Eutectic solvent for dissolving cellulose and method for dissolving cellulose
A low eutectic solvent and technology for dissolving cellulose, applied in the field of cellulose dissolving, can solve the problems of poor dissolving ability of cellulose, weak ability to form new hydrogen bonds of cellulose hydrogen bonds, poor dissolving ability of cellulose and hydrogen bonding, etc. Achieve the effect of improving the solubility, weakening its own hydrogen bonding, and increasing the degree of damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
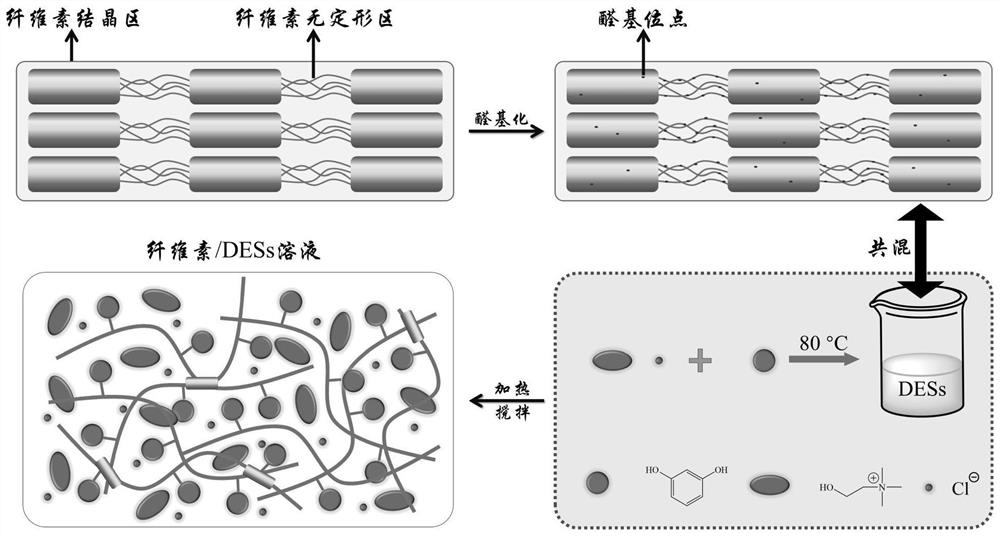
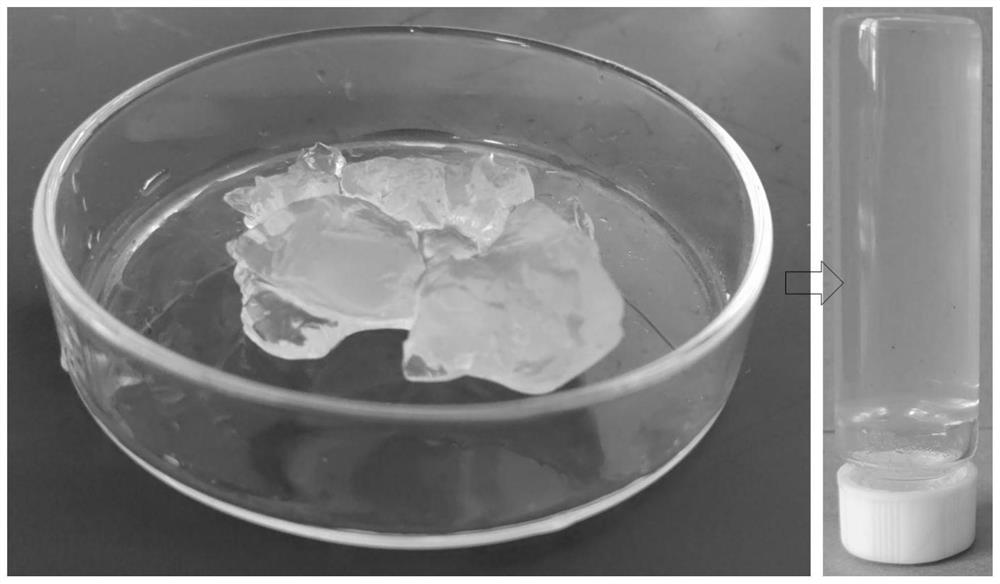
[0044]Mix microcrystalline cellulose, sodium periodate, and deionized water with a mass ratio of 1:0.6:10, and oxidize microcrystalline cellulose at 50°C for 8 hours. After the oxidation is completed, wash and filter with deionized water for 5 times to The reaction reagents are removed to obtain oxidized cellulose. Mix resorcinol and choline chloride at a molar ratio of 1:1 at 80°C for 1 hour to obtain a transparent and uniform deep eutectic solvent at room temperature. Add 1.5 g of oxidized cellulose (absolute dry weight) into 30 g of deep eutectic solvent, stir and dissolve at 80° C. for 2 h to obtain a cellulose solution.
[0045] The process schematic diagram of the deep eutectic solvent dissolving cellulose of embodiment 1 is as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0047] Mix microcrystalline cellulose, sodium periodate, and deionized water with a mass ratio of 1:0.4:8, and oxidize microcrystalline cellulose at 30°C for 22 hours. After the oxidation is completed, wash and filter with deionized water for 5 times to The reaction reagents are removed to obtain oxidized cellulose. Mix phenol and betaine at a molar ratio of 1:0.5 at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a transparent and uniform deep eutectic solvent at room temperature. Add 3 g of oxidized cellulose (absolute dry weight) into 60 g of deep eutectic solvent, stir and dissolve at 100° C. for 1 h to obtain a cellulose solution.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Mix α-cellulose, potassium periodate and deionized water with a mass ratio of 1:0.6:12, and oxidize microcrystalline cellulose at 70°C for 4 hours. After the oxidation is completed, wash and filter with deionized water for 5 times until the reaction Reagents are removed to obtain oxidized cellulose. Mix hydrogen bond donors and hydrogen bond acceptors with a molar ratio of 1:3 at 100°C for 0.5 h to obtain a transparent and uniform deep eutectic solvent at room temperature. Among the hydrogen bond donors, hydroquinone and cresol The molar ratio is 1:1, and in the hydrogen bond acceptor, the molar ratio of tetramethylammonium chloride and methyltriphenylphosphine bromide is 1:1. Add 4.5g of oxidized cellulose (absolute dry weight) into 30g of deep eutectic solvent, react and dissolve in a 70°C internal mixer for 4h to obtain a cellulose solution.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| oxidation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com