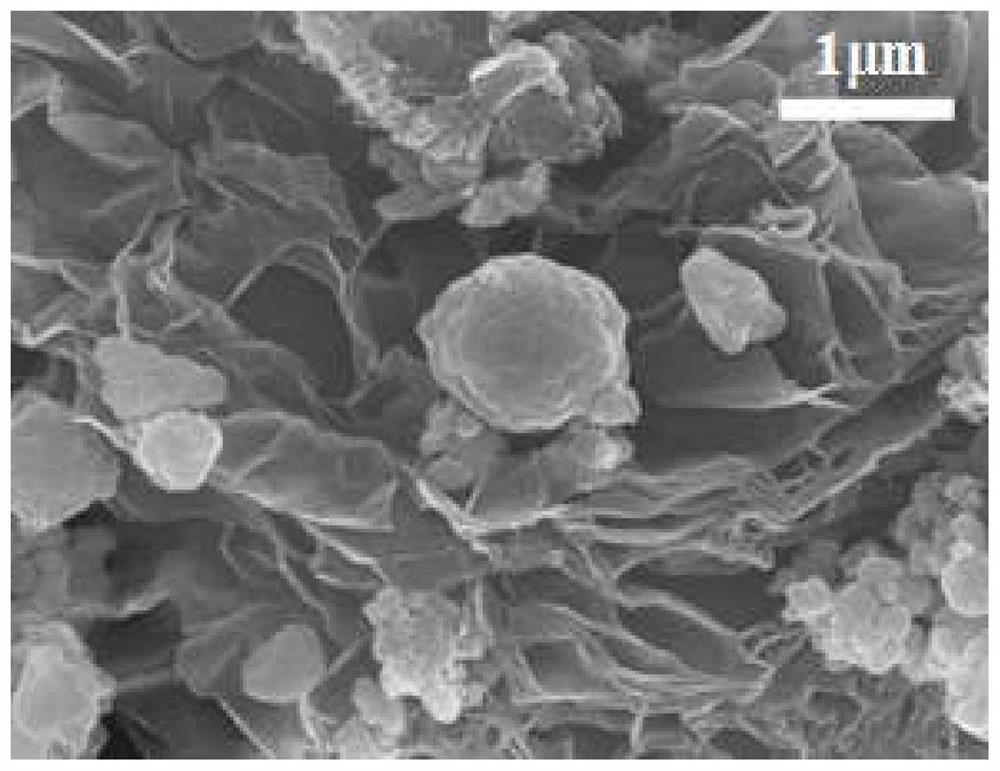
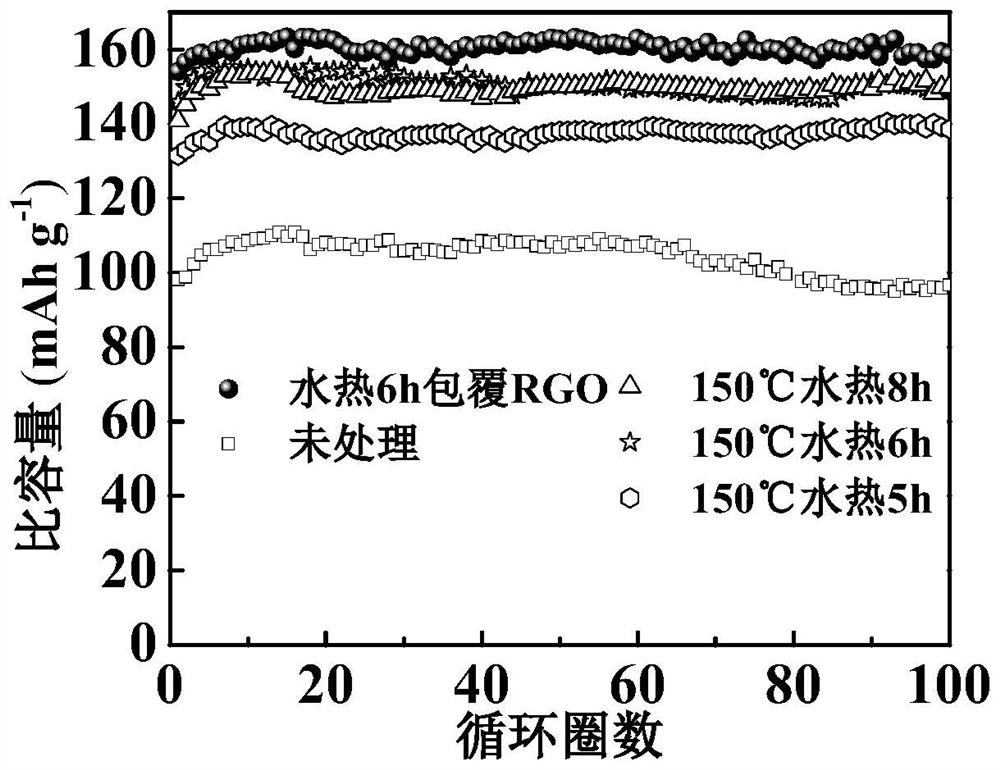
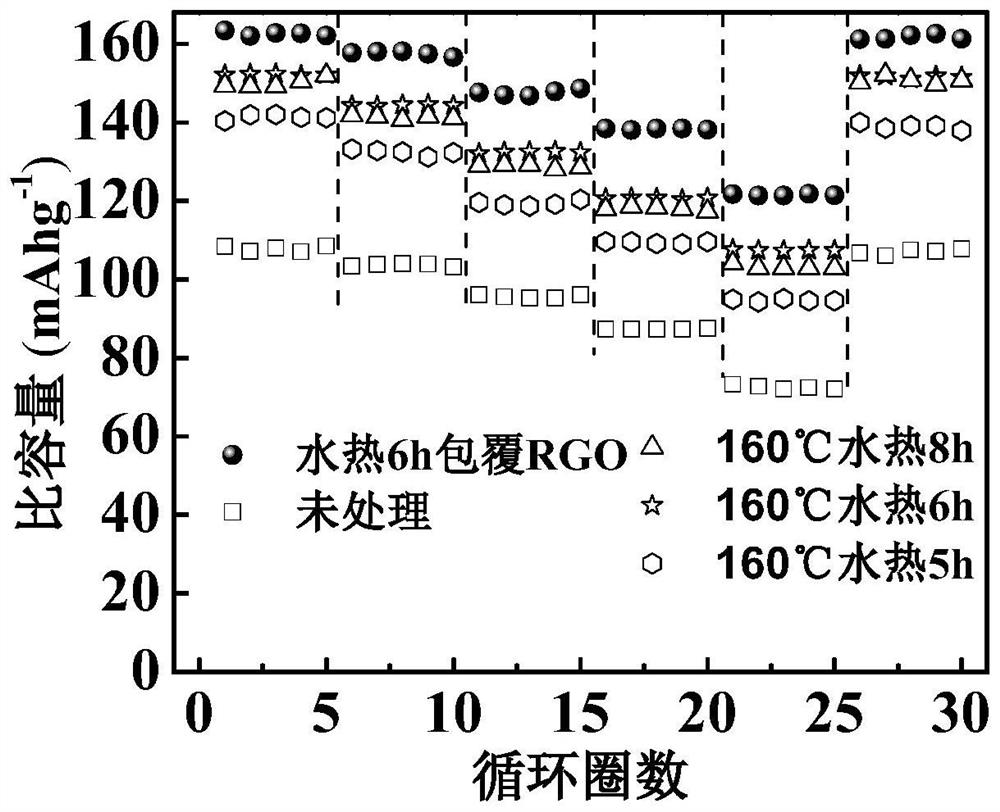
Recycling method of lithium iron phosphate battery, obtained LiFePO4/RGO composite material and application
A technology of lithium iron phosphate battery and recovery method, applied in the field of lithium iron phosphate battery recovery and LiFePO4/RGO composite material, can solve the problems of large waste liquid generation, high energy consumption, environmental pollution of residual acid liquid, etc. Effects of efficiency, small particle size, excellent rate capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] 1) Waste LiFePO that will be provided 4 The battery was first discharged to 2.0V in NaCl solution for 1 day, and then disassembled to obtain a cathode plate, an anode plate, an aluminum casing, an electrolyte and a separator in a sealed box. The positive electrode was soaked in NaOH solution for 7 h. Then the black powder was dried, ball milled and sieved to obtain waste LiFePO 4 Material.
[0037] 2) Add waste LiFePO to 30ml of deionized water at a molar ratio of 1:0.2:2:1 4 powder, LiOH, l-ascorbic acid and sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS, C 18 H 29 SO 3 Na). After stirring for 3 hours, the solution was transferred to the autoclave.
[0038] 3) Before the hydrothermal reaction, the waste graphite anode regenerated graphene oxide is added to the mixture, and the reactor is heated to 150 degrees Celsius for 5 hours to obtain product particles.
Embodiment 2
