Method for detecting glucose by using novel enzyme-free glucose sensor
A glucose sensor and glucose technology, applied in the field of electrochemical detection, can solve problems such as high cost, and achieve the effects of easy operation, enhanced performance, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A method for detecting glucose by a novel enzyme-free glucose sensor, the preparation method of the working electrode of the enzyme-free glucose sensor comprises the following steps:
[0040] Step 1. Precursor preparation
[0041] 1. Ultrasonically mix and disperse 7.5mmol nickel nitrate hexahydrate and 2.5mmol ferric nitrate nonahydrate into 20mL deionized aqueous solution, and record it as solution A;
[0042] 2. Prepare 30 mL of 2.5 mmol sodium hydroxide solution, which is called solution B; add 23 vol.% formamide into 20 mL of aqueous solution containing 0.1 M sodium nitrate, and call it solution C.
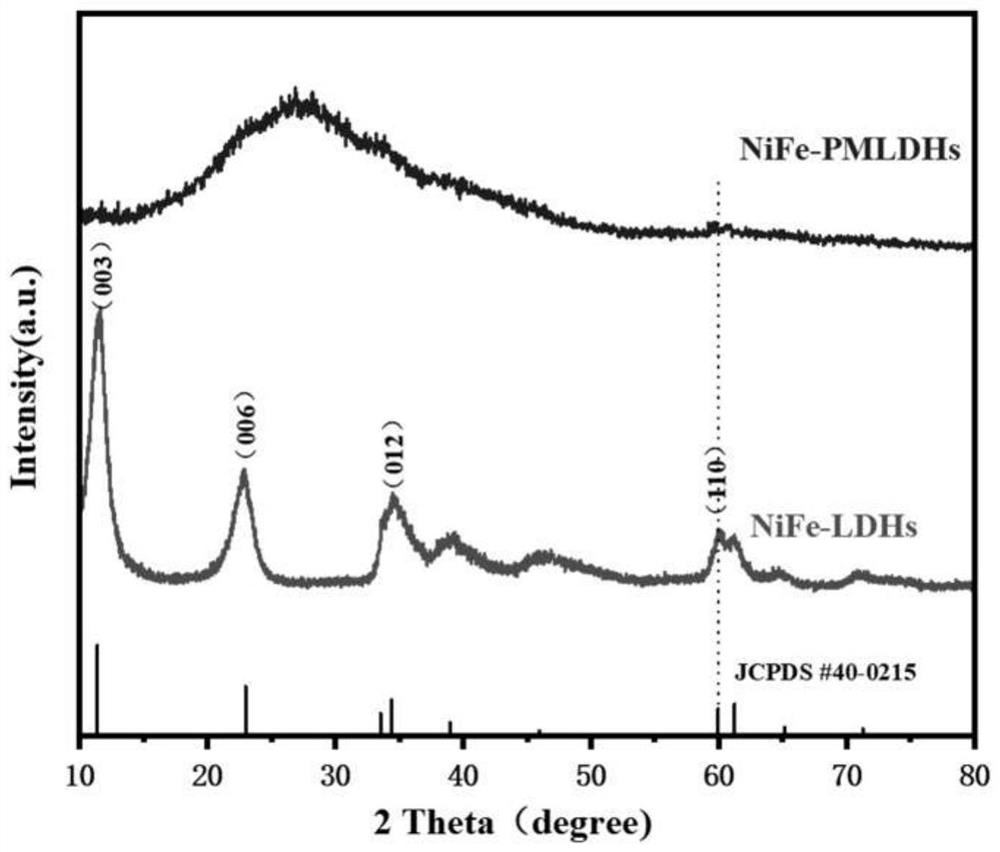
[0043] Step 2, the preparation of NiFe-PMLDHs nanosheet material
[0044] Add solutions A and B to solution C at the same time. After the reaction is completed, centrifuge, wash, and store wet to obtain the material NiFe-PMLDHs; in the magnetic stirring of the water bath, slowly drop solutions A and B into solution C at the same time, and the temperature of the oil ba...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Sensor response to glucose
[0053] Use the modified electrode prepared in Example 1 as the working electrode, the platinum wire as the counter electrode, and the Ag / AgCl electrode as the reference electrode. One end of these three electrodes is connected to an electrochemical workstation (Autolab), and 0.1M NaOH solution is used as the electrolyte for electrochemical testing. .
