Inhalation preparation
A technology for inhalation preparations and buffers, which is applied in the field of inhalation preparations and aerosol inhalation preparations for treating diabetes drugs, and can solve problems such as poor stability and reduced tendency of insulin aspart to form hexamers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
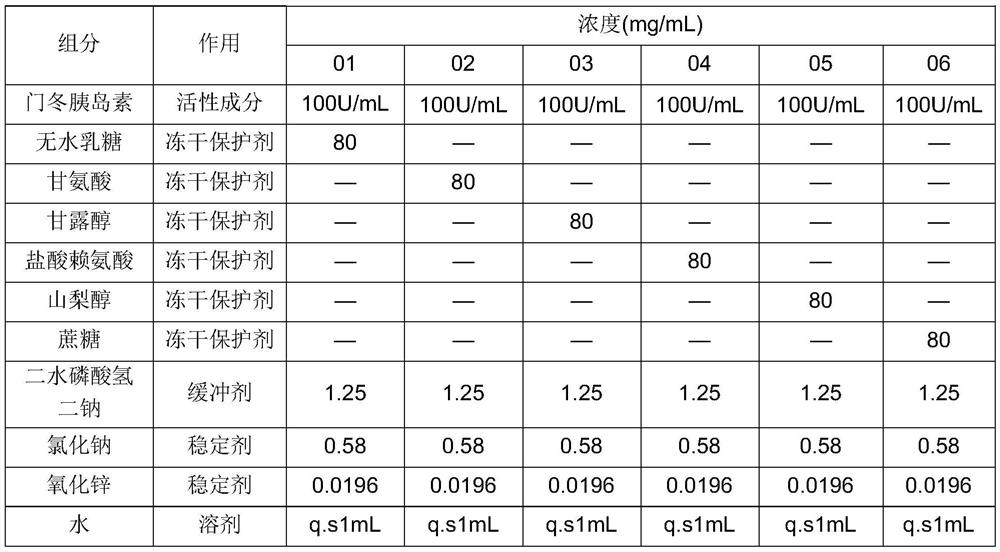
[0094] Example 1 investigation of asparagus insulin lyophilized powder: screening of lyophilized protective agent
[0095] Table 1-1: prescription table
[0096]
[0097] Preparation process:
[0098] (1) Add zinc oxide to dilute hydrochloric acid, completely react and dissolve, and then add water to fix the volume;
[0099] (2) Add disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, sodium chloride and freeze-drying protective agent to water, stir and dissolve completely, add pH regulator to adjust pH to 7.2 ~ 7.6 to obtain solution a;
[0100] (3) Add insulin aspartate into water, stir and disperse, adjust the pH to 2.5-3.0, stir and dissolve until clear, add (1) the prepared zinc ion solution, stir evenly, and then adjust the pH to about 7.2-7.6 to obtain solution B;
[0101] (4) Add solution a to solution B under stirring conditions, stir evenly and freeze dry.
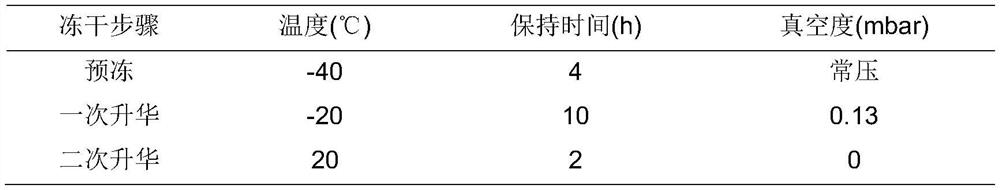
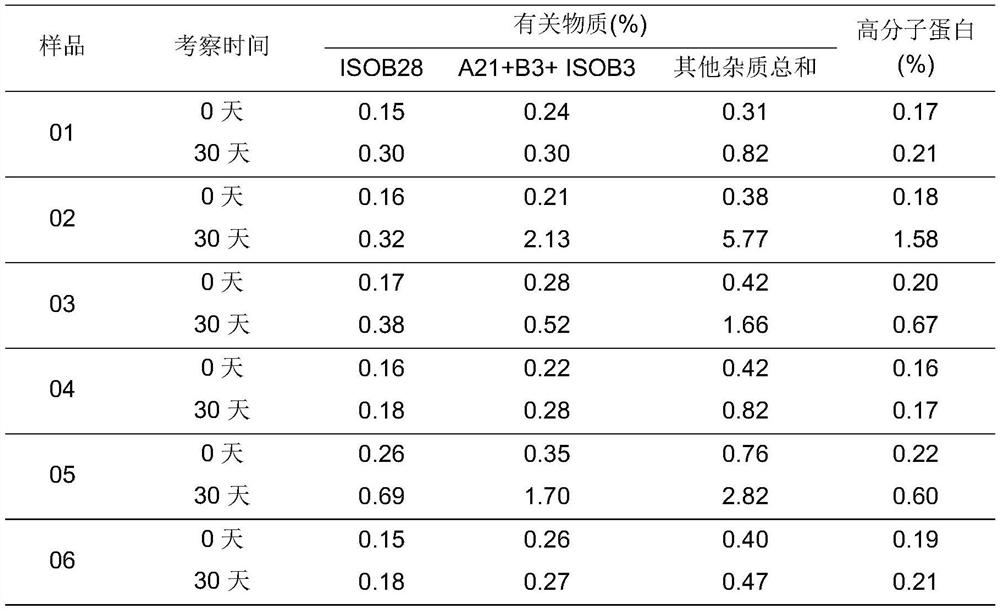
[0102] See table 1-2 for freeze-drying parameters and table 1-3 for stability results.
[0103] Table 1-2: freeze drying param...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2 investigation of asparagus insulin lyophilized powder: buffer screening
[0109] Table 2-1: prescription table
[0110]
[0111] Preparation process:
[0112] (1) Add zinc oxide to dilute hydrochloric acid, completely react and dissolve, and then add water to fix the volume;
[0113] (2) Add anhydrous lactose, sodium chloride and buffer into water, stir and dissolve completely, adjust the pH to 7.2 ~ 7.6 to obtain solution a;
[0114] (3) Add insulin aspartate into water, stir and disperse, adjust the pH to 2.5-3.0, stir and dissolve until clear, add (1) the prepared zinc ion solution, stir evenly, and then adjust the pH to about 7.2-7.6 to obtain solution B;
[0115] (4) Add solution a to solution B under stirring conditions, stir evenly and freeze dry.
[0116] See table 2-2 for freeze-drying parameters and table 2-3 for stability results.
[0117] Table 2-2: freeze drying parameters
[0118]
[0119] Table 2-3: stability results of each batch of samples place...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Example 3 investigation of asparagus insulin solution: screening of antimicrobial agents
[0123] Table 3-1: prescription table
[0124]
[0125]
[0126] Preparation process:
[0127] (1) Add zinc oxide to dilute hydrochloric acid, completely react and dissolve, and then add water to fix the volume;
[0128] (2) Add glycerin, disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, sodium chloride and bacteriostatic agent into water, stir and dissolve them completely, and adjust the pH to 7.2 ~ 7.6 to obtain solution a;
[0129] (3) Add insulin aspartate into water, stir and disperse, adjust the pH to 2.5-3.0, stir and dissolve until clear, add (1) the prepared zinc ion solution, stir evenly, and then adjust the pH to about 7.2-7.6 to obtain solution B;
[0130] (4) Add solution a to solution B under stirring conditions, stir evenly, fix the volume, filter and sterilize.
[0131] The stability results of each batch are shown in table 3-2.
[0132] Table 3-2: stability results of each ba...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com