Material and method for preparing insertion laminated material
A technology of layered materials and intercalated materials, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, layered products, cosmetic preparations, etc., can solve problems such as low structural strength, and achieve the effect of improving physical properties and being easy to produce
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0068] Intercalation / exfoliation of layered materials with the microparticles or nanoparticles of the invention can be effected by any method known in the art for preparing nanocomposites. The order and method of adding the layered materials, microparticles or nanoparticles and optional addenda may vary.
[0069] Materials of the invention comprising layered material and microparticles or nanoparticles with optional addenda may be formed by any suitable method, such as extrusion, coextrusion with or without uniaxial or biaxial orientation, Simultaneous or continuous stretching, blow molding, injection molding, lamination, solvent casting, etc.
[0070] The optional addenda mentioned above may include, but are not limited to, nucleating agents, fillers, plasticizers, impact modifiers, chain extenders, colorants, lubricants, antistatic agents, pigments such as titanium oxide, zinc oxide, mica, Calcium carbonate, dispersants such as fatty acid amides (such as stearamide), metal ...
Embodiment 1-3
[0103] Examples 1-3. Insertion of Na Cloisite(R) into P1
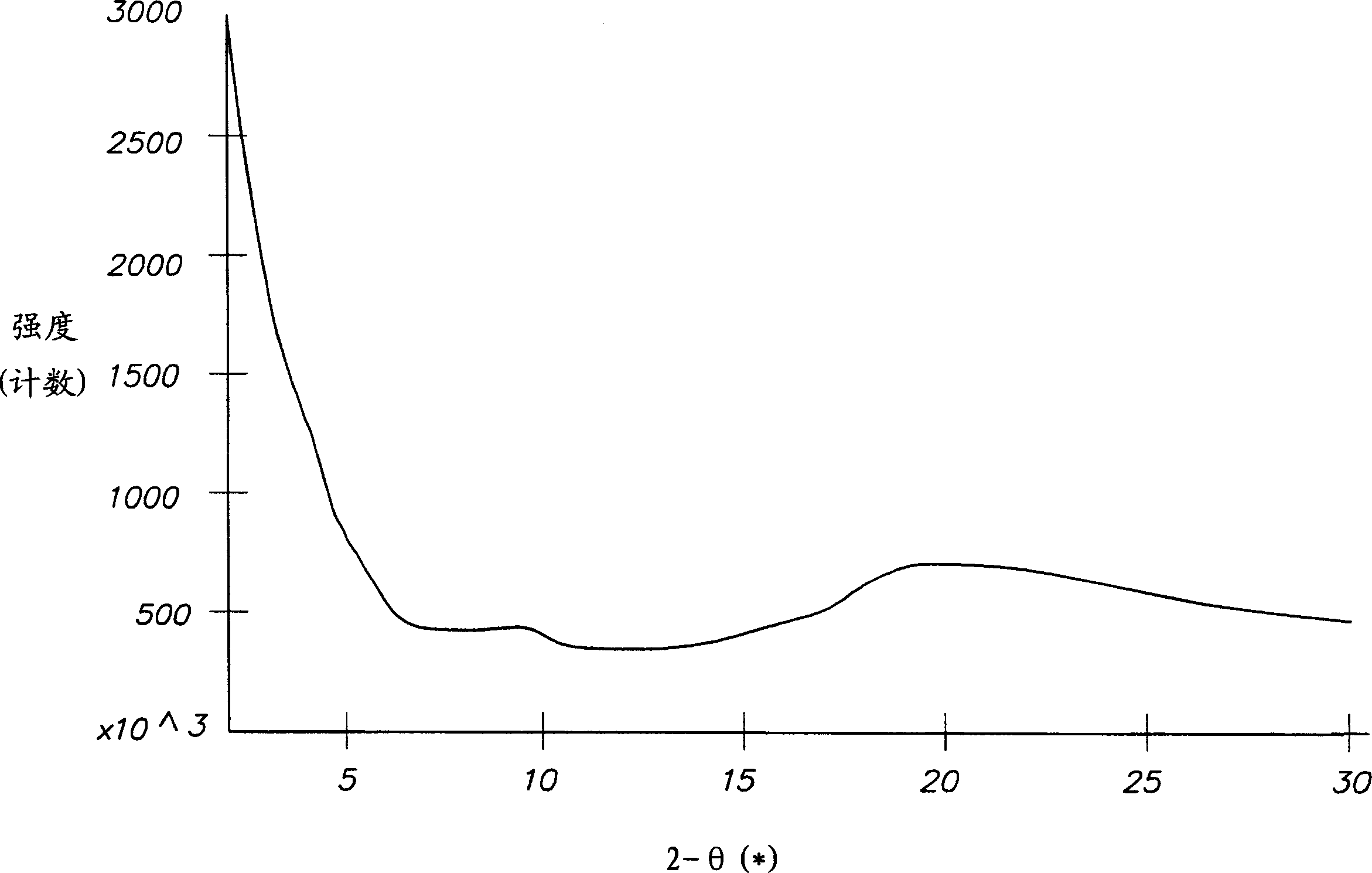
[0104] The Na Cloisite(R) and P1 solution were mixed in water for 18 hours at room temperature. A few drops of solution from each mixture were deposited onto individual glass slides and allowed to dry in ambient air. The structure of the solid film formed on the glass sample holder was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The XRD results are shown in Table 3.
