrogen peroxide to the solution containing lithium chloride and ferrous chloride obtained in step (2), react at 60° C. for 30 minutes, filter to obtain lithium chloride, ferric chloride solution and ferric hydroxide products;
[0051] (4) Lithium chloride, ferric chloride solution in step (3) and lithium iron phosphate battery powder in step (1) are subjected to 15 countercurrent cycle leaching, enriching lithium conten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com