Preparation method of chitosan microspheres for cell immobilization and drug delivery
A technology of chitosan microspheres and cell immobilization, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, microsphere preparation, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of uneven size, time-consuming and labor-intensive, unsuitable for industrial production, etc. Achieve the effects of increasing deacetylation speed, increasing production capacity, cell viability retention and reusability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
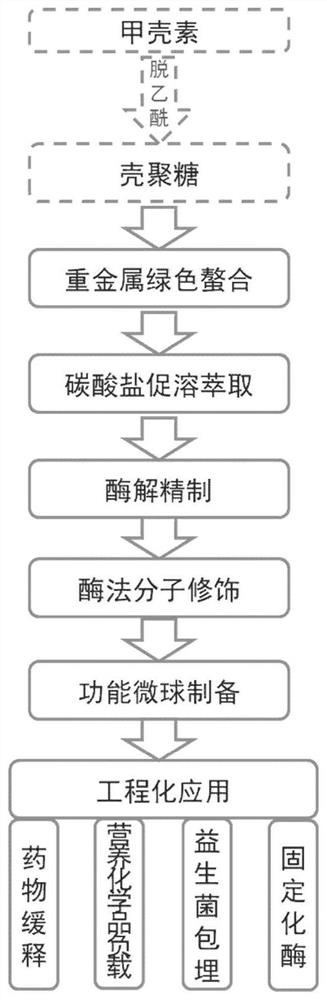
[0036] A preparation method for chitosan microspheres for cell immobilization and drug delivery, comprising the following steps:
[0037] 1) Weigh chitin and chitin deacetylase according to a mass ratio of 1000:1, add water to dissolve, place in a microwave device, treat at 50°C, microwave power 600W for 10 minutes, and inactivate the enzyme to obtain a chitosan solution.
[0038] 2) Using tetrasodium glutamic acid diacetate to prepare a chelating agent with a concentration of 0.02mol / L, the chelating agent and chitosan solution are fully stirred according to the molar ratio of 10:0.2, mixed evenly, and the solution is observed until the solution changes from clarification to From cloudy to clear.
[0039] 3) Add 0.5g / L carbonate to the solution in step 2) for sedimentation, stir fully, improve the extraction and removal ability of the chelating agent to residual metal ions, and obtain a crude chitosan solution.
[0040] 4) Add complex biological enzymes (specific keratinase ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A preparation method for chitosan microspheres for cell immobilization and drug delivery, comprising the following steps:
[0051] 1) Weigh chitin and chitin deacetylase according to a mass ratio of 1000:1, add water to dissolve, place in a microwave device, treat at 50°C, microwave power 400W for 10 minutes, and inactivate the enzyme to obtain a chitosan solution.
[0052] 2) Use citric acid to prepare a chelating agent with a concentration of 0.01mol / L. The chelating agent and chitosan solution are fully stirred according to the molar ratio of 20:1, and mixed evenly. Observe the change of the solution until the solution changes from clear to cloudy and then to clear. .
[0053] 3) Add 2g / L carbonate to the solution in step 2) for sedimentation, stir fully, improve the extraction and removal ability of the chelating agent to residual metal ions, and obtain a crude chitosan solution.
[0054] 4) Add complex biological enzymes (specific keratinase and lipase) to the cru...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Using the immobilized cells prepared in Example 1, the continuous conversion production of niacin was carried out by using a packed bed bioreactor. Nicotinic acid, also known as nicotinic acid and anti-peaceae factor, is converted into nicotinamide in the human body and participates in lipid metabolism in the body, the oxidation process of tissue respiration and the process of anaerobic decomposition of carbohydrates. A packed bed bioreactor is built by using chromatographic columns, peristaltic pumps, super water baths and other related instruments, and the device is used for continuous conversion and production of niacin. The optimum reaction conditions for continuous transformation are: temperature 35°C, pH 7.0, substrate 3-cyanopyridine concentration 350mmol·L -1 , the volume ratio of immobilized cells to substrate 3-cyanopyridine is 1:1, the residence time is 35.2min, and the transformation capacity of cross-linked PVA-CS immobilized cells is 348.4g (3-cyanopyridin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com