Method for increasing yield of antifungal active substance HSAF and application
An active substance, antifungal technology, applied in the field of increasing the production of antifungal active substance HSAF, can solve the problems of bacterial cell death, unsustainable synthesis of HSAF, and complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] The construction of embodiment 1 engineering strain
[0017] The specific program for the knockout of Hfq gene is as follows:
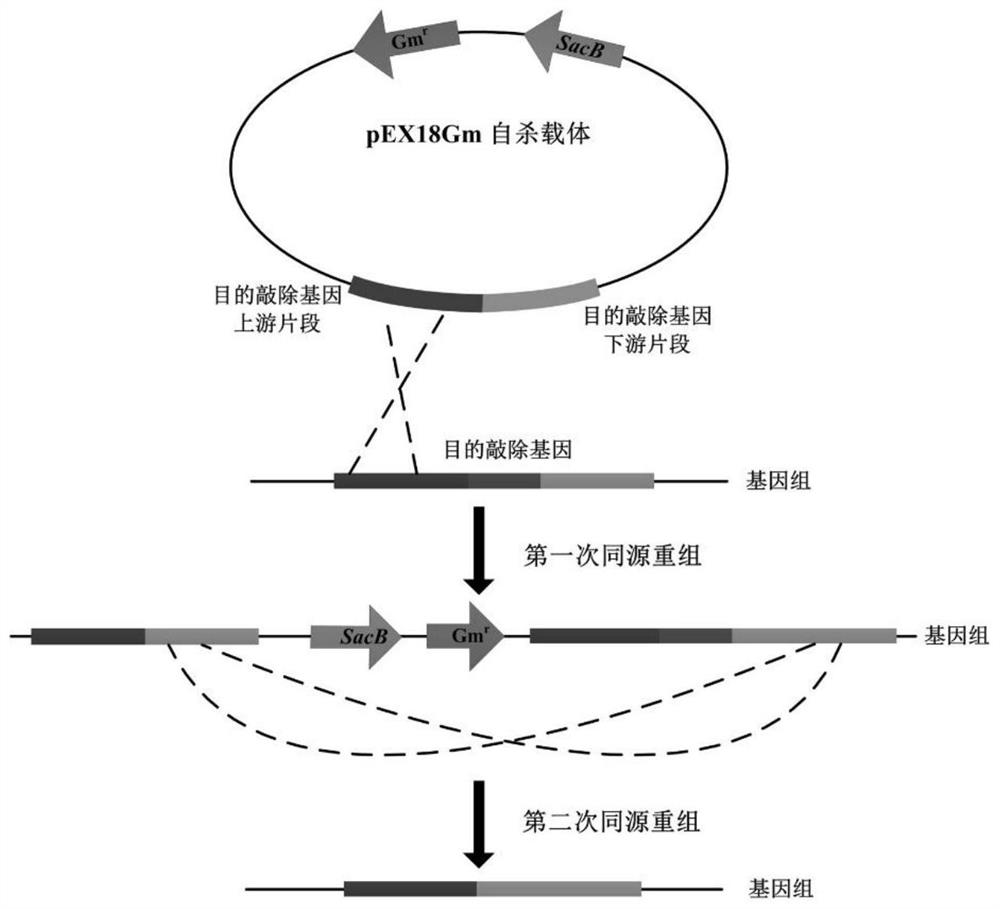
[0018] Gene Knockout Strategy Reference figure 1 .
