Nanometer material based on loaded GSDMD protein N-terminal peptide fragment and application thereof
A technology of GSDMD-N and GSDMD-N-PDPA, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of less tumor cell effect, lack of targeting, many side effects, etc., achieve local immune function enhancement, economical preparation cost, and low preparation cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
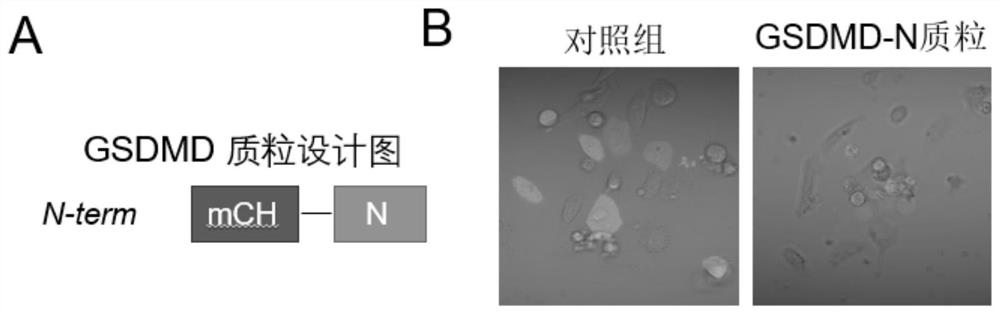
[0044] Example 1 GSDMD-N-terminal plasmid vector design
[0045] Aiming at the characteristics of GSDMD, the present invention designed a plasmid vector ( figure 1 ), and the red fluorescent marker of mcherry was added to the vector. The vector was transfected into tumor cells (MDA-231), and it was found that all cells with red fluorescence (transfected successfully) died, which proved that the plasmid has cytotoxicity and can kill tumor cells. Wherein, the full-length nucleotide sequence of GSDMD is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the nucleotide sequence of GSDMD-N-terminal is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, and the nucleotide sequence of GSDMD-N-terminal plasmid is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 shown.
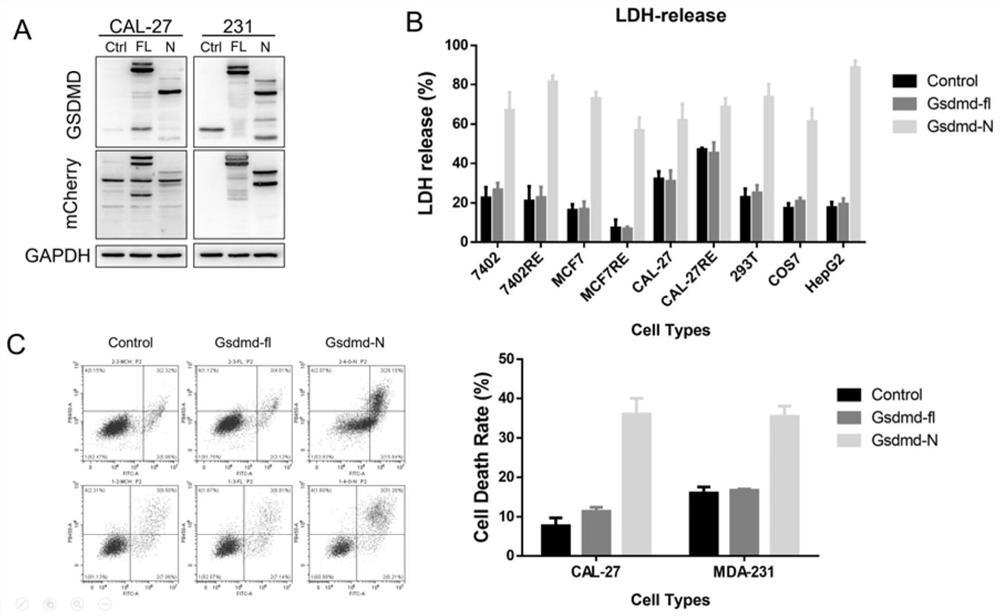
[0046] We believe that GSDMD-N has a general killing effect on tumors, and we have verified this in oral tumor cells, breast cancer cells, liver cancer cells, malignant fibroblasts and other cells ( figure 2 ). The results once again proved that GSDMD-N-terminal vector can kill tumor cells in a l...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 GSDMD-N-terminal plasmid vector has immune cell chemotactic potential
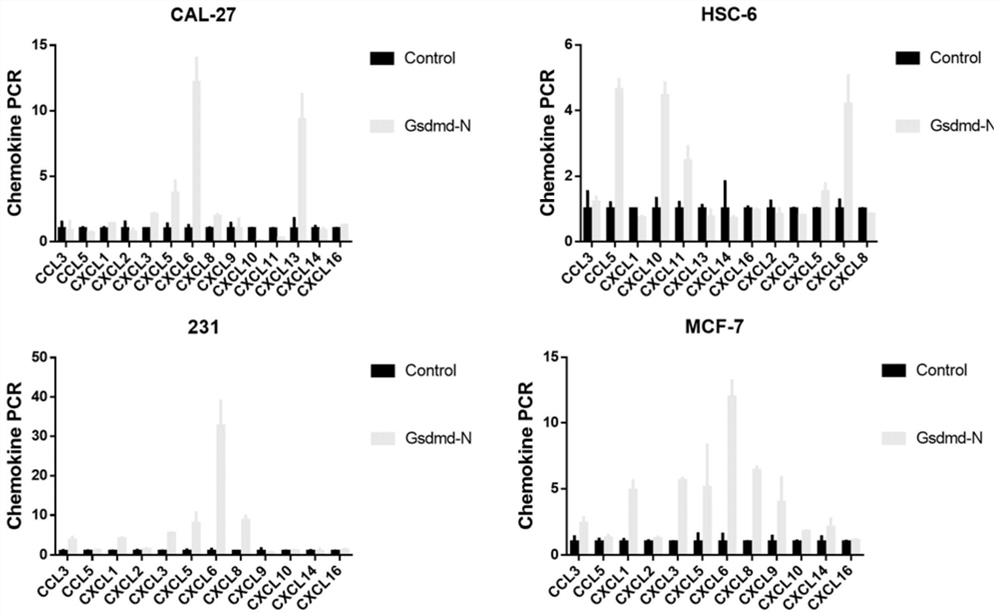
