Method for synthesizing medium-chain fatty acid from planting wastes
A medium-chain fatty acid and waste technology is applied in the field of resource utilization of planting waste to achieve the effects of reducing pollution, realizing resource utilization, and reducing costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
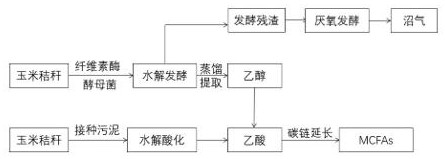
[0025] (1) Corn stalks were used as fermentation raw materials, cellulase and yeast were added to a 0.5L anaerobic fermentation bottle, and anaerobic fermentation was carried out at 30°C, TS 10%, and pH 5 to produce ethanol. After the cellulose is decomposed into glucose under the action of cellulase, the yeast decomposes the sugar into ethanol under anaerobic conditions.
[0026] (2) Distill and extract the ethanol in step (1) under heating conditions; then add livestock and poultry manure as inoculum to the anaerobic fermentation bottle in step (1), mix it with the remaining residue for anaerobic fermentation to generate biogas, Continue anaerobic fermentation to produce biogas at 35°C, TS (solid content) 20%, and pH 6.8;
[0027] (3) Add corn stalks and inoculated sludge containing acid-producing bacteria into another 0.5L anaerobic fermentation bottle, and carry out anaerobic fermentation to produce acid under the conditions of 25°C, TS 6%, and pH 5.5 to generate acetic ac...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Corn stalks were used as fermentation raw materials, cellulase and yeast were added, and anaerobic fermentation was carried out at 35°C, TS 20%, and pH 6 to produce ethanol.
[0031] (2) Distill and extract the ethanol in step (1) under heating conditions, then add cow dung to the remaining fermentation residue as an inoculum, and continue anaerobic fermentation at 40°C, TS 25%, and pH 7 to produce biogas.
[0032] (3) Using corn stalks as fermentation raw materials, adding inoculated sludge rich in acid-producing bacteria, anaerobic fermentation was carried out at 30°C, TS 8%, and pH 6 to produce acid and produce short-chain fatty acids such as acetic acid.
[0033] (4) Ethanol obtained by distillation was added, and the carbon chain extension experiment was carried out at 40°C and pH 7, and the yield of MCFAs could reach 9.4g / L.
Embodiment 3
[0035] (1) Corn stalks were used as fermentation raw materials, cellulase and yeast were added, and anaerobic fermentation was carried out at 40°C, TS was 30%, and pH was 7 to produce ethanol.
[0036] (2) Distill and extract the ethanol in step (1) under heating conditions, then add cow dung to the remaining fermentation residue as an inoculum, and continue anaerobic fermentation at 45°C, TS 30%, and pH 7.2 to produce biogas.
[0037] (3) Using corn stalks as fermentation raw materials, adding inoculated sludge rich in acid-producing bacteria, anaerobic fermentation was carried out at 35°C, TS 10%, and pH 6.5 to produce acid and produce short-chain fatty acids such as acetic acid.
[0038] (4) Ethanol obtained by distillation was added, and the carbon chain extension experiment was carried out at 50°C and pH 8, and the yield of MCFAs could reach 8.7g / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com