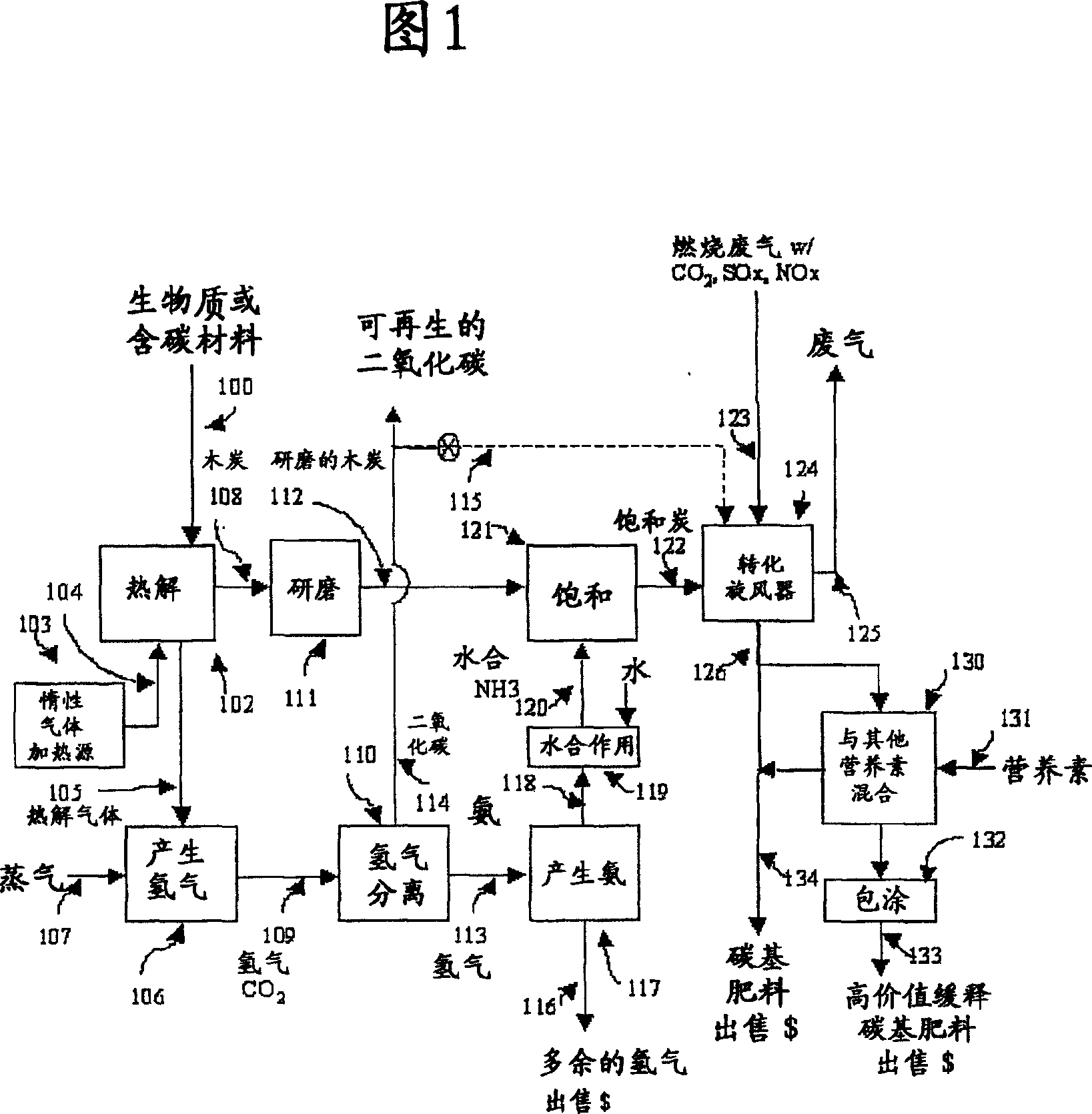
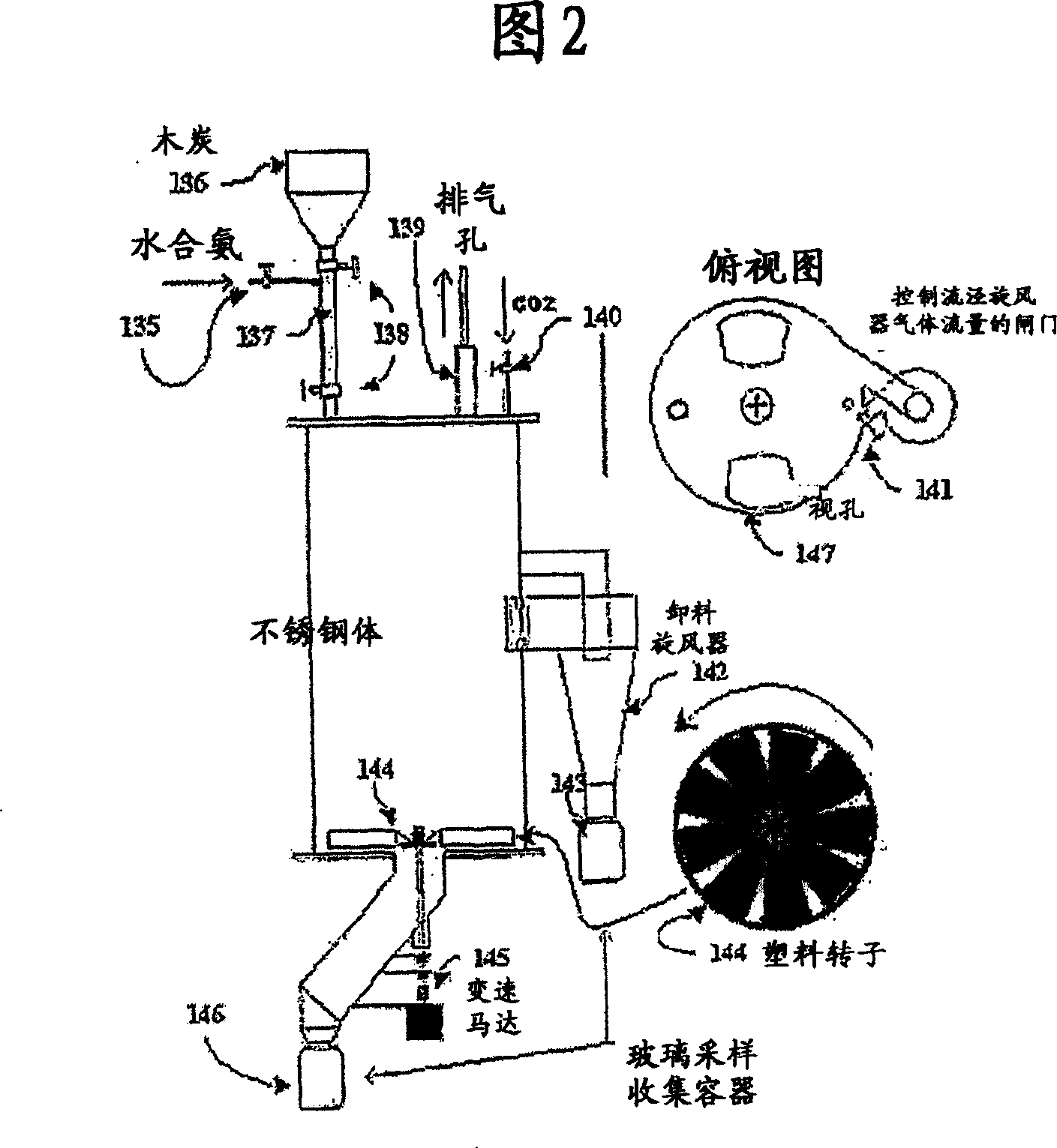
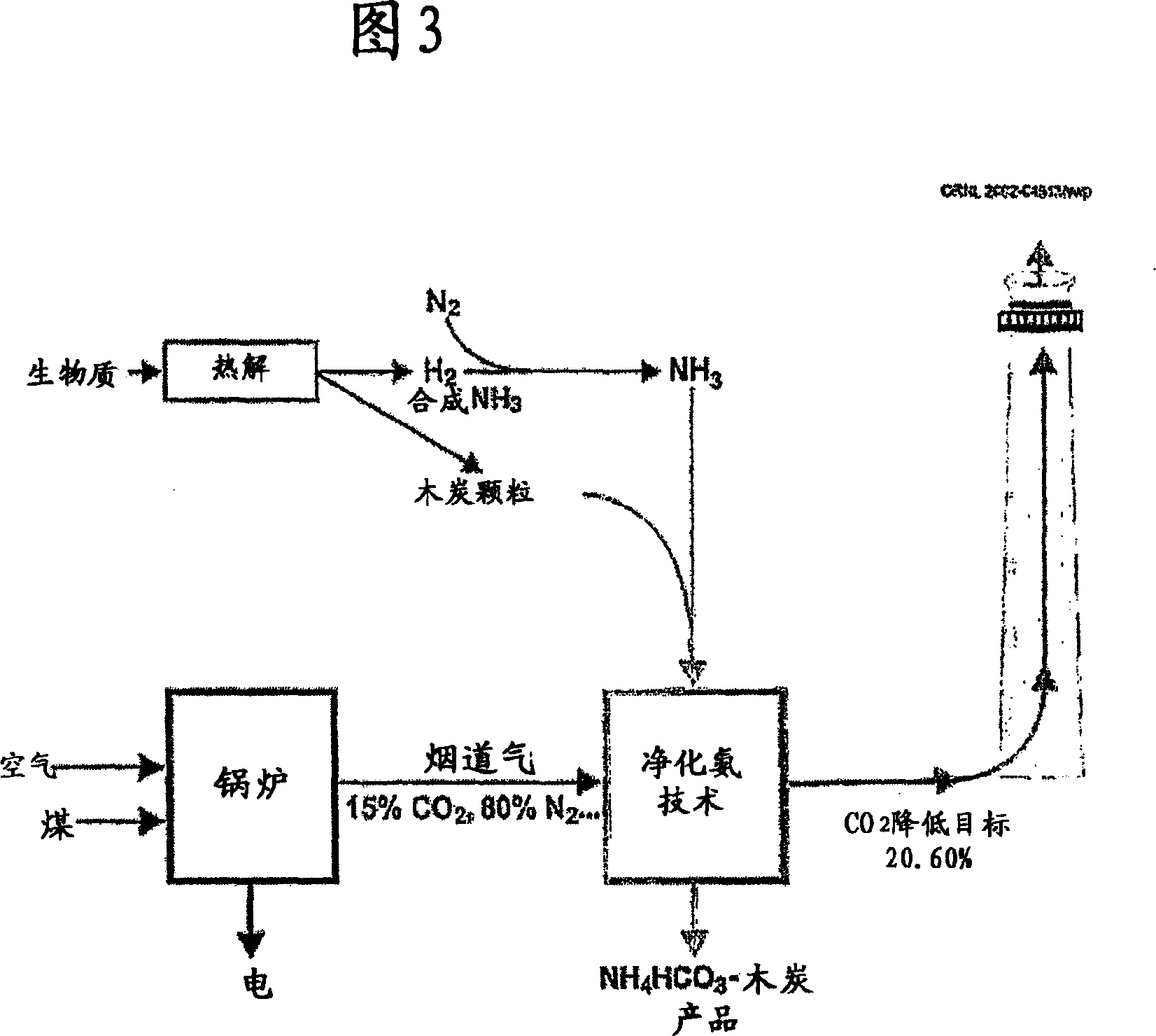
Production and use of a soil amendment made by the combined production of hydrogen, sequestered carbon and utilizing off gases containing carbon dioxide
A carbon dioxide and hydrogen technology, applied in the field of soil amendments and fertilizers, which can solve the problems of increasing the by-products of chelating and without proof, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] We prepared five different charcoals from peanut shells at different temperatures (900°C, 600°C, 500°C, 450°C, and 400°C) in a hypoxic environment. In each case, the samples were heated to the target temperature for 1 minute. The sample is heated to a certain temperature and then allowed to cool. The material was then ground and sieved