[0105] Example
P1 / L1
spacing( * )
1
95 / 5
32,19 1
2
50 / 50
17
3
25 / 75
14
[0106] 1 Two intercalated phases were detected in some samples, possibly due to inhomogeneous mixing, or an area of the sample that was heated for too long (bottom of the vessel), leading to partial degradation of the intercalated material.
[0107] Compared with the (001) basal planar spacing reported for layered material L1 (Table 2), the basal planar spacing of Examples 1-...
Embodiment 4-6
[0108] Examples 4-6, Na Cloisite® inserted into P2
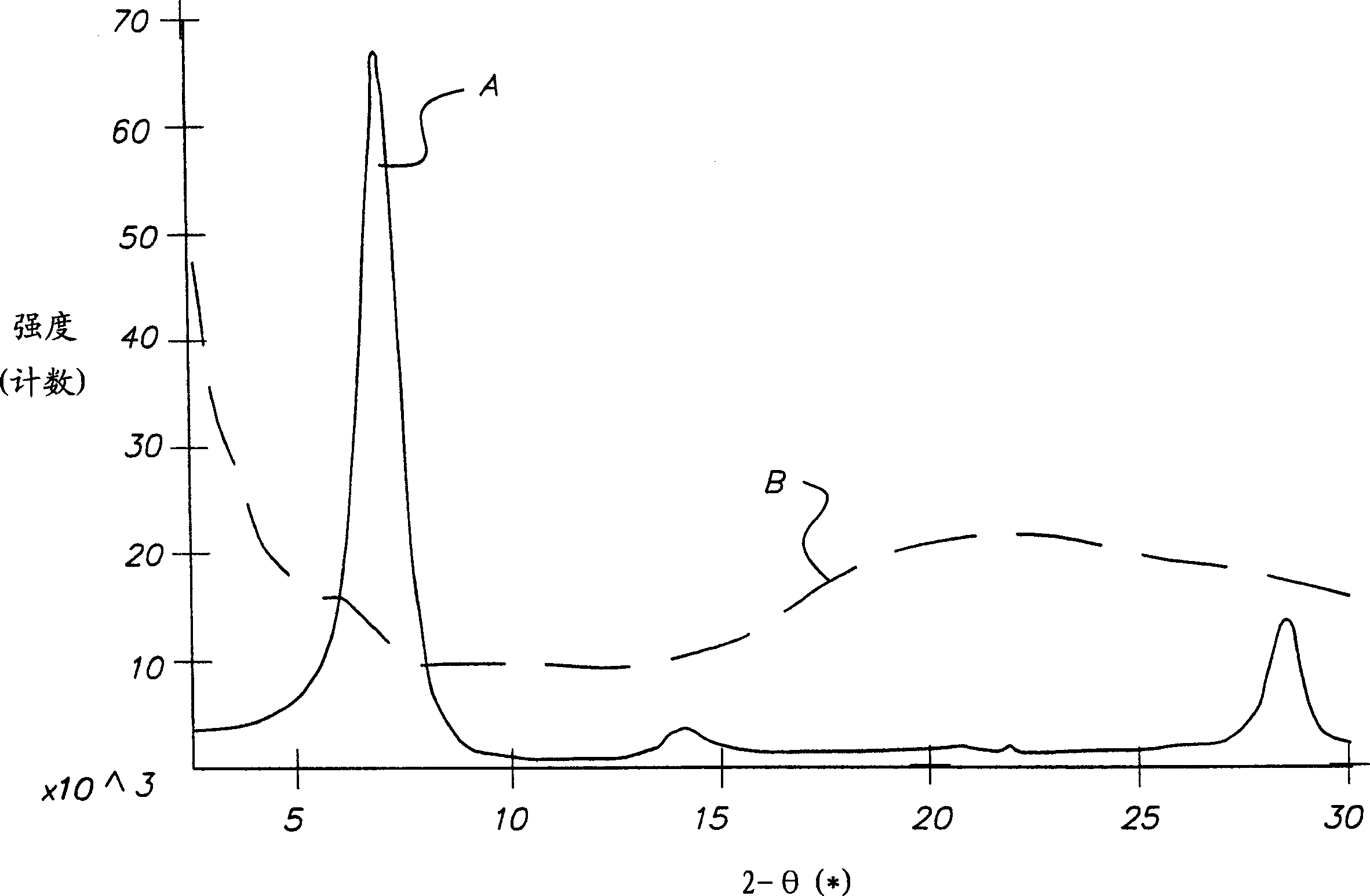
[0109] The clay Na Cloisite(R) was mixed with the polymer colloid solution in water for 24 hours at room temperature, and a few drops of the solution from each mixture were deposited onto separate glass slides and allowed to dry in ambient air. XRD studies the structure of solid films formed on glass sample holders. XRD analysis results are shown in Table 4
[0110] Example
[0111] Compared with the reported (001) basal planar spacing for layered material L1 (Table 2), the basal planar spacing of Examples 4–6 is increased, indicating that intercalation such as intercalation and / or exfoliation has occurred. TEM confirmed these results.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com