Application of corn ZmRIBA1 gene in breeding of high-lysine corn
A high-lysine, corn breeding technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problems of lack of balanced nutrition, affecting human health and livestock and poultry production performance, etc. Simple to use effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: corn ZmRIBA1 Affects grain storage material accumulation and lysine content
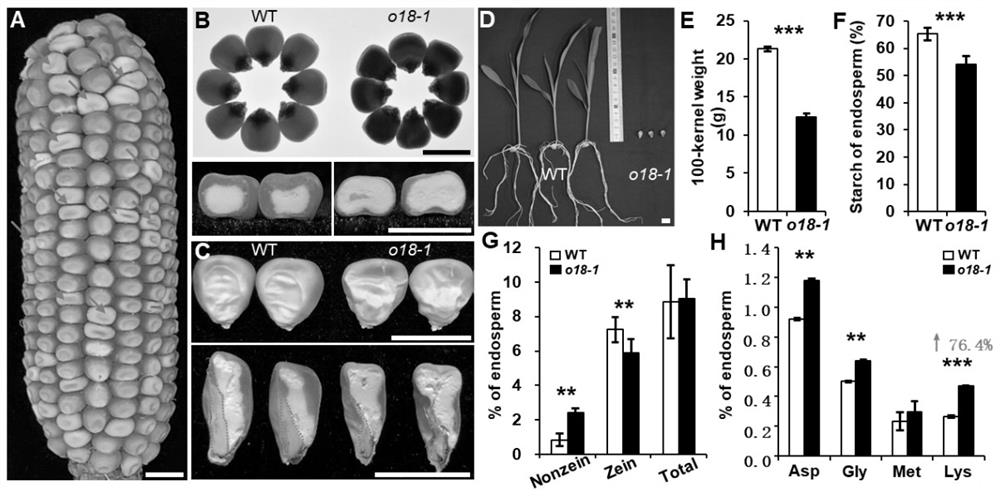
[0033] The EMS mutagenic mutant ( o18-1 ). o18-1 The background is 3605K (dnj*-N1534, o18-1 ), a single gene recessive mutant generated by EMS mutagenesis by Gerald Neuffer et al. right o18-1 Observation of the grain phenotype of mature mutants revealed that the waxy area of the endosperm decreased and the silty area increased, and the embryo was smaller and deformed (see figure 1 A-C). Germination experiments found that the mutants could not sprout (see figure 1 D). The 100-grain weight of the mutant was significantly lower than that of the wild type (see figure 1 e).
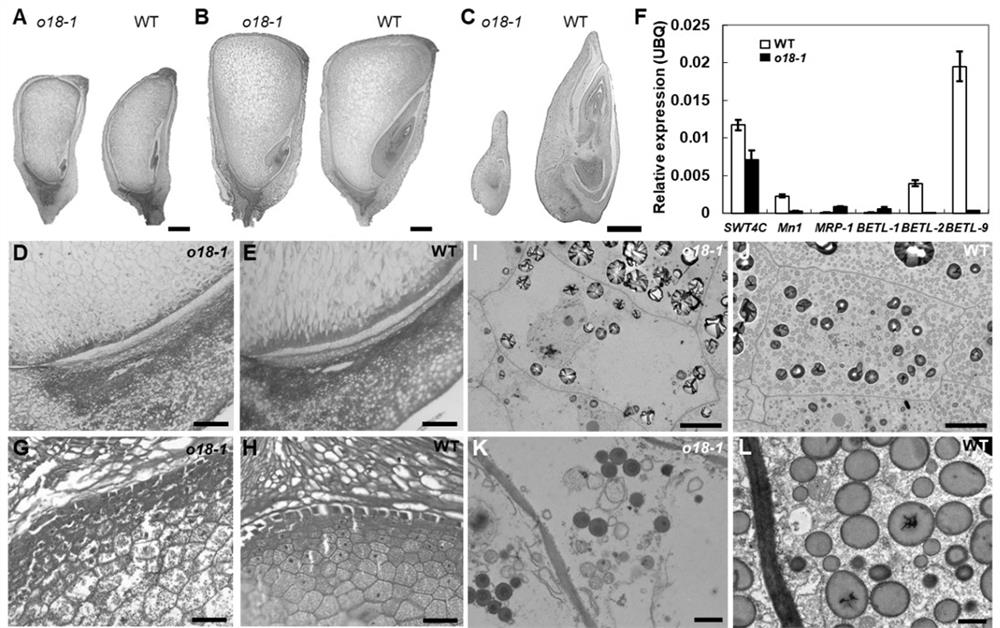
[0034] Using biochemical analysis techniques to analyze the starch and protein content of mature mutant and wild type grains, it was found that the mutant grain starch content was significantly reduced compared with the wild type (see figure 1 F); the total protein content of the mutant has no signif...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: ZmRIBA1 Gene cloning and functional verification
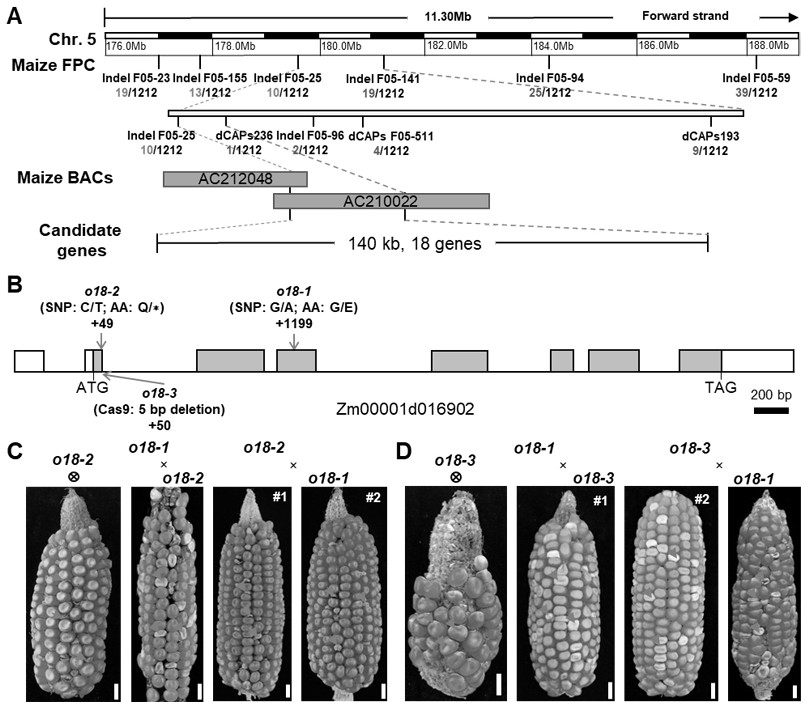
[0037] Utilize the EMS mutagenesis mutant ( o18-1 ) crossed with W64A corn to get F 1 generation group, F 1 F 2 Generation segregation population, through genetic analysis and map-based cloning, the target gene was located in the physical interval of about 140 kb on the 5th chromosome of maize (see image 3 A).