[0040] 1) Waste LiFePO that will be provided 4 The battery was first discharged to 2.0V in NaCl solution for 1 day, and then disassembled to obtain a cathode plate, an anode plate, an aluminum casing, an electrolyte and a separator in a sealed box. The positive electrode was soaked in NaOH solution for 7 h. Then the black powder was dried, ball milled and sieved to obtain waste LiFePO 4 Material.
[0041] 2) Add waste LiFePO to 30ml of deionized water at a molar ratio of 1:0.3:3:1 4 powder, LiOH, l-ascorbic acid and sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS, C 18 H 29 SO 3 Na). After stirring for 3 hours, the solution was transferred to the autoclave.
[0042] 3) Before the hydrothermal reaction, the waste graphite anode regenerated graphene oxide is added to the mixture, and the reactor is heated to 160 degrees Celsius for 6 hours to obtain product particles.
Embodiment 3
[0044] 1) Waste LiFePO that will be provided 4 The battery was first discharged to 2.0V in NaCl solution for 1 day, and then disassembled to obtain a cathode plate, an anode plate, an aluminum casing, an electrolyte and a separator in a sealed box. The positive electrode was soaked in NaOH solution for 6 h. Then the black powder was dried, ball milled and sieved to obtain waste LiFePO 4 Material.
[0045] 2) Add waste LiFePO to 30ml of deionized water at a molar ratio of 1:0.2:2:1 4 powder, LiOH, l-ascorbic acid and sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS, C 18 H 29 SO 3 Na). After stirring for 2 hours, the solution was transferred to the autoclave.
[0046] 3) Before the hydrothermal reaction, the waste graphite anode regenerated graphene oxide is added to the mixture, and the reactor is heated to 180 degrees Celsius for 8 hours to obtain product particles.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com