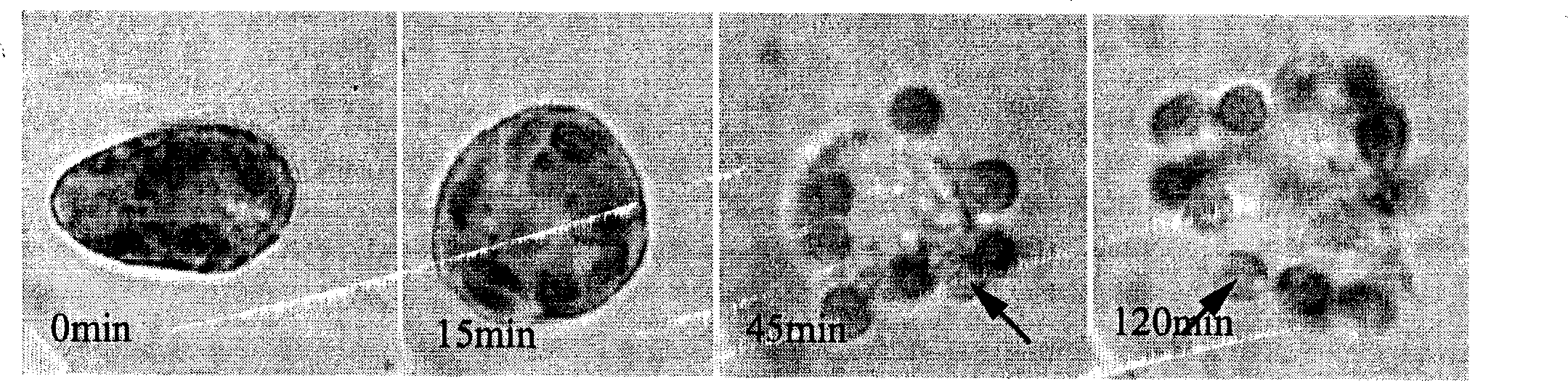Method of controlling red tide of sea water and algalbloom of fresh water
A technology of freshwater algae and red tide, applied in the fields of added material water/sewage treatment, flocculation/sedimentation water/sewage treatment, sterilization/microdynamic water/sewage treatment, etc. Ideal, secondary pollution of the environment and other problems, to achieve the effect of good biodegradability, good promotion and application prospects, and easy storage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1: Inhibition of Sophorolipids to Harmful Algae
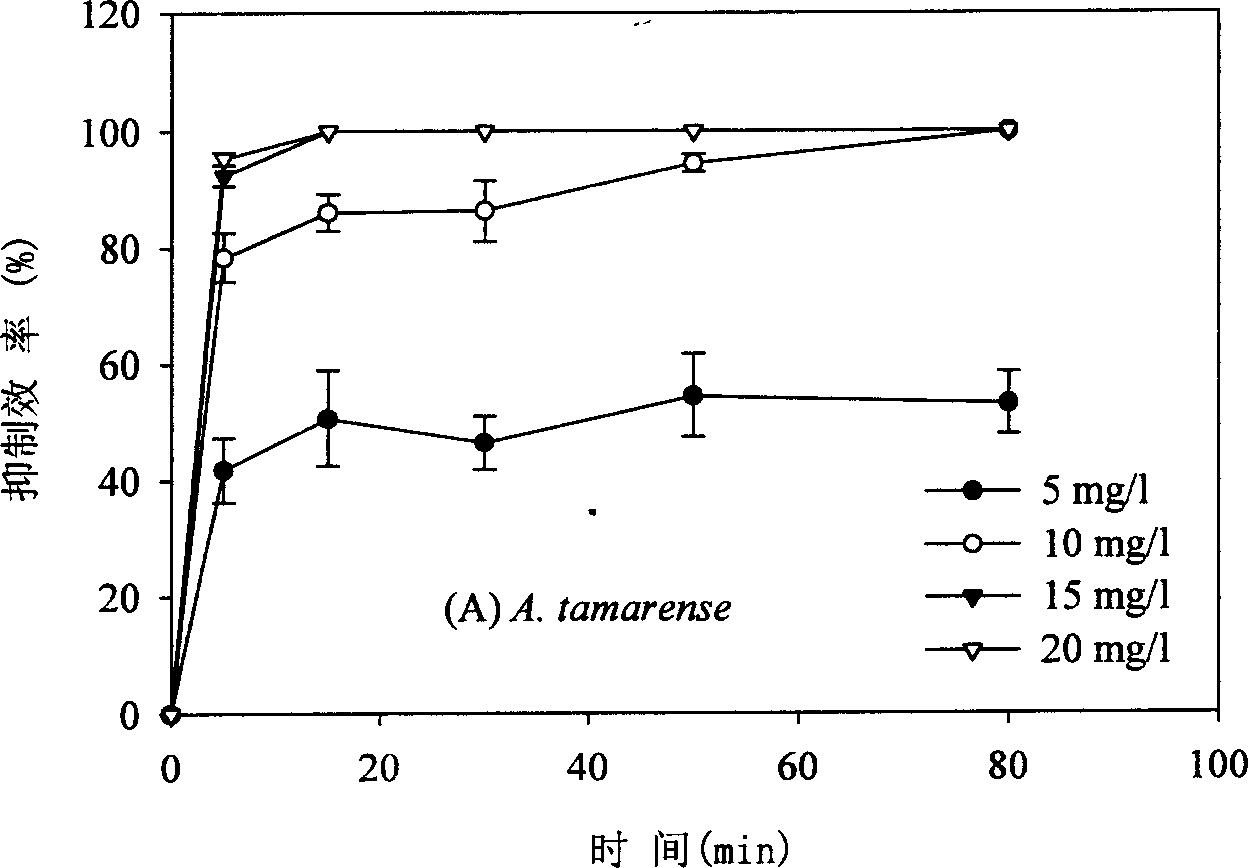
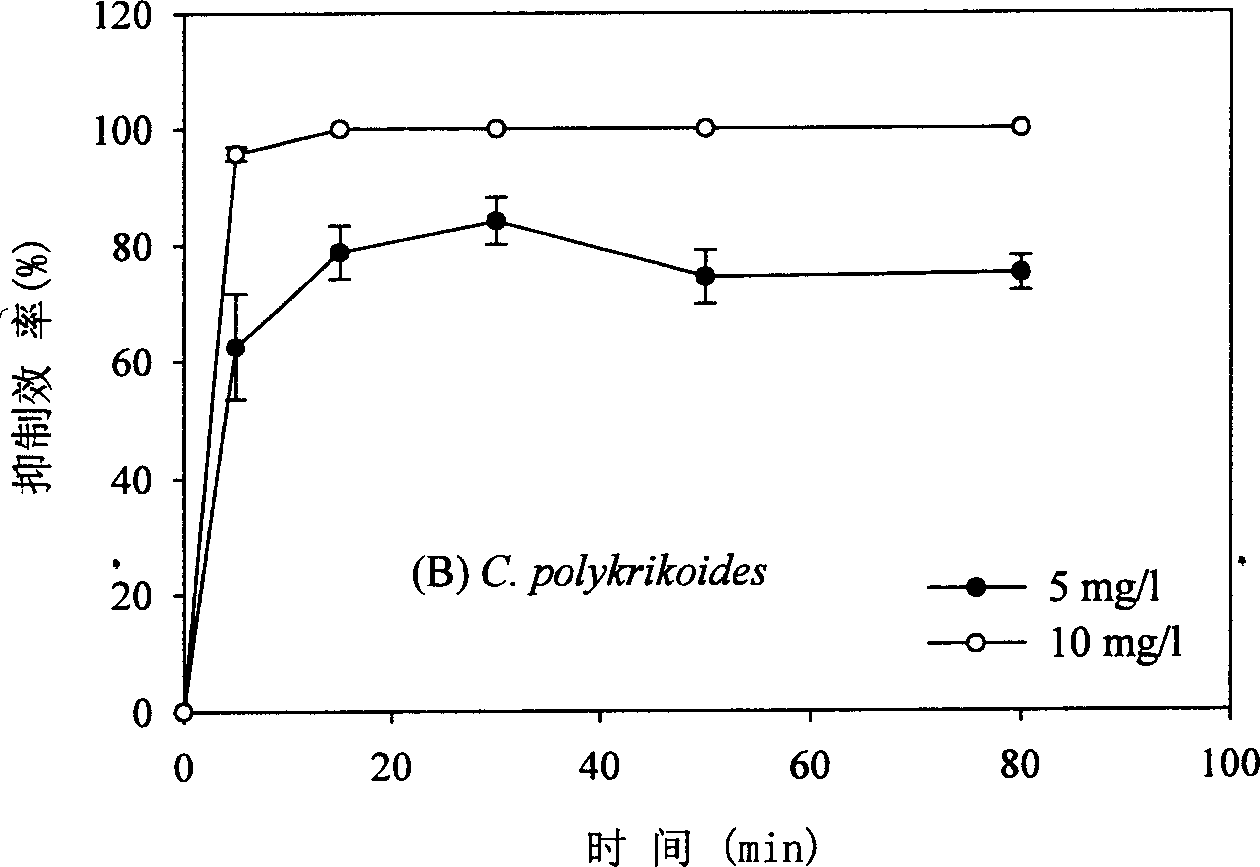
[0019] Weigh quantitative sophorolipids and prepare a 1g / l solution. Take respectively 20 ml of C. polykrikoides and A. tamarense culture fluids in the exponential growth phase, and add the sophorolipid solution so that the final concentrations of the sophorolipids are respectively 5, 10, 15. 