A dna-binding antimicrobial peptide vpdb40 of Penaeus vannamei and its application
An antibacterial peptide, white shrimp technology, applied in the application, antibacterial drugs, peptides and other directions, can solve the problem that there is no nucleic acid sequence, recombinant protein research and application, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
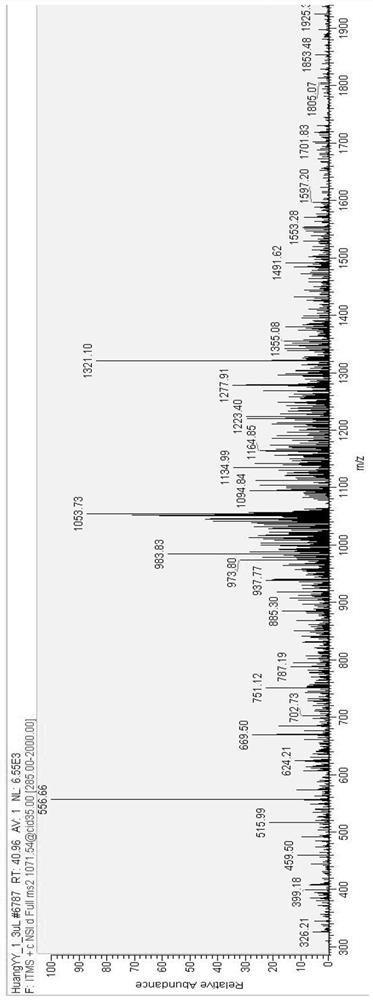
[0041] Example 1 Mass spectrometry analysis of Penaeus vannamei DNA-bound antimicrobial peptides
[0042] First, the samples of Penaeus vannamei were prepared, and 400 healthy Penaeus vannamei were divided into high-intensity ultrasound group, medium-intensity ultrasound group, low-intensity ultrasound group and control group with 100 each. Each shrimp was injected with 0.1 mL of Vibrio parahaemolyticus (1.0×10 5-6 cfu / mL) or an equivalent amount of sodium chloride. Live shrimp were collected 24 hours after infection and minced immediately with PBS buffer. After centrifugation at 100g for 15min, the supernatant was taken and passed through a 3000Da filter. Store at -20°C for further analysis.
[0043] Chromatography was then performed using a Nano Aquity UPLC system (Waters Corp.) instrument. The injection volume was 5.0 μl, and the mobile phases were 0.1% methanol in water and acetonitrile, respectively. The elution gradients are shown in Table 1.
[0044] Table 1. Anti...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination
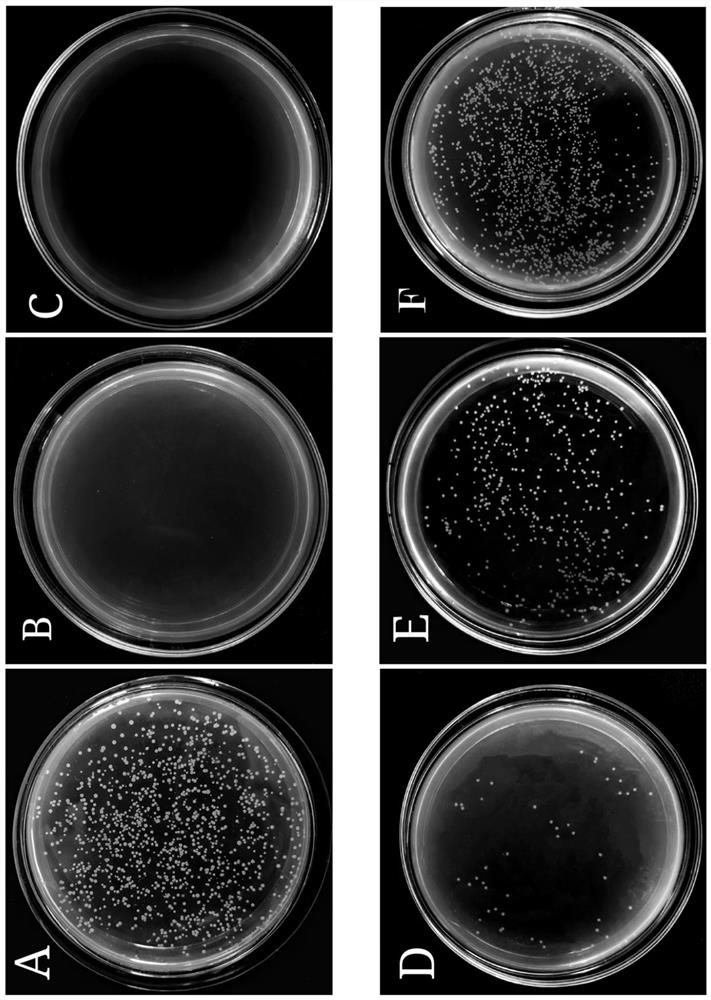
[0061] Vibrio parahaemolyticus was incubated at 37°C for 12h to logarithmic growth phase and diluted to 10 in 0.01M pH 7.2 phosphate buffer 6-7 CFU / mL. The peptides were dissolved in phosphate buffer and mixed with bacteria in equal volume at 37°C for 2h. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of antimicrobial peptide at which no bacterial growth can be seen from the microtiter plate after incubation at 37°C. like figure 2 As shown, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of VPDB40 against Vibrio parahaemolyticus was 1.95 μg / mL.
