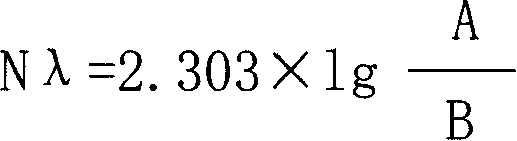Molecular biological quantitative detecting method for pathogenicity paratypic hemolytic vibrio in aquatic products
A quantitative detection method, molecular biology technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
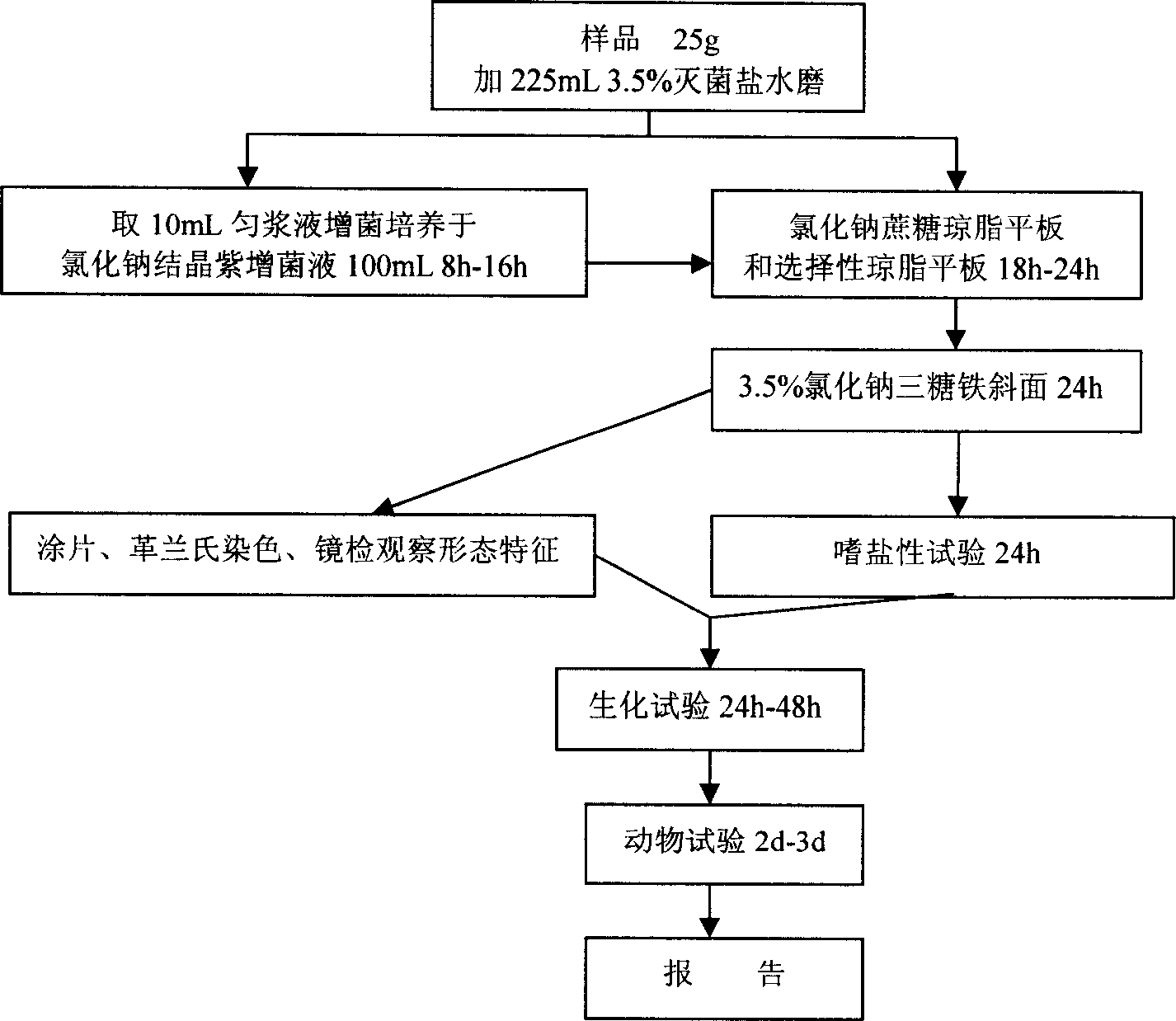
[0106] Basic method description
[0107] 1. Sample processing:
[0108] 1. Sterile and quantitatively take samples to be tested (such as farmed or wild aquatic animals, seafood, finished or semi-finished aquatic products, or various water samples).
[0109] The purpose is to test its freshness and quality: the test site is the bacterial content in the muscle of aquatic food, so as to judge its freshness and quality.
[0110] For the purpose of testing whether a certain pathogenic bacteria is contaminated: the test site should be the digestive tract (or visceral mass) and gills and other respiratory organs: the intestine and gills of fish are cut; the hepatopancreas and digestive caecum in the cephalothorax of shrimp , the intestinal tube at the extension of the abdominal segment; crabs cut off the viscera and gills; shellfish snails cut the part below the gastropod muscle, and shellfish bivalves cut off the outer layer of the axopod muscle Viscera and flap gills.
[0111] S...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Example 2 Rapid quantitative detection of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood
[0136] Using a rapid quantitative detection method, samples such as salmon meat in a restaurant in Qingdao City, live shrimp, and live crabs in an aquarium were enriched and cultured, and three pairs of specific primers for Vibrio parahaemolyticus were designed for PCR amplification and electrophoresis detection. Determine the most probable number of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the sample to be tested.
[0137] Material method:
[0138] 1. Test materials: live shrimp, live crab, clams, and salmon meat in the aquarium of a restaurant in Qingdao.
[0139] Sample processing: Take out 0.234g of shrimp hepatopancreas, 0.221g of crab viscera, 0.231g of crab gills, 0.216g of salmon meat, 0.286g of clam water pipe and skirt tissue, 0.232g of prawn muscle (tissue control), 0.228g of crab muscle ( Tissue control), tissue homogenate respectively, and dilute to 10mL.
[0140] 2. A...
example 1
[0188] Example 1: Tube group
[0189] Tube number 3 3 3
[0190] Sample amount in each tube 10g 1g 0.1g
[0191] Number of positive tubes 3 0 0
[0192] Therefore, N=10, A=10×3+1×3+0.1×3=33.3, B=1×3+0.1×3=3.3
[0193] Substitute into the formula (1) to calculate the results of the column "3", "0" and "0" in the table.
[0194] 2. When there are positive tubes in the two dilution tube groups (denoted as positive tube group 1 and positive tube group 2), use formula (2) to calculate:
[0195] N 1 λ = 2.303 × lg ( A - N 2 γ - A × 10 - 0.4343 N 2 λ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com