Cellulose magnetic microspheres prepared by improving reaction activity of eucalyptus fibers as well as preparation method and application of cellulose magnetic microspheres
A technology of magnetic microspheres and reactivity, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve problems such as poor distribution of magnetic nanoparticles and poor cellulose reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
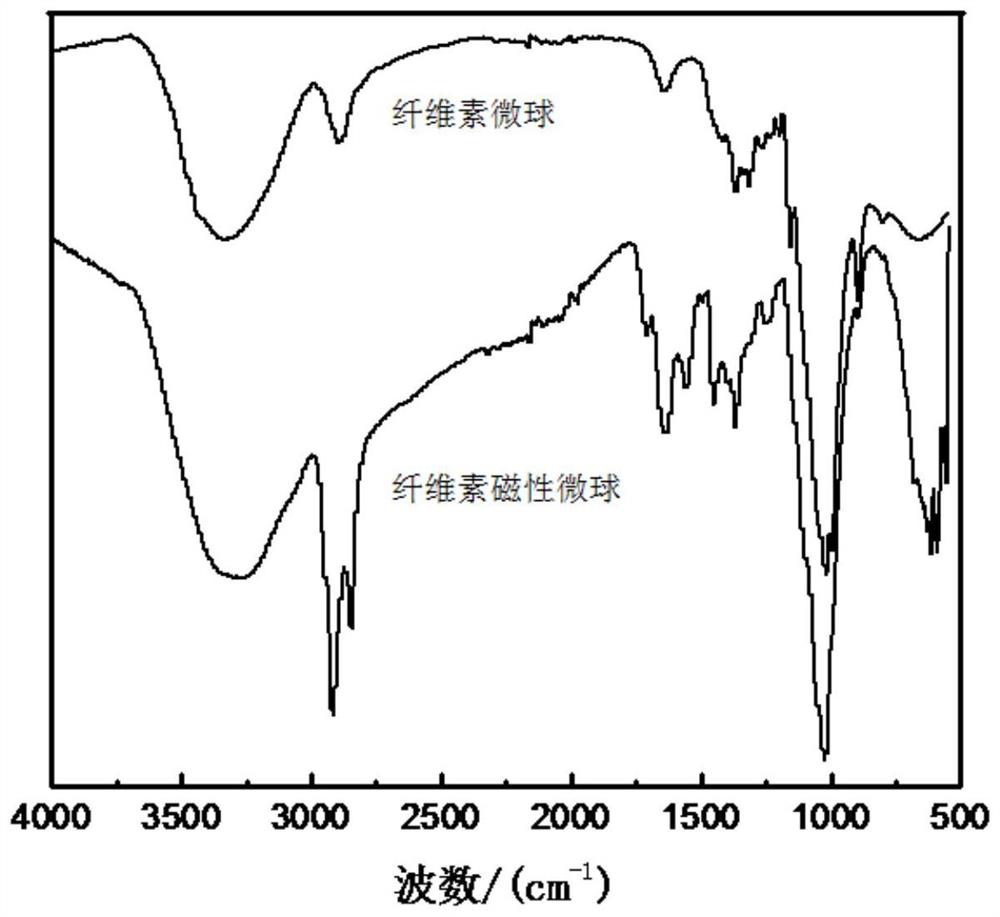
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Take 30 g of dry eucalyptus fiber, add deionized water to prepare a wet slurry with a mass concentration of 10%, put the wet slurry into a PFI refiner for mechanical beating, and obtain a beating slurry. The beating conditions are beating gap 0.20mm, beating pressure 33.3N cm -1 , The beating speed is 1500rpm, and the beating degree is 70000r.
[0028] (2) Take 1.0g of the beating slurry and add it to 50mL of 9wt% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, stir to make it evenly mixed, place it at -10°C for 9 hours of freezing and low temperature treatment, take it out and thaw it at room temperature, and then slowly drop it into 1mol L -1 hydrochloric acid to regenerate and precipitate the cellulose, wash to neutral, dehydrate and dry to obtain active eucalyptus fiber.
[0029] After the eucalyptus fiber is treated with the above-mentioned PFI refiner and lye, the original dense fiber structure is destroyed, the cellulose structure becomes loose, and its specific surface...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Compared with Example 1, the difference of Example 2 is that in the step (4), the autoclave was reacted at a temperature of 180° C. for 7 hours, and the rest of the operations were the same as in Example 1. It is measured that the adsorption rate of cellulose magnetic microspheres to methylene blue is 93%
Embodiment 3
[0038] Compared with Example 1, the difference of Example 2 is that in the step (4), the autoclave was reacted at a temperature of 180° C. for 8 hours, and the rest of the operations were the same as in Example 1. It is measured that the adsorption rate of the cellulose magnetic microsphere product to methylene blue is 99%. And the methylene blue adsorption rate is still as high as 98% when it is recycled for the third time; the adsorption rate drops significantly when it is used for the fourth time, but it can keep the adsorption rate above 91% when it is used for 5 times.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com