Enzymatic-method-assisted low-temperature preparation method of fermented bean curd
An enzymatic, fermented bean curd technology, applied in dairy products, cheese substitutes, food science and other directions, can solve problems such as unfavorable protein decomposition and fermented bean curd ripening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
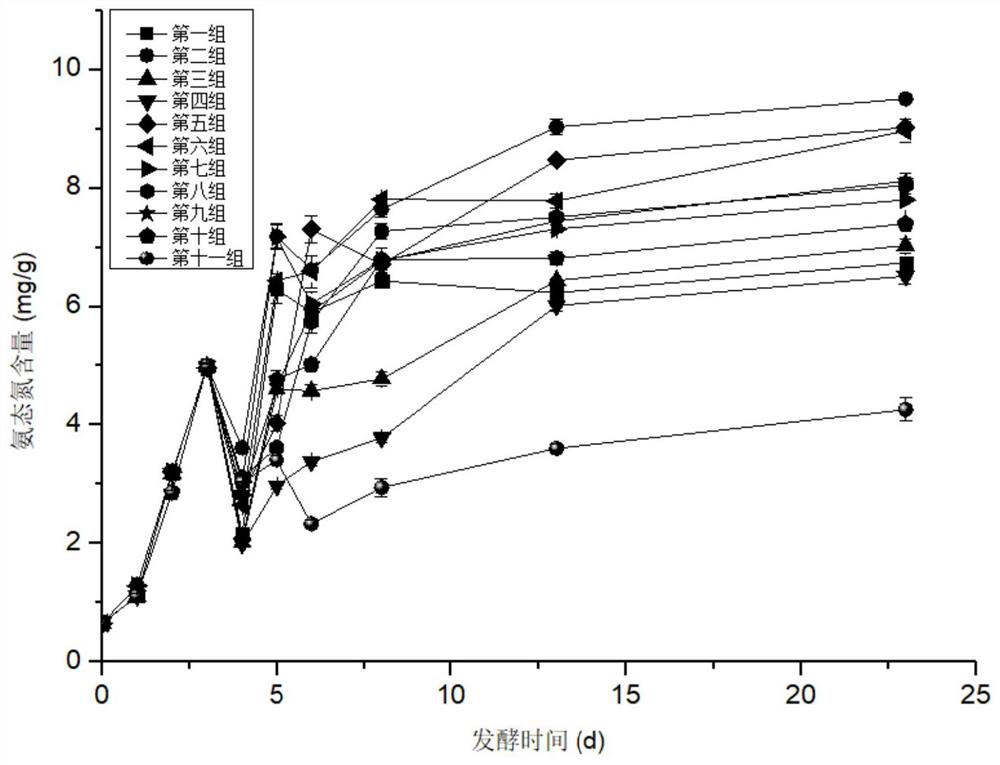
[0029] Example 1 The enzyme-assisted low-temperature preparation method of fermented bean curd changes the microbiota at different post-fermentation temperatures
[0030] The soybeans are soaked, refined, filtered, boiled, pulped, billet-made, billet-marked, inoculated and fermented, rubbed, pickled and post-fermented, and fermented bean curd is prepared at different post-fermentation temperatures. The specific process is:
[0031] (1) Soybean soaking: Soybean is used as raw material, soaked in water according to the mass ratio of material to liquid at 1:3, and the soaking time is: soak for 10 hours at room temperature of 15°C;
[0032] (2) Refining: after the soaked soybeans in step (1) are pulled out, clear water is added according to the mass ratio of material to liquid at 1:5, and ground into soybean milk;
[0033] (3) Filtration: the soya-bean milk that step (2) is obtained is filtered bean dregs with 170 order nylon gauzes, collects and filters soya-bean milk;
[0034]...
Embodiment 2
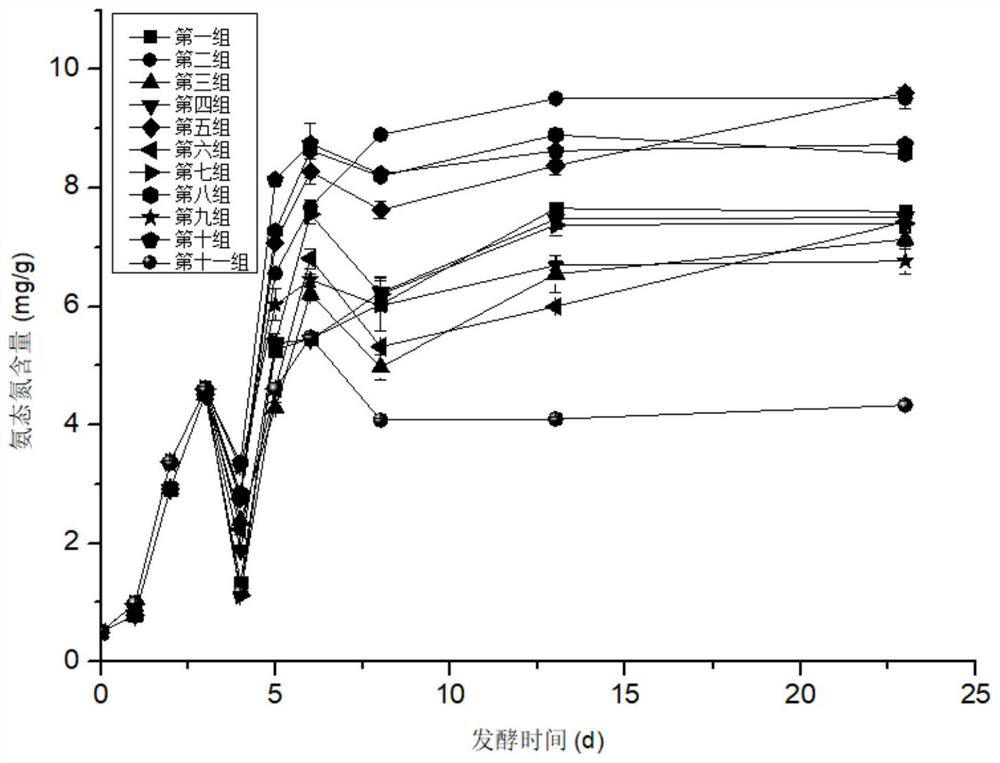
[0054] Low-temperature fermentation of fermented bean curd under the assistance of different composite proteases of embodiment 2
