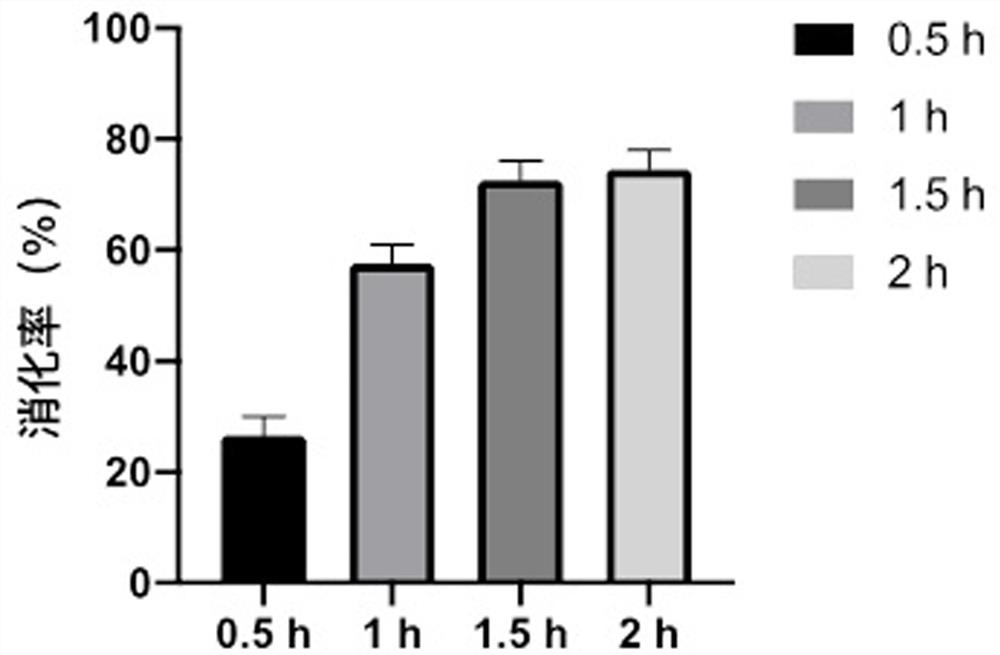
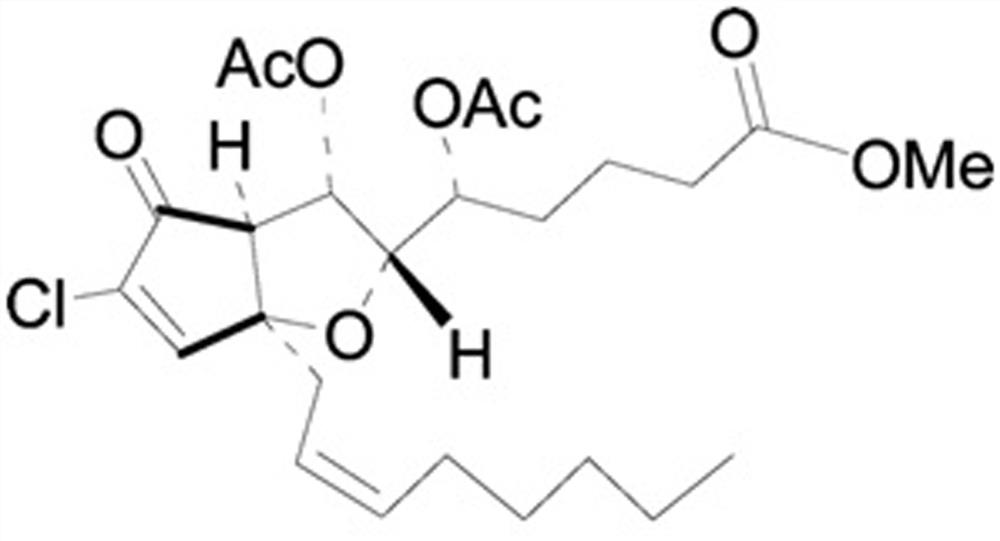
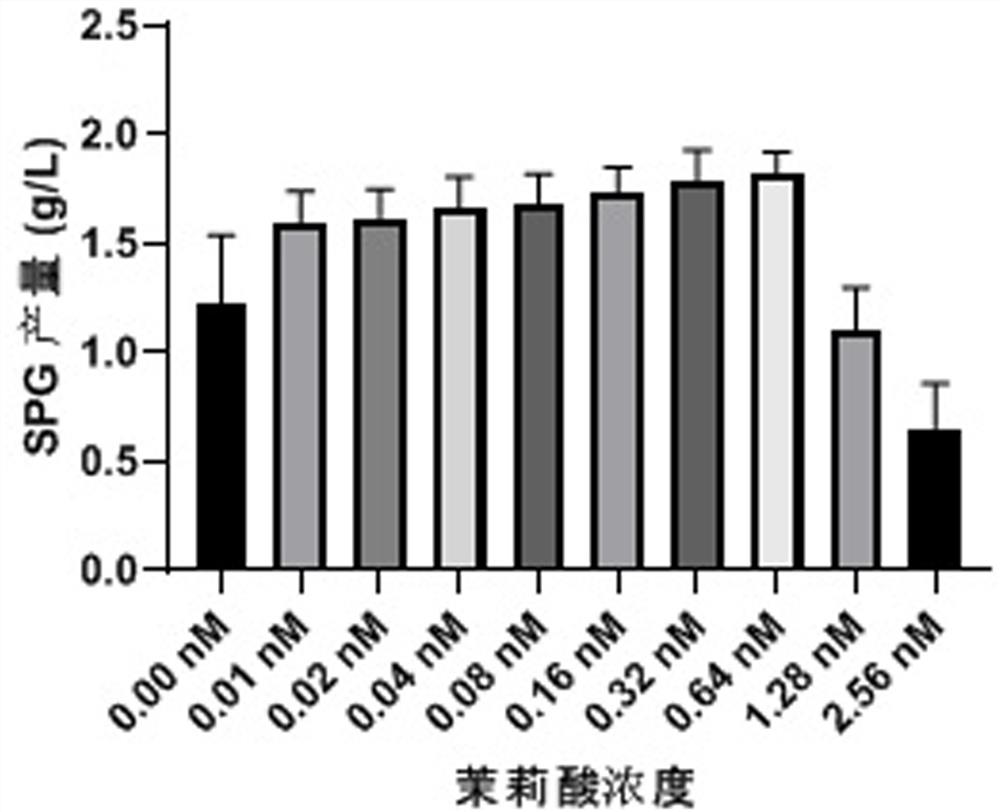
Fermentation and cultivation method of schizophyllum producing schizophyllum polysaccharide
A technology for fermenting and culturing Schizophyllum, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve problems such as the inability to meet the needs of polysaccharide production, and achieve the effects of increasing yield, increasing content and increasing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: Preparation of soybean meal protein.
[0028] The following four schemes A, B, C, and D are used to prepare soybean meal protein respectively, and the parts mentioned refer to parts by mass.
[0029] A: Soak 80 parts of soybean meal with 300 parts of water for 24 hours; adjust the pH value to 6-7, add papain according to 2% of the weight of soybean meal, stir evenly, and carry out enzymatic hydrolysis at 55° C. for 0.5 hour. The enzymatic hydrolyzate was deactivated at 100° C. for 10 minutes, and soybean meal protein A was obtained after the treatment.
[0030] B: Soak 80 parts of soybean meal in 300 parts of water for 24 hours; adjust the pH value to 6-7, add papain according to 2% of the weight of soybean meal, stir evenly, and carry out enzymatic hydrolysis at 55° C. for 1 hour. The enzymolyzate was deactivated at 100° C. for 10 minutes, and soybean meal protein B was obtained after the treatment.
[0031] C: Soak 80 parts of soybean meal in 300 parts...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Initial culture of Schizophyllum.
[0035] Schizophyllum commune SCSIO z046 was inoculated with PDA comprehensive medium (potato 200g, glucose 20g, agar 15-20g, water 1000mL, pH natural), and cultured at 30°C in the dark for 5-10 days after inoculation.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3: Optimization of SPG basal medium.
[0037] The production of SPG was optimized using the experimental method of Design Expert version 7.0.1.0 (Statcon, USA). The independent variables selected for optimization were as follows: starch, soybean meal protein prepared by Protocol C of Example 1, yeast extract, sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and oleic acid. Table 1 presents the factors evaluated at five different levels. The total experiment was 50 runs, including 32(2 5 ) factor points, 10 axial points, and 8 replicates of the center point. The dependent response is the SPG yield (y 1 ) and biomass production (y 2 ).
[0038] Table 1: Experimental independent variables and their levels in the central composite design (CCD)
[0039]
[0040] Effective factors such as carbon and nitrogen sources and appropriate concentration ranges were investigated in this study through a one-factor-at-a-time approach, as considered in previous studies. Based on the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com