[0019] Use primers Hfq-F1 / R1 and Hfq-F2 / R2 to amplify the upstream and downstream fragments Hfq-s and Hfq-x of the hfq gene, respectively. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0020] Hfq-F1: CGGAATTCGAACTGGAGCACGCCCTGAG (the underline indicates the EcoRI restriction site)
[0021] Hfq-R1: GCTCTAGAGCAGCTTGATGCCGTTGACC (underlined indicates XbaI restriction site)
[0022] Hfq-F2: GCTCTAGAGGCAGCGACGAGAACGAATAAG (underlined indicates XbaI restriction site)
[0023] Hfq-R2: CCCAAGCTTAACGGGTGGTTGACCAGGATC (underlined indicates HindIII restriction site)
[0024] The Hfq-s fragment was treated with restriction endonucleases EcoRI and XbaI, and the fragment under Hfq-x was treated with XbaI and HindIII, then the above fragment was ligated to the suicide vector pEX18Gm treated with EcoRI and Hin...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Growth curve determination
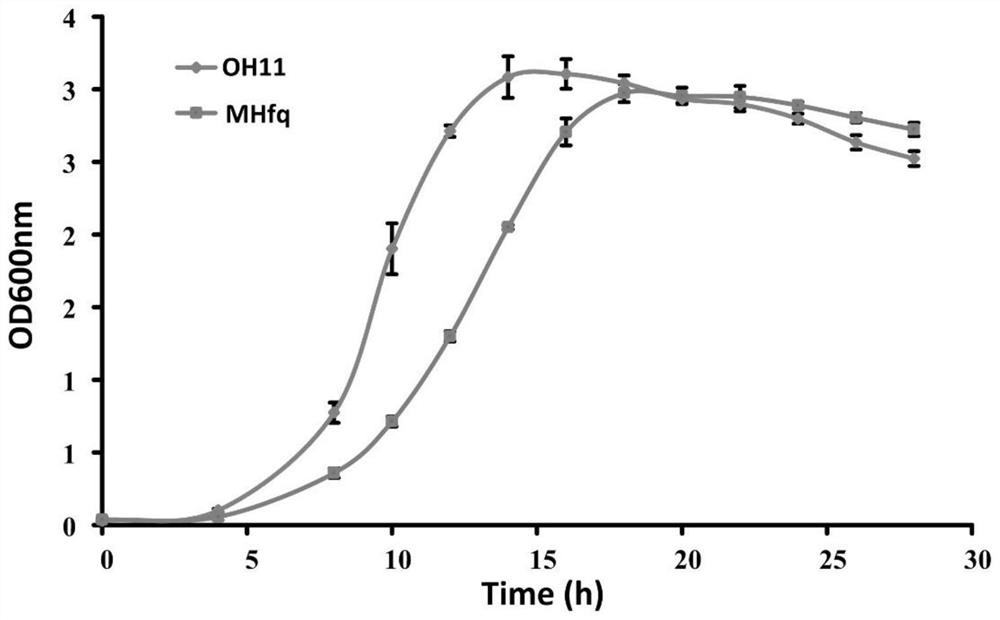
[0033]A single colony of the wild-type OH11 and the engineered strain MHfq were picked and cultured overnight in LB liquid medium at 28°C with shaking. The bacterial solution was inoculated into a new 10% TSB liquid medium at a ratio of 1%, and the culture was continued at 28°C with shaking. Every 2 hours, take out 500 μL of bacterial solution, measure and record the OD600nm value with a spectrophotometer, and finally form a complete growth curve, such as image 3 shown. It can be seen from the figure that the OD value of the wild-type OH11 decreased from about 16 hours, while the engineering strain Mhfq showed obvious autolysis at 24 hours. Therefore, the engineered strain prolongs the fermentation time by about 8 hours by delaying the autolysis time.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 HSAF yield assay
[0035] A single colony of the wild-type OH11 and the engineered strain MHfq were picked and cultured overnight in LB liquid medium at 28°C with shaking. The bacterial solution was inoculated into a new 10% TSB liquid medium at a ratio of 1%, and the culture was continued at 28°C for 24 hours with shaking. Take 4 mL of bacterial liquid, add 16 μL of concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust the acid, and then use 4 mL of ethyl acetate to extract the metabolites of Lysobacter enzyme-producing bacteria, and then evaporate the ethyl acetate to dryness to obtain the bold substance of HSAF. After the crude substance was dissolved in 200 μL of methanol, the HSAF production could be detected by a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system. The result is as Figure 4 shown, the HSAF production of the mutant Mhfq was significantly higher than that of the wild-type OH11, with an approximately 66% increase in production.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com