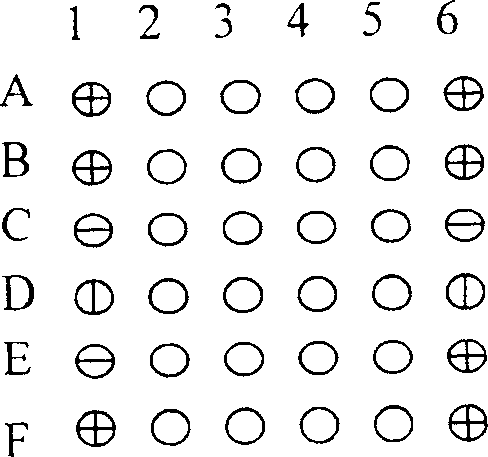Peptide nucleic acid chip for detecting muatatonal site of hepatitis B virus and its preparing method
A technology of hepatitis B virus and mutation sites, applied in the field of gene chips
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
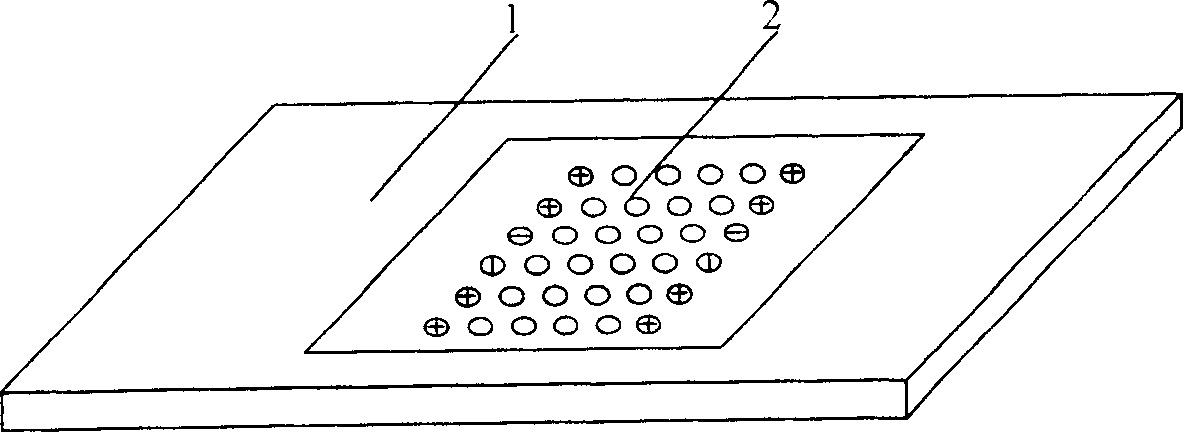
[0065] Example 1: The structure is attached figure 1 Shown:
[0066] Peptide nucleic acid probes and control dot coating 2 are uniformly distributed on the substrate 1 in an array, which contains 24 detection probes with known mutation sites and wild sites in the pre-hepatitis C and S regions, and 2 are positive Control probe, 1 negative control probe and blank spot liquid control. The positive probes are located around the array. It is not only a positive control, but also a positive signal to locate the array. The PCR amplified product of hepatitis B DNA sample is transcribed and labeled in vitro and hybridized with the peptide nucleic acid array, and the result is obtained by scanning with a laser confocal scanner, and then analyzed and judged.
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2: Modification of glass slides and immobilization of peptide nucleic acid probes
[0068] 1. Modification of slides
[0069] The blank glass slide was washed with 10% NaOH, then washed with 1% HCI acid solution, washed with water and then dried to obtain a clean glass bare chip. Treated with 1% 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane in 95% acetone solution for 30 minutes, and then washed with acetone 3 times for 5 minutes each time, and baked at 80°C for 15 minutes to obtain the aminated glass slide. Continue to treat with 10% glutaraldehyde aqueous solution for 30 minutes, then wash with double distilled water, and dry in vacuo to obtain an aldehyde modified glass slide.
[0070] 2. Fixation of peptide nucleic acid detection probe (taking aldehyde-based glass slide as an example)
[0071] The design and selection of peptide nucleic acid detection probes are shown in Table 1.
[0072] Fixation of peptide nucleic acid detection probes on aldehyde-based glass slides, using sa...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Example 3: DNA extraction, PCR amplification and labeling of hepatitis B samples
[0080] 1. DNA extraction of hepatitis B samples
[0081] 1) Take 100 μl of hepatitis B serum, add 3 times the volume of lysis buffer (4M guanidine thiocyanate, mercaptoethanol, 0.1 M Tris-CI, pH 7.5), and mix.
[0082] 2) Add an equal volume of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol solution (24:1) and mix well. Centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 15 minutes at room temperature.
[0083] 3) Carefully transfer the supernatant to another 1.5ml centrifuge tube, and add 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol. Place at -20°C for 2 hours. Centrifuge at 12000rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C.
[0084] 4) The precipitate obtained after centrifugation was washed twice with 70% ethanol, and centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C each time.
[0085] 5) The precipitate is naturally dried and dissolved in 16 μl pure water.
[0086] 2. Amplification and purification of PCR target fragments
[0087] 1) The PCR amplificatio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com