[0048] GSDMD-induced pyroptosis can induce chemotaxis of immune cells in tumors. Therefore, we have reason to speculate that the GSDMD-N-terminal plasmid can promote immune infiltration in tumors. Plasmid transfection and PCR detection of intracellular chemokines were performed on oral cancer cell lines (CAL-27, HSC-6) and breast cancer cells (MDA-231 and MCF-7) ( image 3 ). The results showed that after transfection of GSDMD-N-terminal plasmid, a large number of innate immune cell chemokines in tumor cells were significantly increased.
[0049] To clarify the above problems, we confirmed that GSDMD-N has tumor-killing function and potential innate immune chemotactic function. To construct new immune enhancers and tumor drugs through GSDMD-N plasmids, we use nanomaterials for packaging. In response, we designed a weak acid-responsive nanomaterial of Meo-PEG-b-PDPA.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Synthesis of nanocarrier Meo-PEG-b-PDPA
[0051] ① Synthesis of brominated polyethylene glycol (Meo-PEG-Br).
[0052] Polyethylene glycol (Meo-PEG-OH) and triethylamine were dissolved in dichloromethane. In an ice-salt bath, α-bromoisobutyryl bromide was added dropwise. After stirring the reaction at room temperature for 24 hours, the reaction solution was washed with 1 mol / L sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid aqueous solution respectively, and finally washed with deionization. The organic phase was collected, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, the solution was concentrated, and cold ether was added to precipitate the product. After repeated precipitation 3 times, the white powdery product was collected after vacuum drying. Figure 4 is the chemical structure and H NMR spectrum of Meo-PEG-Br.
[0053] ②Meo-PEG-b-PDPA was synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization.
[0054] 2-(Diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate (DPA-MA, 2.6 g, 12 mmol), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com