Lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A lithium iron phosphate, cathode material technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems affecting the cycle performance and low temperature performance of lithium ion batteries, poor low temperature performance and cycle performance, and the compaction of positive pole pieces. Low density and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving low temperature rate discharge performance, improving electrical conductivity, and improving electronic conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This embodiment provides a lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material, the preparation method of the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material is as follows:
[0039] (1) Mix lithium hydroxide, ferrous chloride, ammonium phosphate and ethanol, and conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 160°C and a pressure of 0.7Mpa for 2 hours to obtain lithium iron phosphate crystals;
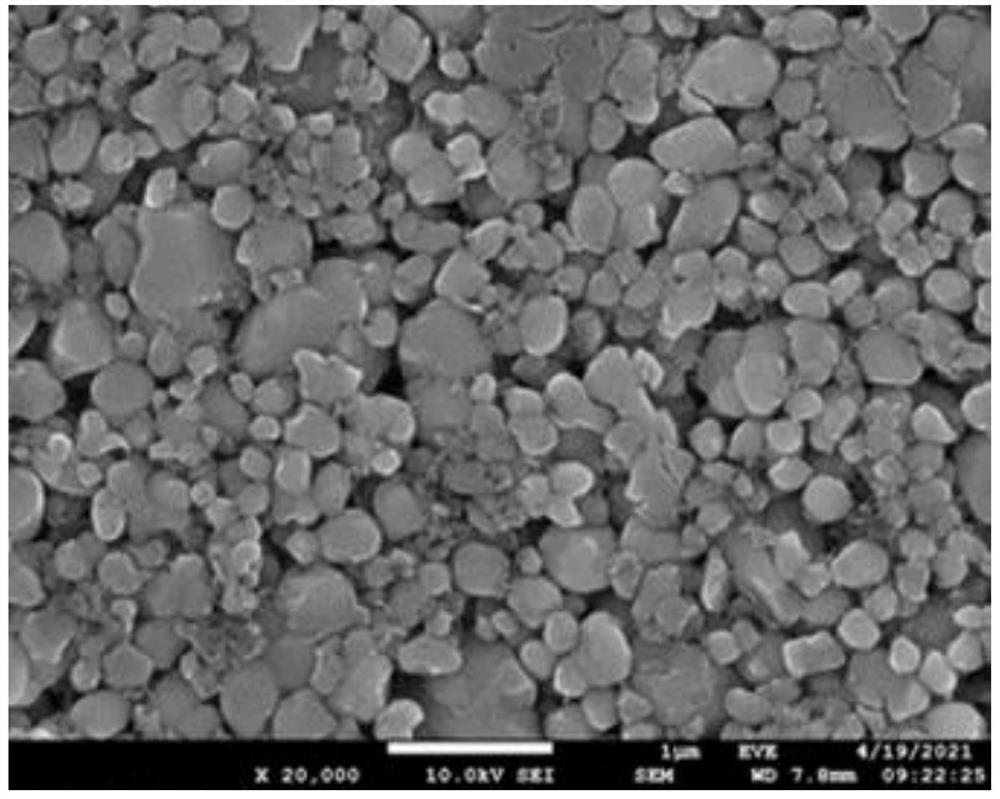
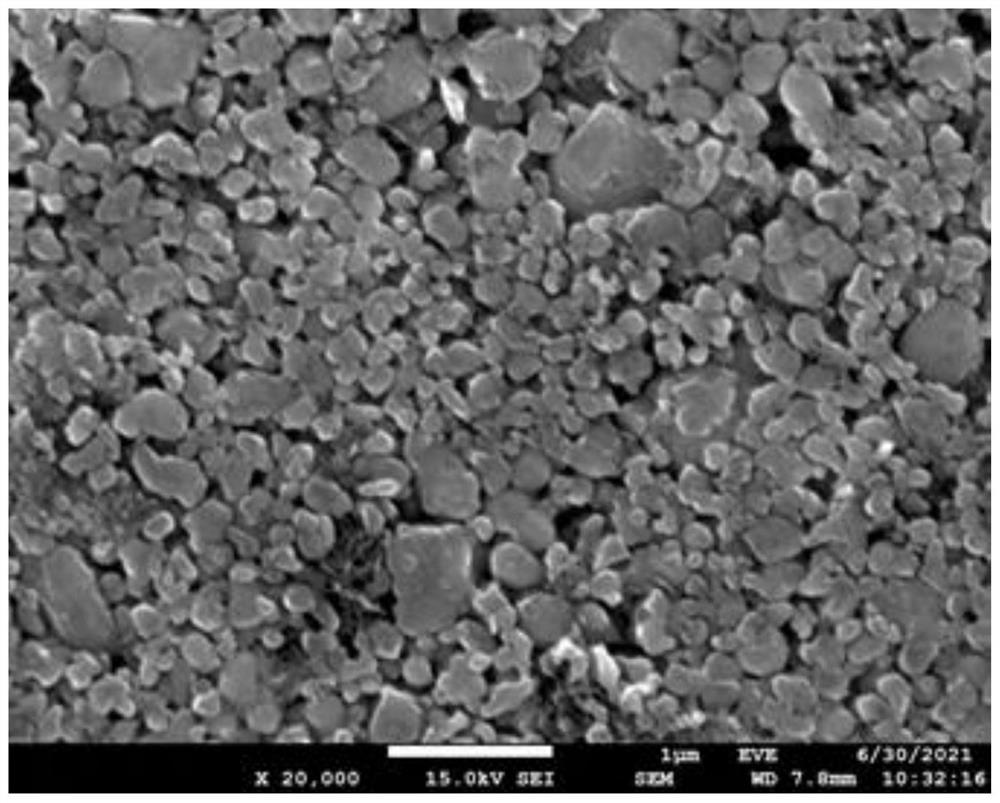
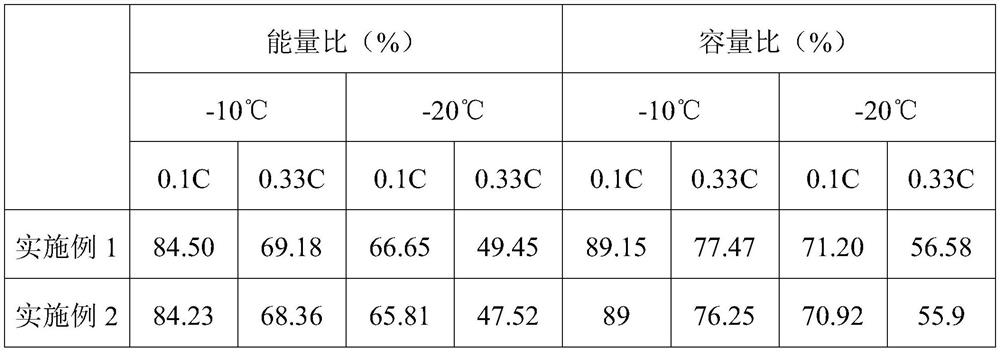
[0040] (2) Grinding the lithium iron phosphate crystal obtained in step (1), and sieving to obtain the first lithium iron phosphate particle whose D50 is 1.04 μm and the second particle whose D50 is 0.81 μm and D90-D10=7.11 lithium iron phosphate particle, the SEM figure of the first particle size lithium iron phosphate particle is as follows figure 1 As shown, the SEM image of the second particle size lithium iron phosphate particles is as follows figure 2 shown;
[0041] (3) The lithium iron phosphate particles with the first particle size obtained in step (2) and the lithium iron pho...
Embodiment 2
[0043] This embodiment provides a lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material, the preparation method of the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material is as follows:
[0044] (1) Mix lithium hydroxide, ferrous chloride, ammonium phosphate and ethanol, and conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 165°C and a pressure of 0.75Mpa for 2.2 hours to obtain lithium iron phosphate crystals;
[0045](2) Grinding the lithium iron phosphate crystal obtained in step (1), and sieving to obtain the first lithium iron phosphate particle whose D50 is 1.05 μm and the second particle whose D50 is 0.80 μm and D90-D10=7.12 Lithium iron phosphate particles;
[0046] (3) Mix the lithium iron phosphate particles with the first particle size and the lithium iron phosphate particle with the second particle size obtained in step (2) according to a mass ratio of 1:1 to obtain the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material.
Embodiment 3
[0048] The only difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the pressure of the hydrothermal reaction in step (1) is 0.5 MPa, and other conditions and parameters are exactly the same as in embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com