Neo-cartilage constructs and a method for preparation thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
The Production of Human Neo-Cartilage Construct
[0358] This example describes conditions for production of neo-cartilage for human use.
[0359] The patient undergoes arthroscopic biopsy of a small (200-500 mg) piece of healthy cartilage from the ipsilateral knee. The biopsy is taken from the non-weight bearing portion of the femoral condyle or from the femoral notch as deemed most appropriate for the patient. The biopsy sample is placed into a sterile, non-cytotoxic, non-pyrogenic specimen container which is packaged and shipped to the laboratory.
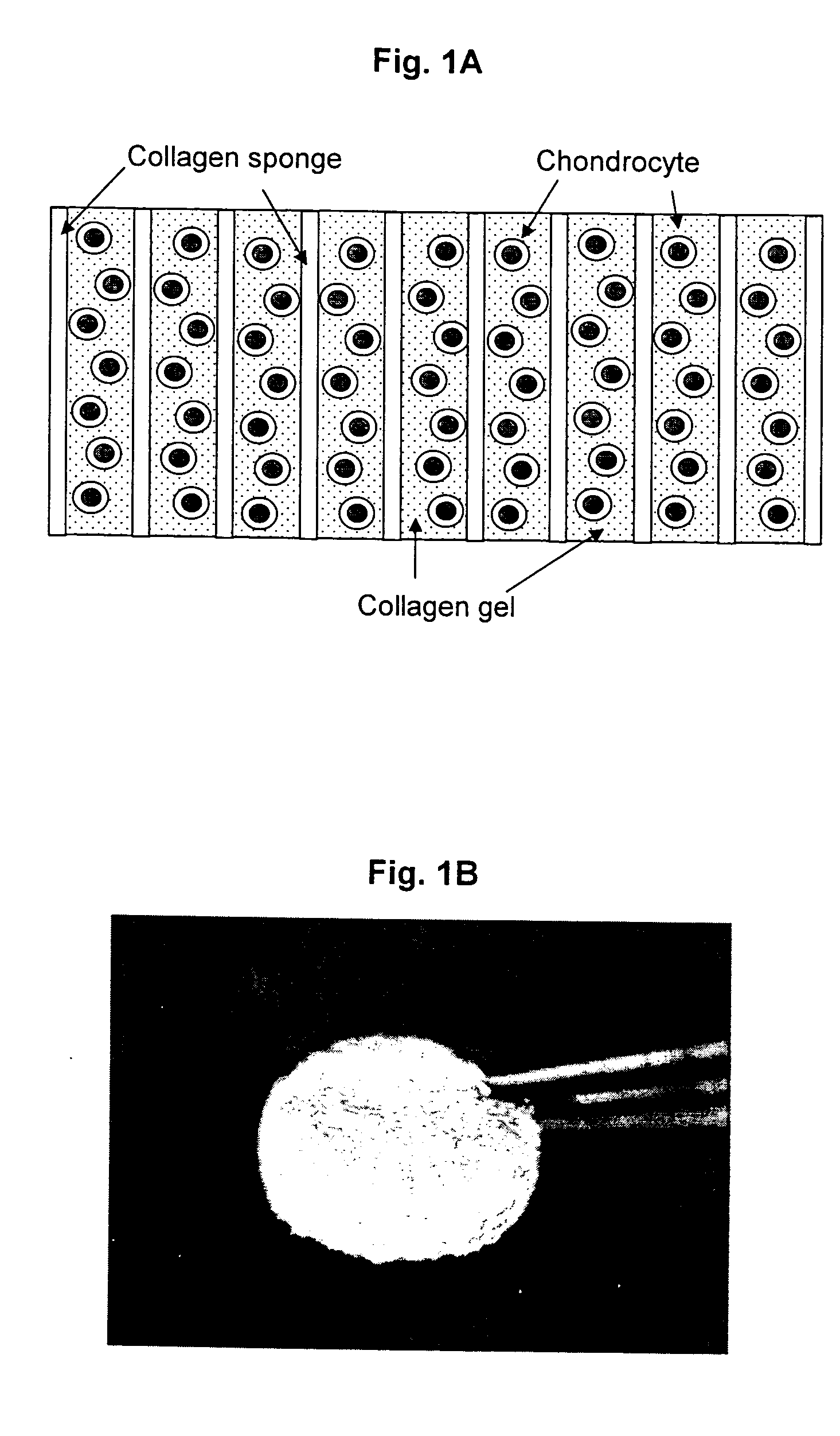
[0360] At the laboratory the biopsy sample is examined against acceptance criteria and then transferred to the chondrocyte isolation and expansion area. Samples from the biopsy specimen transport buffer are tested for sterility and for mycoplasma. The expanded chondrocytes are suspended in VITROGEN.RTM. gellable collagen solution, commercially available from Cohesion Corp., Palo Alto, Calif. A pre-formed collagen sponge (22.times.22 mm square ...
example 3
Preparation of Support Matrices
[0363] This example illustrates preparation of the cellular support matrix, also called the TESS matrix.