20 mg / l. After mixing, let it stand still, take samples after 5, 15, 30, 50, and 80 minutes respectively, count the algae cells that have lost their motility under a microscope, and calculate the inhibition efficiency. The results are as follows: Figure 1a -b. Depend on Figure 1a -b It can be seen that at a concentration of 5 mg / l, 50-80% of Alexandrium tamari and Duchrichia polycyci rapidly lose their motility within 15 minutes; increasing the concentration to 10 mg / l, the inhibition efficiency is close to 100%.
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2: Lysis effect of sophorolipids on harmful algae cells
[0021] The sophorolipid solution was prepared under the same conditions as in Example 1, and added to the liquid of Heterocurvium akashiwo so that the final concentration of the sophorolipid was 10 mg / l. Samples were taken regularly during the 48-hour experiment period, and the morphological changes of algae cells were observed under a microscope. The results were as follows figure 2 . Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that 15 minutes after the addition of sophorolipids, the algal cells rapidly swelled and deformed; 45 minutes later, the algal cells ruptured, and the pigment bodies flowed out; 120 minutes later, the algal cells were completely lysed.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Embodiment 3: the promotion effect of sophorolipids on loess flocculation harmful algae
[0023] Prepare the sophorolipid solution under the same conditions as in Example 1; Weigh quantitative loess (formed as SiO 2 50-65%, Al 2 o 3 16-24%, Fe 2 o 3 4-9%, MgO 0.6-2.5%, others 5-15%), prepared into a 100g / l solution; mixing sophorolipid and loess at a mass ratio of 1:200 to prepare a mixed solution. Add loess, sophorolipid, and loess-sophorolipid mixture to 20ml of polycyclic dilute algae culture solution respectively, so that the final concentration is loess 1g / l, loess 5g / l, sophorolipid 5mg / l, loess 1g / l+sophorolipid 5mg / l. After 2 hours, get the supernatant and count under the microscope, calculate the removal rate of algae, the results are as follows: image 3 . Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the mixed use of sophorolipids and loess has the highest algae removal efficiency, exceeding 90%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com