[0054] The specific test conditions are:
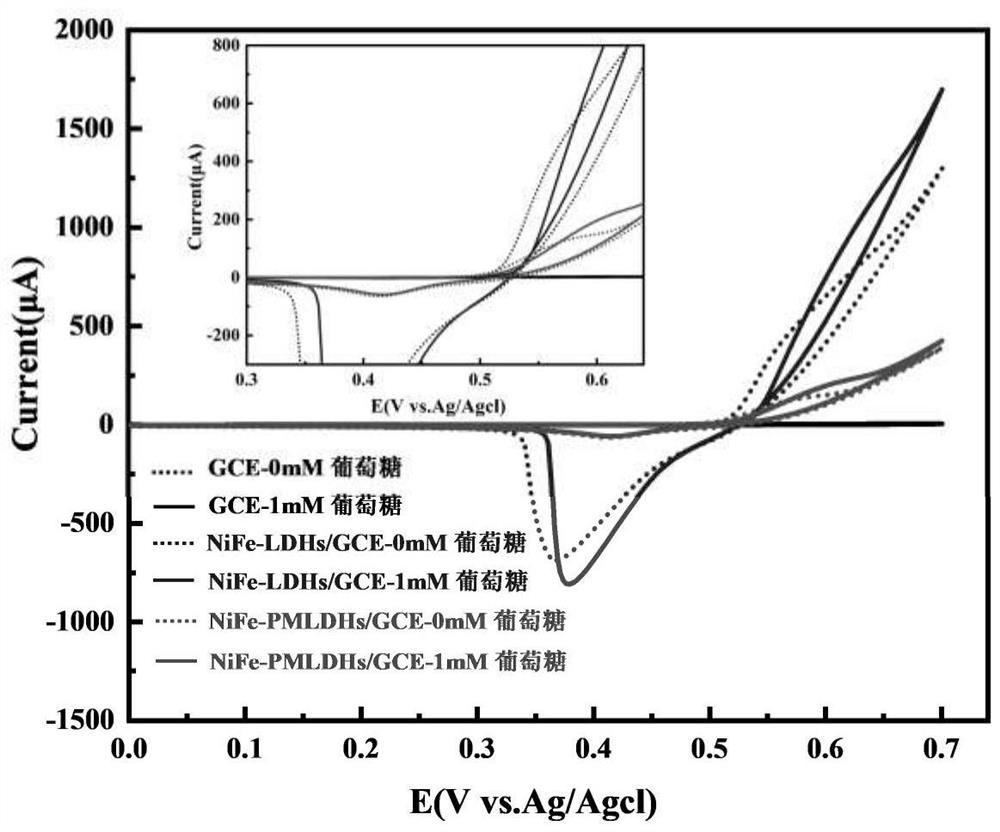
[0055] The cyclic voltammetry test technology is adopted, and the sensor is used to perform cyclic voltammetry scanning in the potential range of 0V to 0.7V. The cyclic voltammogram comparison of the sensor in the solution of 1mM glucose / 0.1M sodium hydroxide and the solution without glucose ( image 3 ).
[0056] The measurement result is:
[0057] It can be found that after adding 1mM glucose, the oxidation peak current has a significant increase of about 400μA, indicating that the sensor has an obvious electrochemical response to glu...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Application of the sensor in the detection of glucose in actual serum samples
[0066] Use the modified electrode made by implementing a modified electrode as a working electrode, platinum wire as a counter electrode, and an Ag / AgCl electrode as a reference electrode. One end of these three electrodes is connected to an electrochemical workstation (Autolab), and 0.1M NaOH solution is used as an electrolyte for electrochemical testing.
[0067] The specific test conditions are:
[0068] Under the applied potential of 0.5V, the current response value of the enzyme-free glucose sensor based on the porous single-layer nickel-iron layered double hydroxide nanosheets to the known concentration of glucose solution was tested, and the 1% human serum sample was detected by the standard sample recovery method. glucose. Prepare three serum samples by adding glucose with known concentrations of 6.0, 7.0, and 8.5mM, perform an amperometric experiment, and detect the curr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com