Preparation method of thin-layer two-dimensional material
A two-dimensional material and thin-layer technology, applied in the field of two-dimensional materials, can solve the problems of limited application, difficulty in obtaining few-layer or even single-layer two-dimensional materials, etc., and achieve the effect of improving quality, large area and improving contact effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
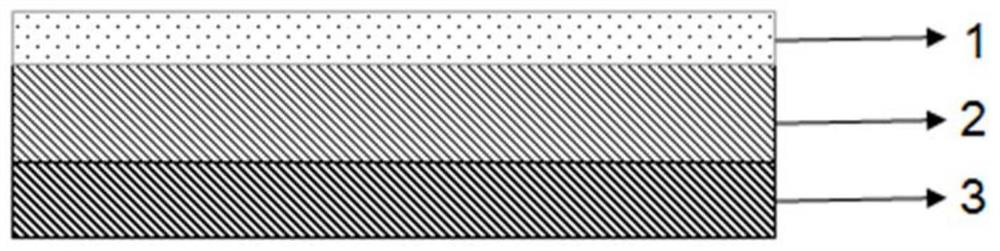
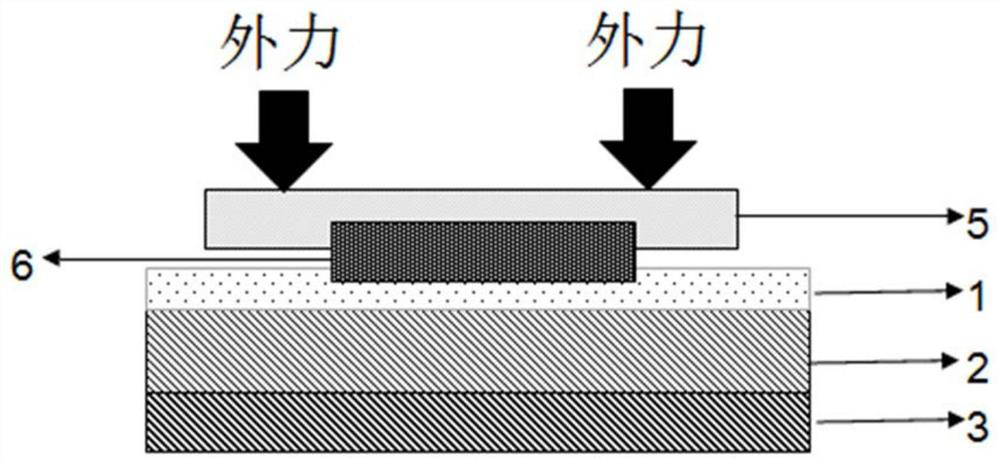
[0044] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 Shown, the preparation method of thin-layer two-dimensional material comprises the following steps:
[0045] In the first step, the SiO 2 Dropping the first solvent on the surface of the substrate 2 to obtain the first solvent layer 1;
[0046] In the second step, use 3M-Scotch tape 5 to stick MoS 2 , and the MoS 2 Coated with tape to SiO with first solvent layer 1 2 on substrate 2;
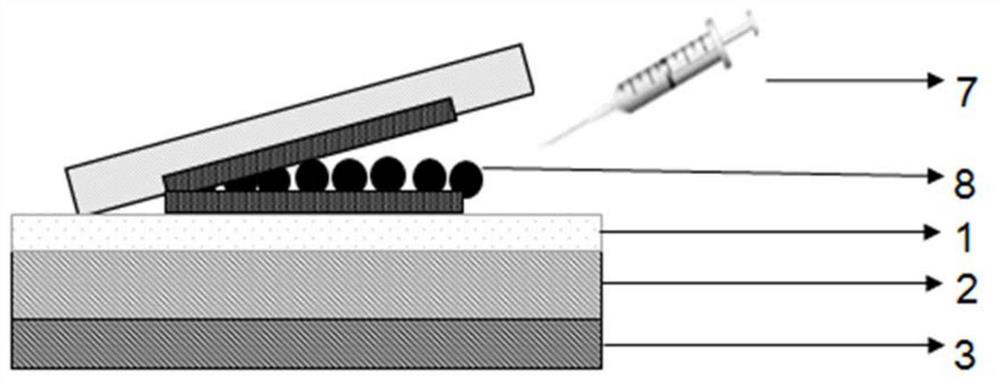
[0047] The third step is to use the syringe 7 to extract the second solvent 8, fill the gap in the adhesive tape 5, and completely fill the adhesive tape 5 with the second solvent 8 through penetration;
[0048] In the fourth step, the above-mentioned sample is put into an oven as a whole, and heat-treated at a temperature of 66°C, and the sample is taken out of the oven after 24 hours;
[0049] In the fifth step, thermal peeling is obtained to adhere to the SiO 2 MoS on substrate 2 2 Two-dimensional materials6. Such as Figure 4 As shown...
Embodiment 2
[0052] SiO after treatment for different second solvents 8 2 MoS obtained by stripping the surface tape 2 The yield and area of the lamina were counted. The statistics are divided into two items: one for MoS 2 The size is more than 0.2*10 each 5 μm 2 , 1.2*10 5 μm 2 The number of thin layers, such as Figure 8 shown; the other is the maximum size achieved by the thin layer, such as Figure 9 shown. S1-S5 in the figure represents the corresponding sample (S1-acetone; S2-isopropanol; S3-ethanol; S4-deionized water; S5-untreated) processed by different second solvents 8, and the sample selected in the experiment is in SiO 2 The substrate 2 with a layer of ethanol spin-coated on the surface can be seen from the figure, based on the process method of four solvents: acetone, isopropanol, ethanol, and deionized water, which exceeds 0.2*10 5 μm 2 The number of thin layers are 20, 31, 19, 10 respectively, more than 1.2*10 5 μm 2 The numbers of samples are 5, 13, 10, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Field-effect transistors were prepared by using the two-dimensional material prepared in Example 1 and the two-dimensional material prepared by the traditional solvent stripping method, respectively. Substrate 2 is made of silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ) layer, and the insulating layer 3 adopts a silicon (Si) sheet. The electrical contact material is composed of electronic or hole-type organic semiconductors, in which the hole-type semiconductor layers are respectively made of copper phthalocyanine (CuPc), nickel phthalocyanine (NiPc), zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc), cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPc), platinum phthalocyanine (PtPc), free phthalocyanine (H 2 Pc), Tetrathiophene (4T), Pentathiophene (5T), Hexathiophene (6T), Bis(biphenyl-4,4')-2,2'-dithiophene (BP2T) , the electronic semiconductor layer is made of fluorocopper phthalocyanine (F16CuPc), fluorophthalocyanine zinc (F16ZnPc), fluorophthalocyanine iron (F16FePc), fluorophthalocyanine cobalt (F16CoPc), chlorophthalocyanine c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com