to less than US 30 mesh and greater than US 45 mesh, and a 20.0 gram sample was prepared. Formulated 48% NH 4 NO 3 (ammonium nitrate) aqueous solution. Each sample was soaked for 5 minutes, poured into cone filter paper and allowed to air dry for 24 hours. Then pour 100 ml of tap water (pH 8) into the conical filter paper for rinsing. The pH of each rinse was measured and showed a corresponding decrease in pH with the leaching rate of each material.
[0056] Except for the sample prepared at 400°C, the differences were small for the other samples. After three or four rinses, material carbonized at higher temperatures will stabilize...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Although this method can be used for a variety of structures, this example uses relatively simple production techniques. In this example we use CO which is easily adaptable to any gas flow and injection 2 and a mechanically fluidized bed of ammonia hydrate. A charge of 250 g 30-45 mesh (0.4-0.6 mm) 400°C charcoal was added regularly at 15-30 minute intervals. Higher rotational speeds increase fluidization and suspend particles until particles are deposited due to NH 4 HCO 3 becomes too heavy to be supported by the fluidizing airflow. Longer time intervals produce larger particles. The particle range was 1.0-2.0 mm at 10-15 minutes and 3.0-6.00 mm at 20-30 minutes. The interior of the particles was then examined under a scanning electron microscope. Inner pore structure shows significant NH formation at 10-15 min 4 HCO 3 structure. The pores and cavities of the resulting material were completely filled at 20-30 minutes.
[0062]
[0063] global potential ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com