Cement-based material and preparation method thereof
A cement-based material, cement technology, applied in the field of concrete maintenance, can solve problems such as high cost and difficult operation, and achieve the effects of increasing carbonation rate, increasing solubility, broad market prospects and economic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
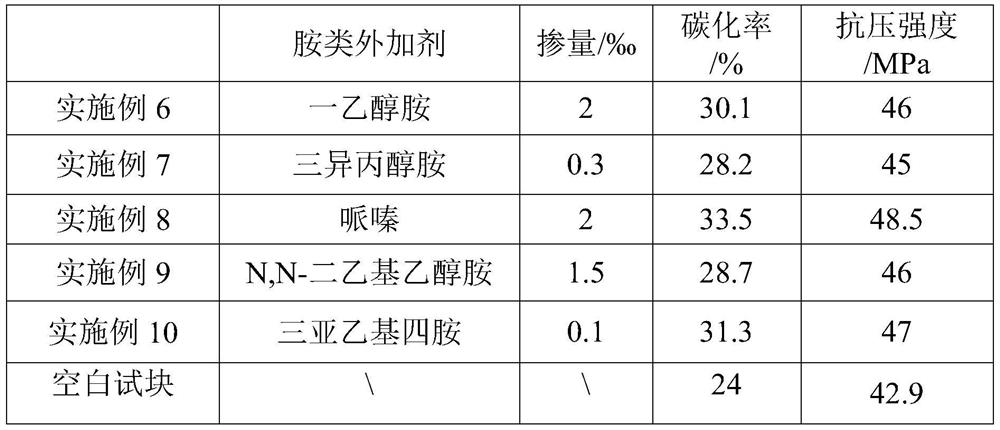
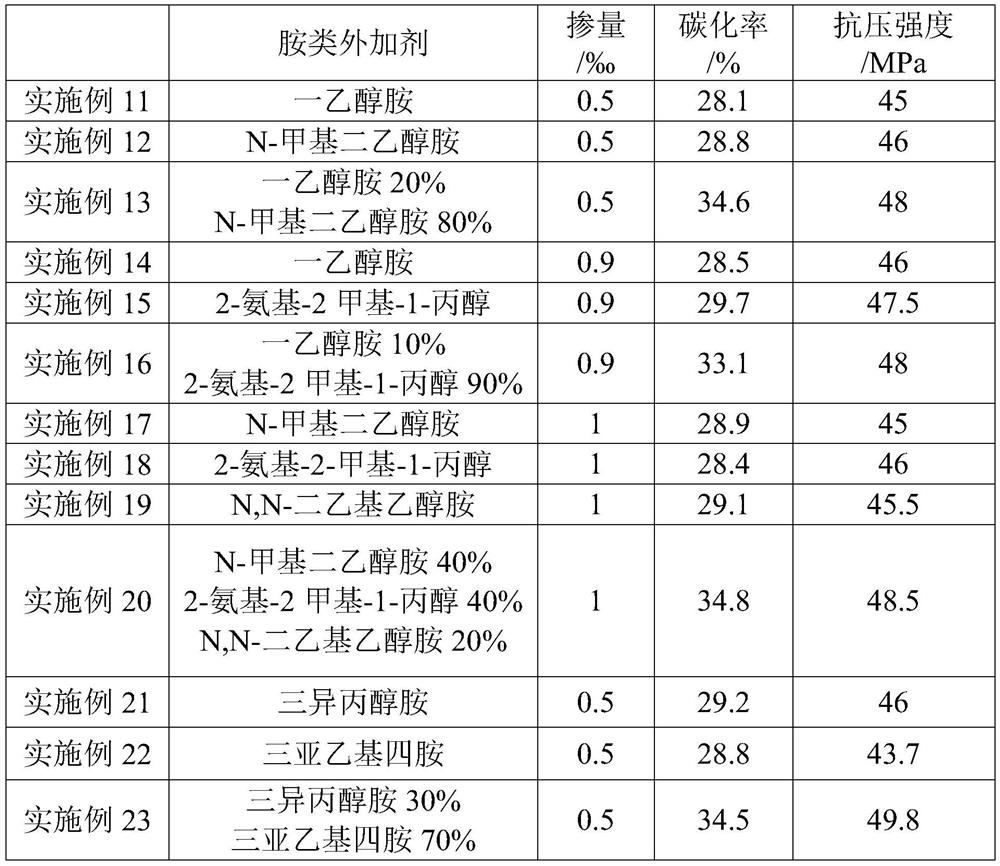
[0027] One embodiment of the present invention proposes a method for preparing cement-based materials, which includes: mixing the raw materials of cement-based materials, adding amine admixtures during the raw material mixing process, adding water and mixing to shape, performing high-temperature pretreatment and CO 2 Mineralization maintenance; wherein, the added amount of the amine admixture is 0.01‰~2‰ of the cement mass in the raw material.
[0028] When the addition amount of amine admixture is less than 0.01‰, the expected effect cannot be achieved due to the addition of too little amine admixture, and the addition of too much amine admixture may easily cause the strength of the cement-based material to shrink, affecting the performance and performance of the product. Durability, while also increasing production costs.
[0029] In the embodiments of the present invention, by adding amine admixtures, preferably alcohol amines, the depth of carbon dioxide mineralization and...
Embodiment 1
[0047] (1) Take 100kg of benchmark cement, add 10g of triethanolamine (mass ratio 0.1‰), and mix at a water-cement ratio of 0.4 to prepare a cement slurry test block; take the same batch of cement and make a blank test block at the same water-cement ratio;
[0048] (2) Place the formed clean pulp test block in an air atmosphere, and pretreat it at a temperature of 120°C for 30 minutes;
[0049] (3) Place the test block obtained in step (2) in CO 2 In the mineralized curing atmosphere, the curing pressure is 0.2MPa, CO 2 The partial pressure is 80%, and it is cured for 4 hours in the temperature range of 40°C to 50°C.
[0050] After testing, the carbonization rate and compressive strength of the cement slurry test block and the blank test block in Example 1 are shown in Table 1.
[0051] Table 1 Carbonization rate and compressive strength
[0052] Carbonization rate / % Compressive strength / MPa Example 1 30 47 blank test block 24 39
Embodiment 2
[0054] (1) Take 100kg of benchmark cement, add 30g of triisopropanolamine (mass ratio 0.3‰), and mix at a water-cement ratio of 0.35 to prepare a cement slurry test block; take the same batch of cement and use the same water-cement ratio as a blank test block ;
[0055] (2) Place the formed clean pulp test block in an air atmosphere, and pretreat it at a temperature of 130°C for 20 minutes;
[0056] (3) Place the test block obtained in step (2) in CO 2 In the mineralized curing atmosphere, the curing pressure is 0.3MPa, CO 2 The partial pressure is 90%, and the curing time is 2 hours in the temperature range of 50°C to 60°C.
[0057] After testing, the carbonization rate and compressive strength of the cement paste test block and the blank test block in Example 2 are shown in Table 2.
[0058] Table 2 carbonization rate and compressive strength
[0059] Carbonization rate / % Compressive strength / MPa Example 2 28.5 45.8 blank test block 23.6 42.9 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| carbonization coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com