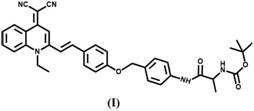
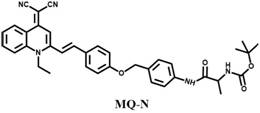
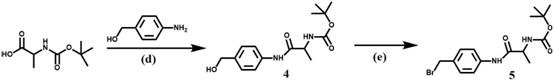
Aggregation-induced emission fluorescent probe for detecting aminopeptidase N and preparation of aggregation-induced emission fluorescent probe
A technology of aggregation-induced emission and fluorescent probes, which is applied in the field of fluorescent probes to achieve the effects of fast response, low interference, good sensitivity and selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for preparing an aggregation-induced emission fluorescent probe for detecting aminopeptidase N, the steps comprising:
[0025] 1) Synthesis of Compound 1:
[0026] in N 2 Under atmosphere, 2-methylquinoline (1.79 g, 12.5 mmol) and iodomethane (5.50 g, 35 mmol) were dissolved in acetonitrile (25 mL), and the reaction solution was refluxed for 10 hours, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain Compound 1, yield 75%.
[0027] Synthesis of compound 2:
[0028] Compound 1 (1.74 g, 6 mmol) and malononitrile (1.20 g, 18 mmol) were dissolved in absolute ethanol (15 mL), stirred continuously at 0°C, and reacted for 6 hours after adding sodium ethoxide, and the mixture was Pour into ice water, adjust the pH to 8, filter the resulting precipitate, wash with water and vacuum dry to obtain compound 2 with a yield of 85%.
[0029] Synthesis of compound 3:
[0030] Compound 2 (1.40 g, 7.5 mmol) and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde (1.65 g, 13.5 mmol) were dis...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Measurement of Absorption Spectrum and Fluorescence Spectrum of Probe MQ-N
[0039] Take the MQ-N synthesized in Example 1 in a test tube to prepare a stock solution (1.0 mM) of the probe MQ-N in DMSO. Preparation of NaCl, KCl, CaCl in distilled water 2 , ZnCl 2 , MgCl 2 , CuCl 2 , H 2 o 2, NaClO, glucose, GSH, Cys, Hcy, alkaline phosphatase, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, nitroreductase, carboxylesterase and other stock solutions. All the above stock solutions were adjusted to a final volume of 5 mL with phosphate buffered saline. For spectroscopic experiments, after incubating the MQ-N stock solution with a certain amount of analyte in a quartz cuvette at pH = 7.4 for 30 min, transfer 3 mL of the reaction solution to a 1 cm quartz cuvette, and set the excitation to 480 nm, the emission wavelength is 500-700 nm. Meanwhile, a control group without aminopeptidase N was prepared and compared under the same conditions. MQ-N showed double absorption peaks around 350 nm...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Evaluate the effect of different pH and temperature on the fluorescence of probe MQ-N
[0042] Taking the MQ-N stock solution (10 μM) in Example 2, the probe is almost non-fluorescent when the pH range is 4.0-8.0 and the temperature range is 23-40°C, which shows that the probe has high stability . After reaction with aminopeptidase N, the probe produced a significant fluorescent response throughout the pH range tested, although the maximum fluorescence intensity occurred in the pH range of 6.0–7.4. On the other hand, the strongest fluorescence of the reaction solution occurs at about 37°C, which is consistent with the fact that enzymes generally have maximum activity at 37°C. The results indicated that the probe MQ-N has good function under normal physiological conditions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com