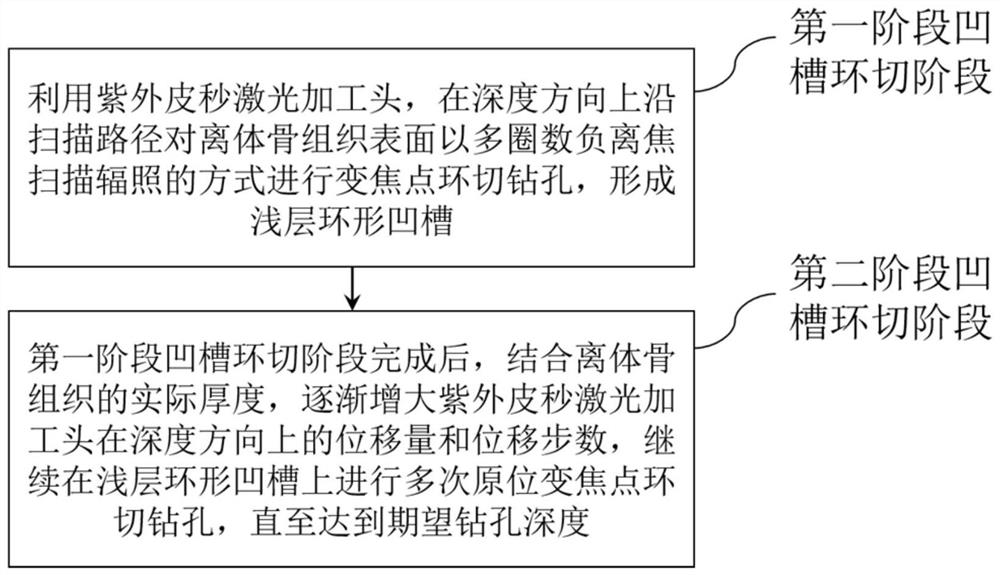
Process method for non-carbonization deep hole of in-vitro bone drill through ultraviolet picosecond laser variable-focus ring cutting
A process method and technology of focusing point, applied in laser welding equipment, manufacturing tools, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problem of serious carbonization, achieve the solution of carbonization of bone tissue, overcome the carbonization of bone tissue, remove bone pillars, small thermal diffusion Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
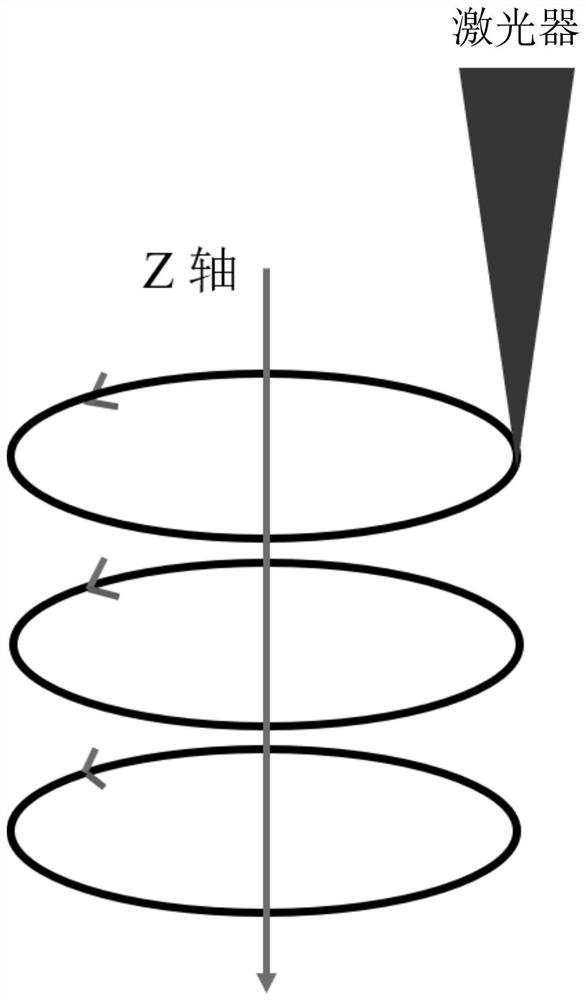
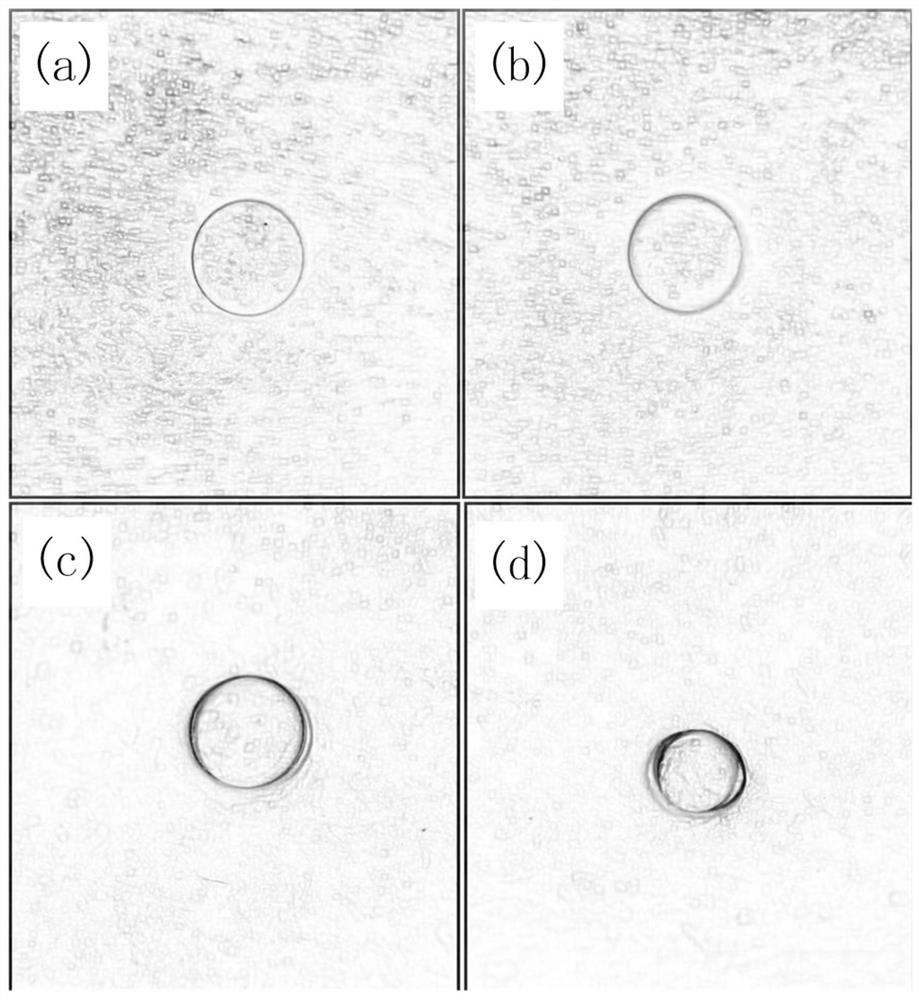
[0033] like image 3As shown in a-3d, the isolated porcine femur from which the soft tissue and periosteum have been removed is drilled. In the case of continuously spraying water on the bone tissue around the drill hole, the average power is first used in the first stage of groove circumcision drilling. 12W, repetition frequency 500KHz, picosecond 355nm UV laser with defocus of -1mm is used for zoom point circumcision drilling, scanning speed is 2000mm / s, number of scanning circles is 500, Z axis displacement is -0.1mm, along Z The number of axial displacement steps is 10. After the circumcision, the appearance of the drilled bone tissue is as attached image 3 As shown in a, the drilling depth measured by confocal at this time is 0.5 mm, and the displacement of the laser head along the z-axis direction is twice the drilling depth.
[0034] After that, the second stage of groove circumcision drilling is carried out in situ, the Z-axis displacement is increased to -0.12mm, an...
Embodiment 2
[0037] like Figure 4 a and Figure 4 As shown in b, drill the isolated porcine femur with soft tissue and periosteum removed. In the case of continuously spraying water on the bone tissue around the drill hole, first use the average power of 6W in the first stage of groove circumcision, and the repetition frequency 500KHz, picosecond 355nm UV laser with defocus of -1mm starts to drill with zoom focus circumcision, scanning speed is 2000mm / s, number of scanning circles is 500, Z axis displacement is -0.1mm, and the number of displacement steps along Z axis is 10, a shallower annular groove is obtained, as attached Figure 4 a is the surface topography of the annular groove. At this time, the drilling depth measured by confocal is 0.56 mm, and the displacement of the laser head along the z-axis direction is 1.78 times the drilling depth.
[0038] Afterwards, the second stage of groove circumcision drilling is carried out in situ, the displacement of the processing head along ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Defocus amount | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com