[0038] The linked markers and their sequences used in the map-based cloning process are shown in Table 1. Gene annotation and sequencing analysis in the candidate segment showed that the gene encoding the first step reaction of riboflavin synthesis Zm00001d016902Gene (CDS sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2) is a potential candidate gene, in the mutant ( o18-1 )middle Zm00001d016902 The gene contains 7 exons, and there is a single-base mutation from G to A at the third exon +1199bp, resulting in the mutation of amino acid 185 from glycine to glutami...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: Corn ZmRIBA1 Molecular markers
[0050] against o18-1 Develop an easy-to-detect PCR molecular marker dCAPS1 at the mutation site, as follows:
[0051] o18-1 The actual position of the mutation site in the fourth version of the maize B73 reference genome is 179,648,012, and the following dCAPS1 primers were designed:
[0052] dCAPS1-F1: 5' ACAGAGGGCTTCACATCAATTG 3'; (SEQ ID No. 5)
[0053] dCAPS1-R1: 5' CGTTTCAGAACACCCCCTTCT 3'; (SEQ ID No. 6)
[0054] dCAPS1-F2: 5' GAGGCTATGGCTTTTATAGTAAGGCCC 3'; (SEQ ID No. 7)
[0055] dCAPS1-R2: 5' CACTGTAACAGTGAAAGCAGTGC 3'; (SEQ ID No. 8)
[0056] Among them, dCAPS1-F1R1 is the outer primer pair, which can specifically amplify ZmRIBA1 gene sequence (see Figure 4 B). dCAPS1-F2R2 is the inner primer pair, and the PCR product of dCAPS1-F1R1 is used as the template for the second round of amplification.
[0057] against o18-1 Molecular marker detection of mutants, comprising the following steps:
[0058] (1) The r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com