Application of anti-double-stranded DNA antibody as congenital megacolon diagnostic marker
A Hirschsprung and antibody technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as the impact of results, unobvious barium enema, and lack of abnormal intestinal innervation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Example 1. Collection and Grouping of Plasma and Tissue Samples
[0080] Plasma samples were divided into Hirschsprung children group (37 cases), other enteropathy control group (18 cases), healthy children group (30 cases), aged from 3 months to 3 years old, male sex 3 / 4 Male, disease and control groups were age and sex matched. All samples came from Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center, and the healthy children group was the remaining blood samples after physical examination of healthy children. The blood collection method is anticoagulant blood collection, centrifugation to separate plasma, and cryopreservation of samples. The colon tissue samples belonged to the Hirschsprung children group (36 cases), which were surgically resected diseased tissues. Other enteropathy control group (including 11 cases of colon tissue with anal stenosis and intestinal stricture stoma).
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2. Human autoimmune antigen chip screening and differentially expressed autoantibody analysis
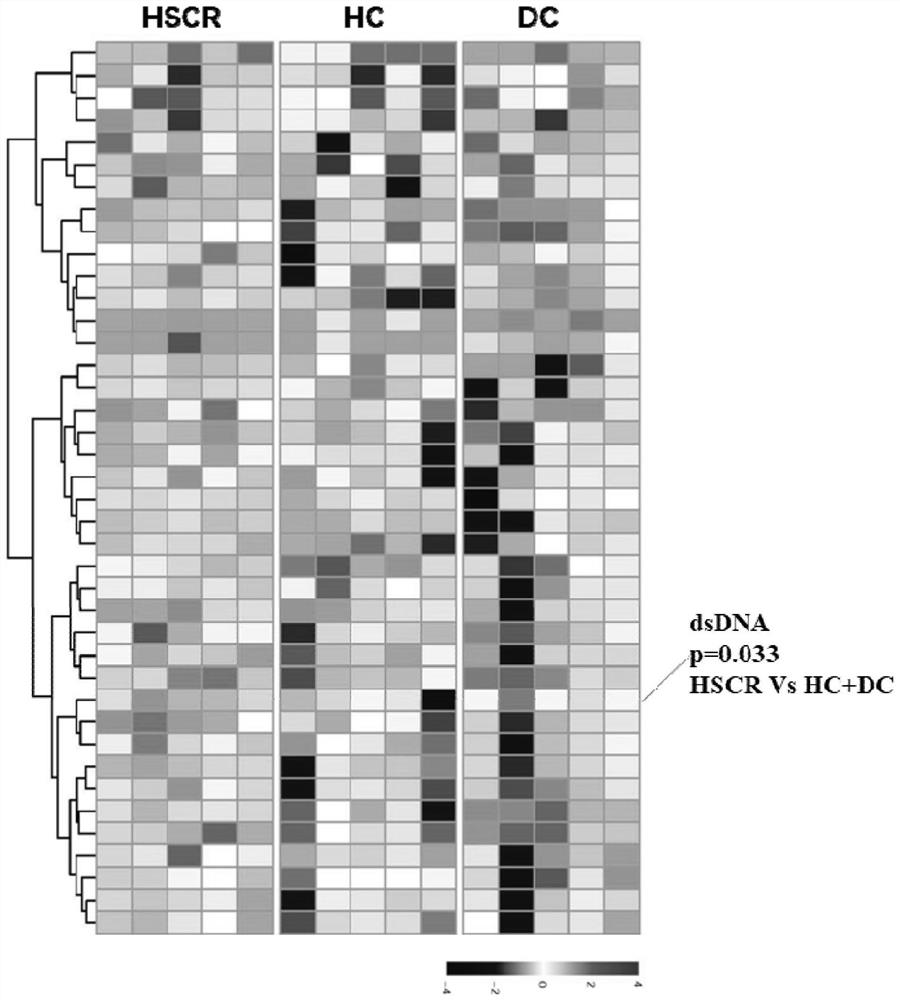
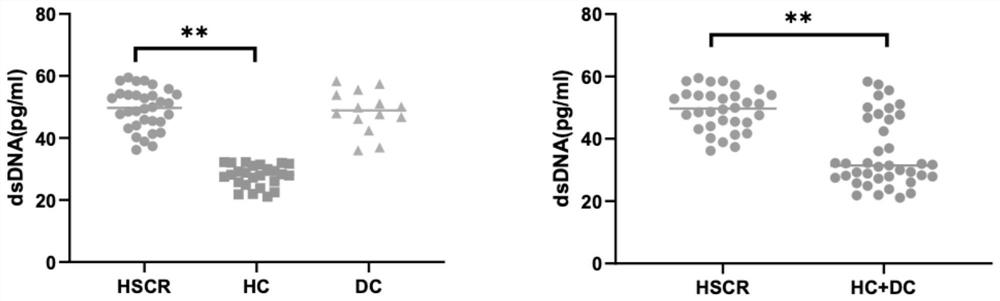
[0082] Plasma from 5 cases of children with Hirschsprung’s disease (HSCR), 5 cases of plasma from children in the healthy group (HC) and 5 cases in other enteropathy (DC) groups, were used for the screening of human autoimmune antigen chips, which were provided by Guangzhou Yijin Provided by Biotechnology Co., Ltd., it includes IgG detection of more than 100 kinds of autoimmune antibodies. The original data, after subtracting the negative control, is normalized by the RLM method, and the results are analyzed by M statistics. figure 1 The cluster analysis graph of the differential autoantibodies is shown, from which it can be seen that the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in the plasma of children with Hirschsprung's disease is significantly higher than that in the control group (p=0.033).
