Secondary lithium cell having negative pole of carbon with deposited nanomter alloy on its surface
A secondary lithium battery, surface deposition technology, applied in secondary batteries, lithium batteries, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems of loss of kinetic advantages, long-term cycle deterioration, etc., to achieve electrode Inexpensive materials, high current charge and discharge resistance, and good cycle performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
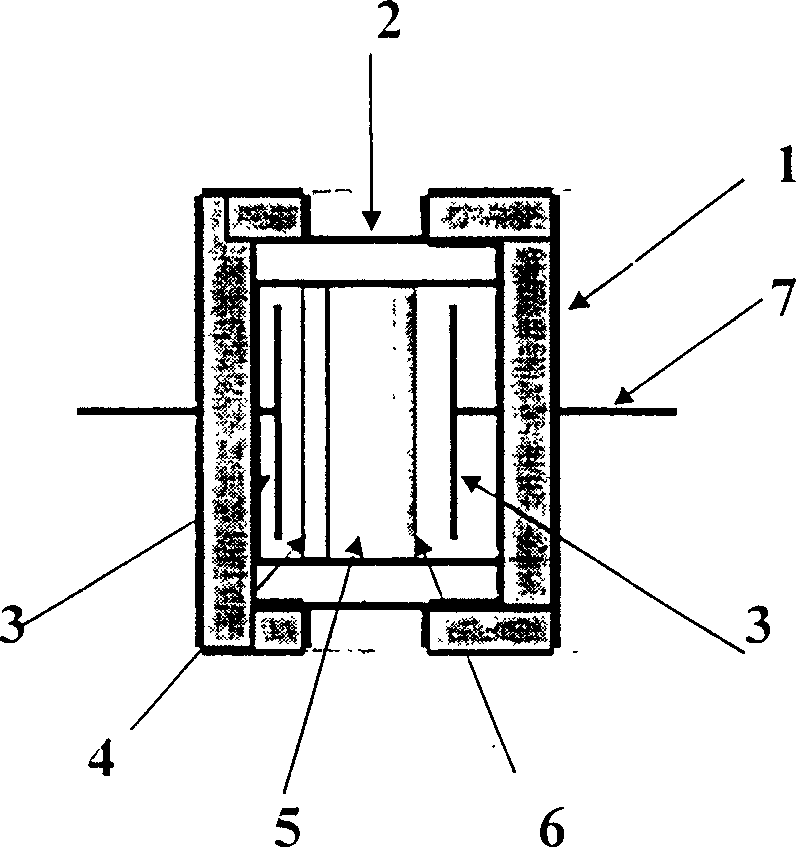
[0032] In order to study the electrochemical performance of the carbon material deposited on the surface of the nano-alloy of the present invention as the negative electrode active material of the secondary lithium battery, an experimental battery is used for research. The experimental battery structure is as figure 1 shown. Among them, 1 is a stainless steel sealing nut, 2 is a polytetrafluoroethylene nut, 3 is a stainless steel spring, 4 is a working electrode with a carbon material deposited on the surface of nano-metal or alloy as the active material, and 5 is a porous polypropylene diaphragm Celgard 2300 (soaked in electrolyte), 6 is the counter electrode of metal lithium sheet, 7 is the measuring wire. The electrolyte is 1 mole lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF 6 ) was dissolved in a mixed solvent of ethylene carbonate (EC) and diethyl carbonate (DEC) (1:1 by volume).
[0033] The preparation method of the active material of working electrode in the present embodimen...