[0055] Through the analysis of post-fermentation microorganisms of low-salt fermented bean curd, it was found that lactic acid bacteria may be an important factor affecting the taste, texture and flavor of low-salt fermented bean curd. Therefore, the low-temperature post-fermentation conditions are used in the process to cooperate with the edible ethanol and high-salt conditions in the traditional process to inhibit the growth of lactic acid bacteria. At the same time, compound protease is added to catalyze the degradation of protein, promote the ripening of fermented bean curd, and shorten the fermentation period of fermented bean curd. The specific process is:
[0056] (1) Soybean soaking: Soybean is used as raw material, soaked in water according to the mass ratio of material to liquid at 1:2, and the soaking time is: soak for 8 hours at room t...
Embodiment 3
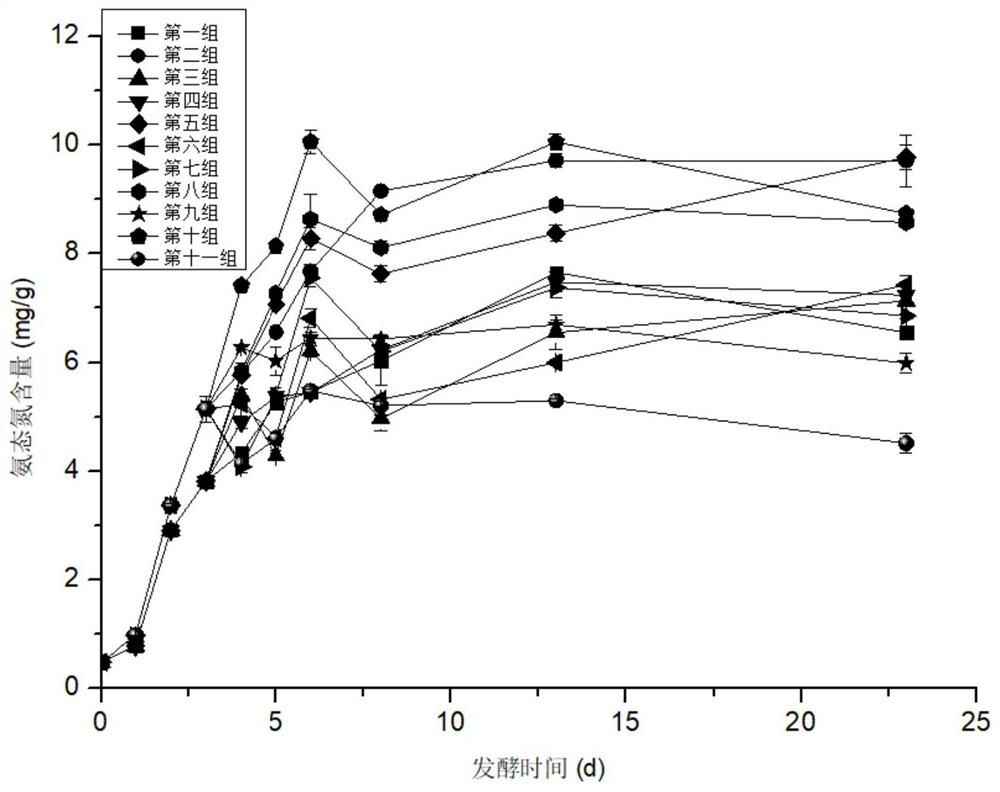
[0072] Example 3 Enzyme-assisted low-temperature fermentation preparation method and quality analysis of fermented bean curd under different salt concentrations
[0073] The soybeans are soaked, refined, filtered, boiled, pulped, billet-made, billet-marked, inoculated and fermented, rubbed, pickled and post-fermented, and fermented bean curd is prepared under different salt concentrations. The specific process is:
[0074] (1) Soybean soaking: Soybeans are used as raw materials, soaked in water according to the mass ratio of material to liquid at 1:4, and the soaking time is: soak for 8 hours at room temperature of 10°C;
[0075] (2) Refining: after the soaked soybeans in step (1) are pulled out, clear water is added according to the mass ratio of material to liquid at 1:6, and ground into soybean milk;
[0076] (3) Filtration: the soybean milk obtained in step (2) is filtered with a 180 order nylon gauze to filter the soybean dregs, and the filtered soybean milk is collected...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com