Embodiment 3
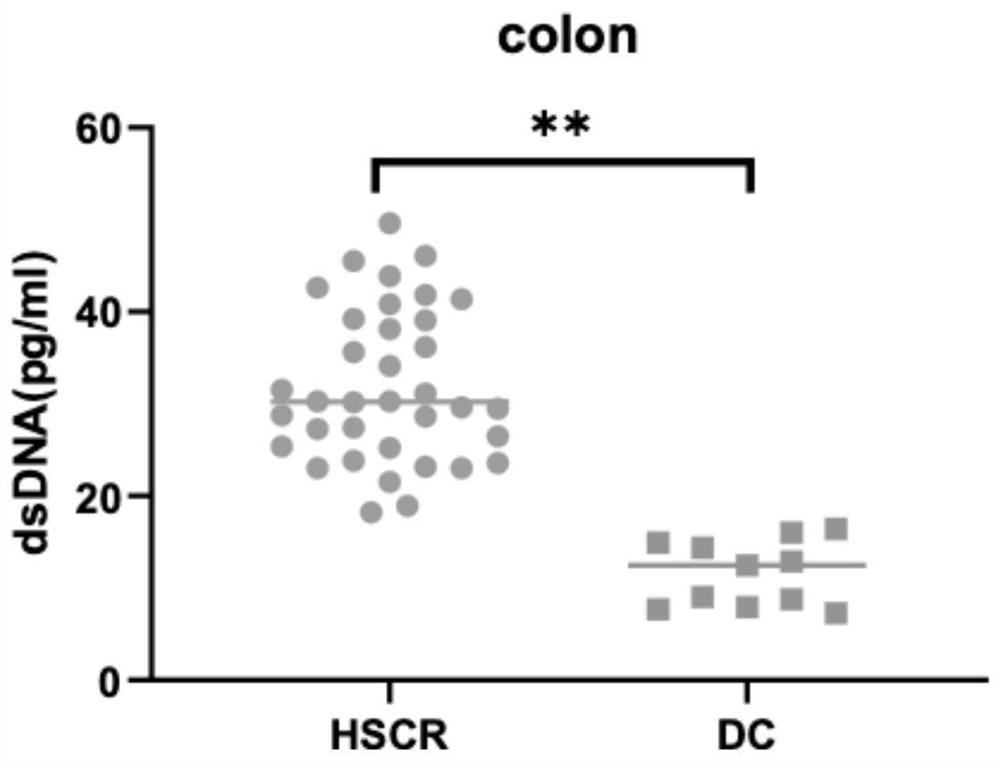
[0083] Example 3. Detection of anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibody in Hirschsprung disease tissue
[0084] Double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) is a protein expressed specifically in nerve tissue. Autoantibodies to this protein have been reported in encephalitis, but not in peripheral enteric nervous system diseases. In order to verify that the anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibody is indeed derived from the intestinal nerve tissue of the lesion of patients with Hirschsprung, the intestinal tissues of the lesion of patients with Hirschsprung (36 cases), as well as colon tissues of other intestinal diseases (including anal stenosis and There were 11 cases of intestinal stricture and fistula), the level of anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibody in the tissue was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent immunoassay (ELISA), and the detection kit was human anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibody ELISA ) Kit (Shanghai Zhenke Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). figure 2 The results sho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com