Embodiment 2
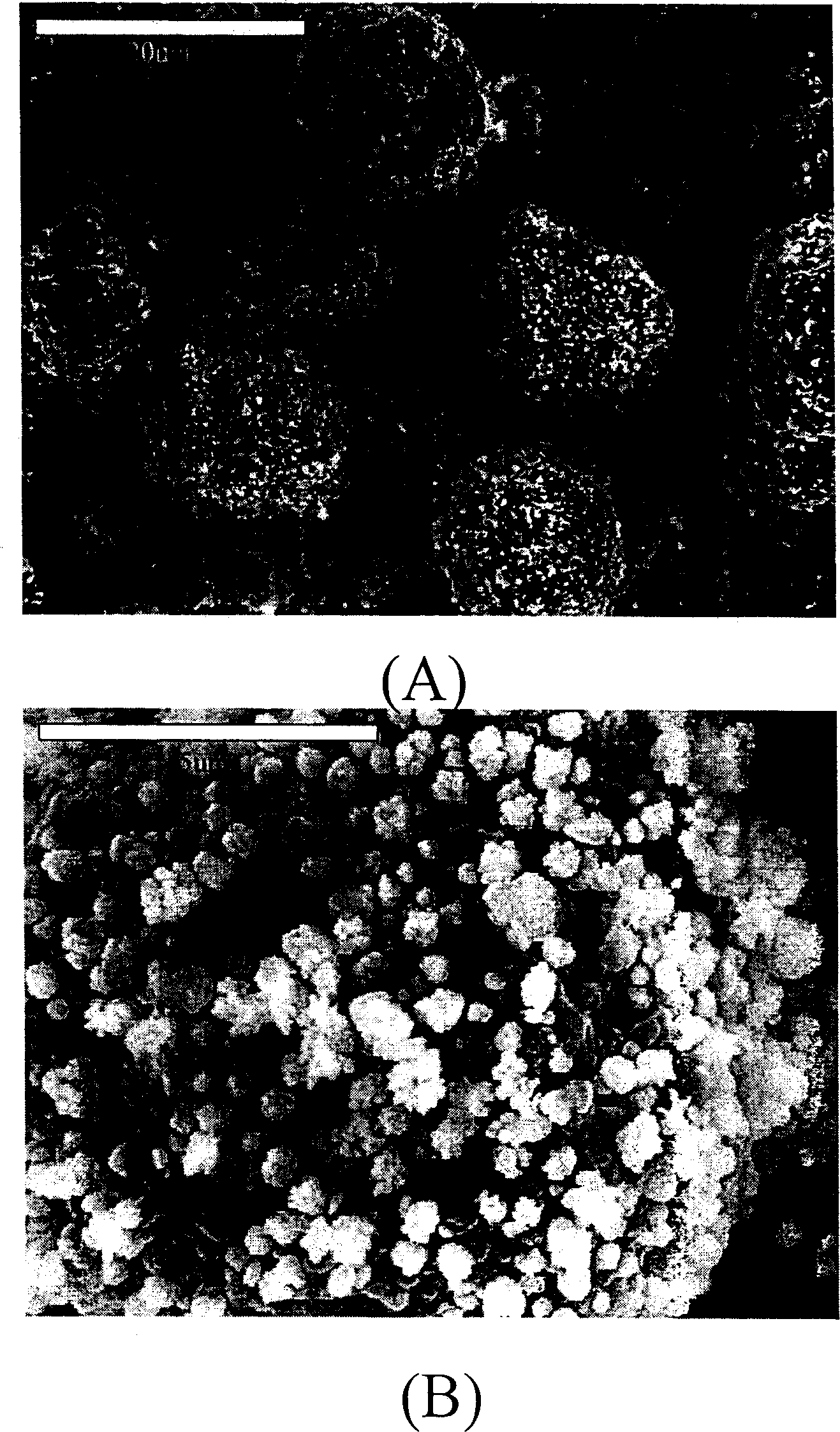
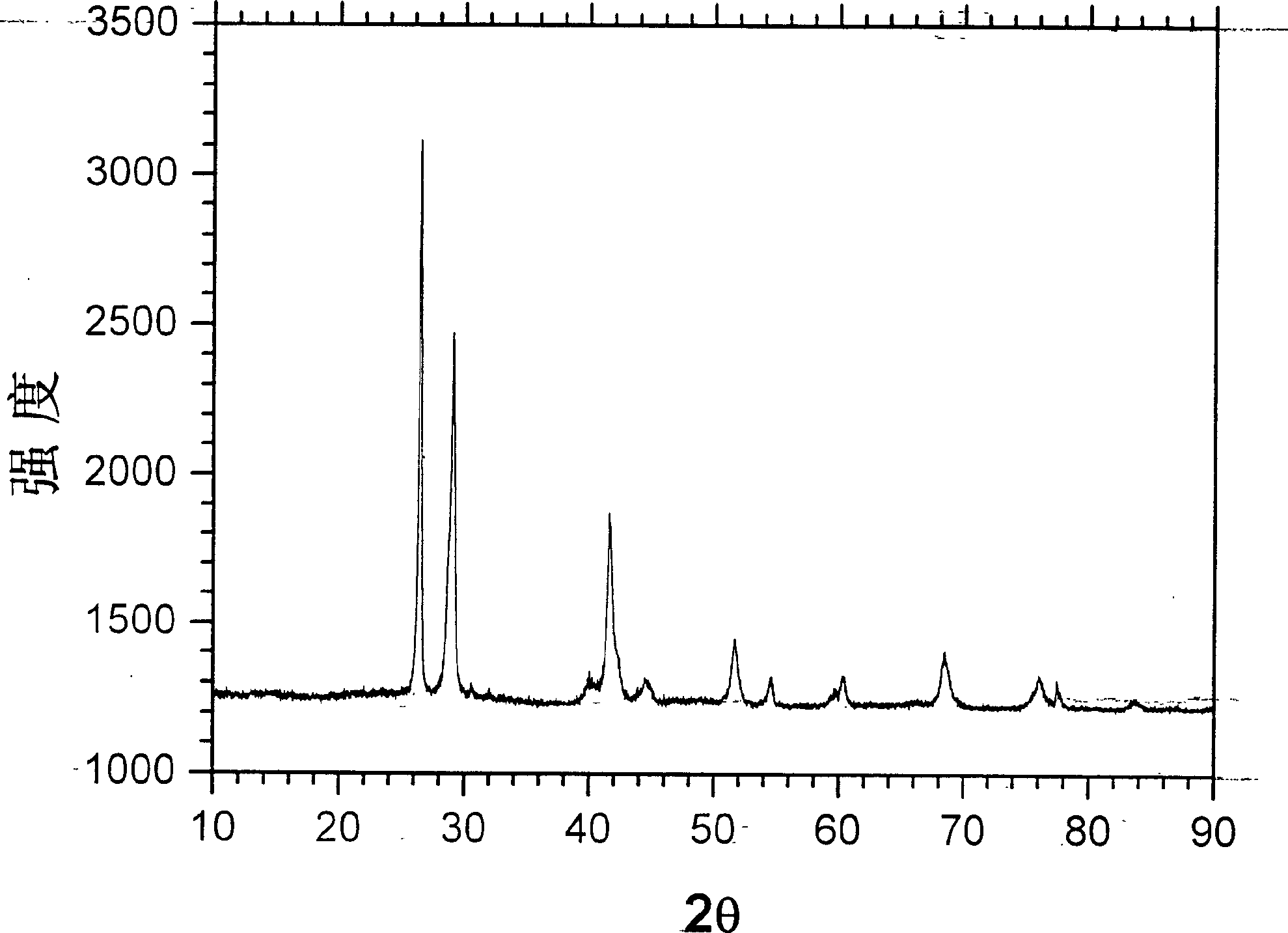
[0039] According to the synthesis method described in Example 1, it is 30% carbon composite material that the nano-alloy accounts for the weight percentage of the composite material, and the average grain size of the SnSb alloy observed by scanning electron microscope is 80nm, and the ratio of the free SnSb alloy accounted for the whole alloy is lower than 15%. The obtained product has an oxygen content of less than 2% through elemental analysis. The X-ray diffraction pattern of the composite material is shown in figure 2 , and its scanning electron microscope photo is shown in image 3 . Its structure and morphology are typical of such carbon / nanoalloys.
[0040] The composite carbon powder in this example, carbon black and N-methylpyrrolidone solution of polyvinylidene fluoride are mixed at normal temperature and pressure to form a slurry, which is evenly coated on the copper foil substrate, and the thickness of the obtained film is about 100 μm. After drying the compos...
Embodiment 3
[0043] According to the synthesis method described in Example 1, the control reaction temperature is 130°C, and the carbon composite material in which the nano-alloy accounts for 70% by weight of the composite material is prepared, wherein the average grain size of the SnSb alloy observed by a scanning electron microscope is 200nm, and the free SnSb Alloy accounts for less than 10% of the total alloy. The obtained product has an oxygen content of less than 1% through elemental analysis.
[0044] The composite carbon powder in this example, carbon black and N-methylpyrrolidone solution of polyvinylidene fluoride are mixed at normal temperature and pressure to form a slurry, which is evenly coated on the copper foil substrate, and the thickness of the obtained film is about 100 μm. After drying the composite carbon powder, the weight percentage of carbon black and polyvinylidene fluoride is 90:5:5, and the rest of the working electrode preparation steps are the same as in Exampl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com