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Time-kill curve (Time kill) determination
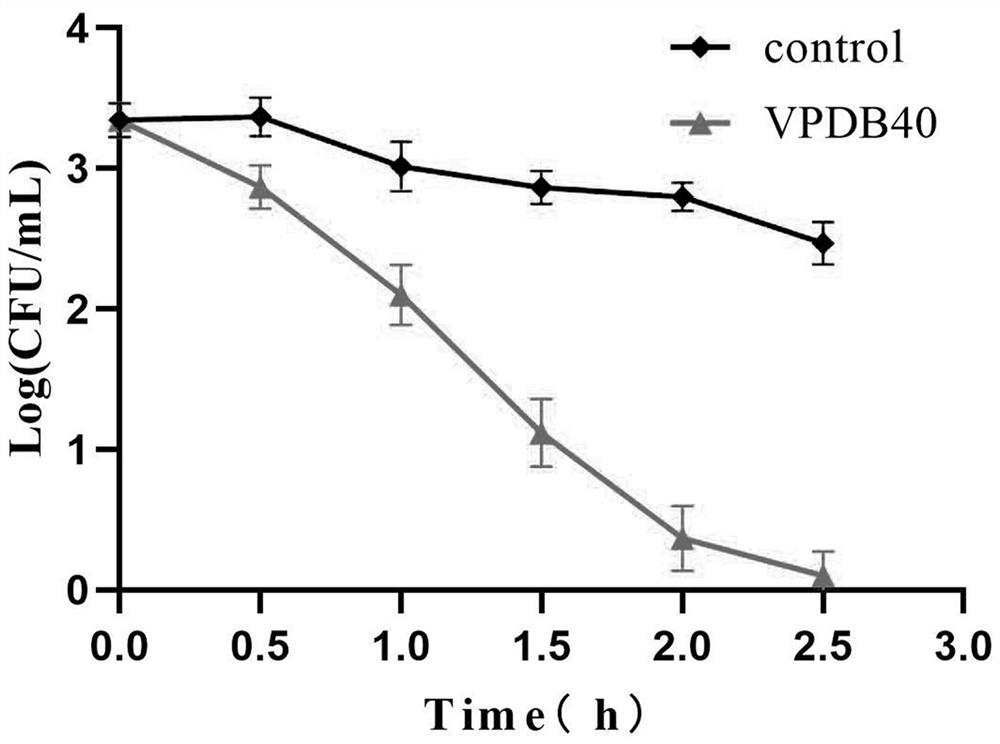
[0063] The time-kill curve of peptide VPDB40 was determined using the plate colony count method. Vibrio parahaemolyticus was incubated at 37°C for 12h to logarithmic growth phase and diluted to 10 in 0.01M pH 7.2 phosphate buffer 6-7 CFU / mL. Peptides were dissolved in phosphate buffer and diluted to 3.91 μg / mL, an equal volume was mixed with bacteria and incubated at 37°C. At different time points (ie 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 and 3 hours), 0.2 mL of bacterial suspension was obtained and colonies were counted after culturing on nutrient broth plates at 37°C for 24 hours. like image 3 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com