[0364] 300 grams of a 1% aqueous atelocollagen solution (VITROGEN.RTM.), maintained at pH 3.0, is poured into a 10.times.20 cm tray. This tray is then placed in a 5 liter container. A 50 ml open container containing 30 ml of a 3% aqueous ammonia solution is then placed next to the tray, in the 5 liter chamber, containing 300 grams of said 1% aqueous solution of atelocollagen. The 5 liter container containing the open trays of atelocollagen and ammonia is then sealed and left to stand at room temperature for 12 hours. During this period the ammonia gas, released from the open container of aqueous ammonia and confined within the sealed 5 liter container, is reacted with the aqueous atelocollagen resulting in gelling said aqueous solution of atelocollagen.
[0365] The collagenous gel is then washed with water overnight and, subsequently, freeze-dried to y...
example 4
Seeding Cells in the TESS Matrix
[0369] This example describes procedures used for seeding cells in the TESS matrix.
[0370] Isolated chondrocytes were incubated for a period of five days at 37.degree. C. in a standard incubator. Cells were then collected by trypsinization.
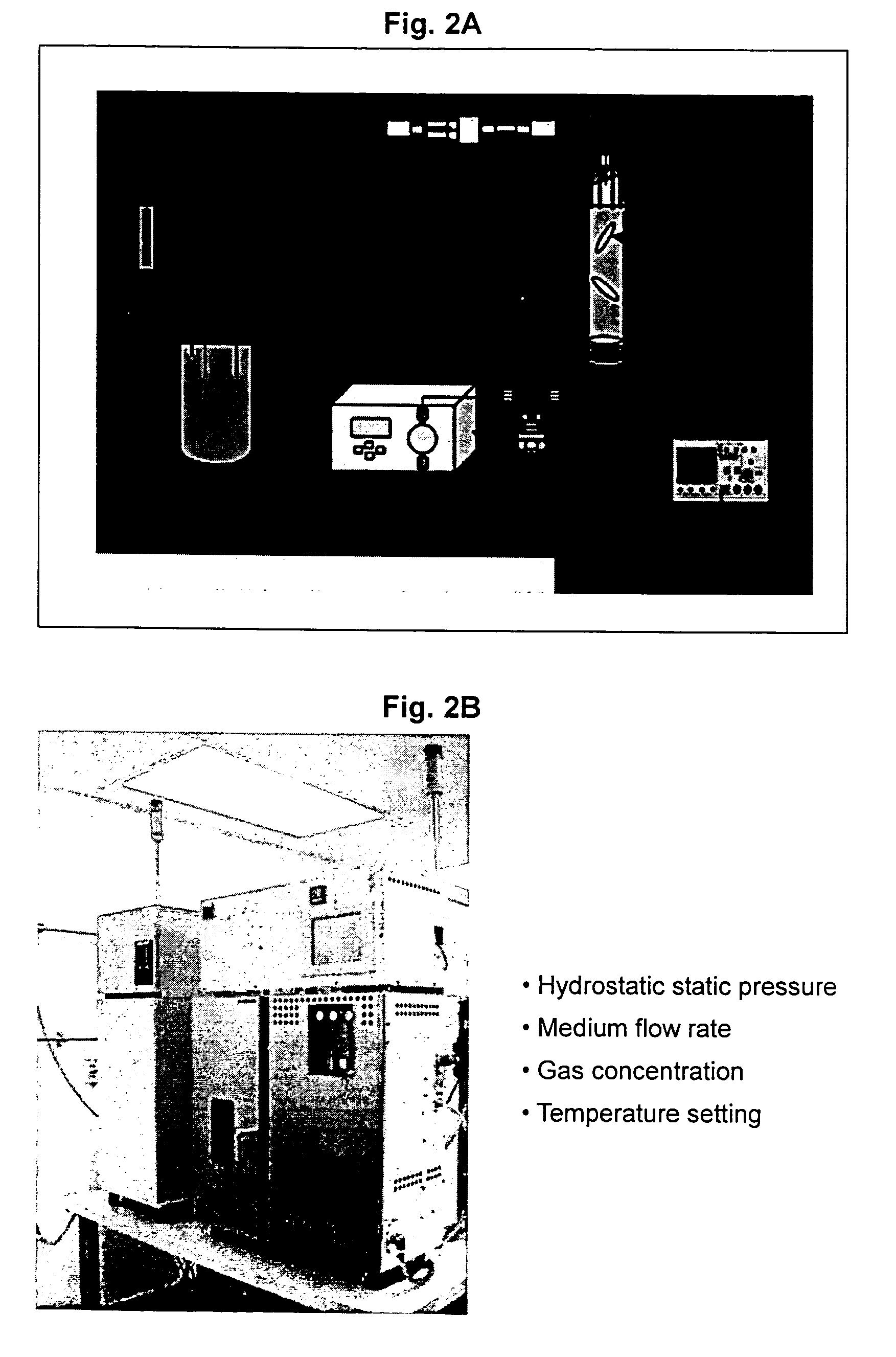
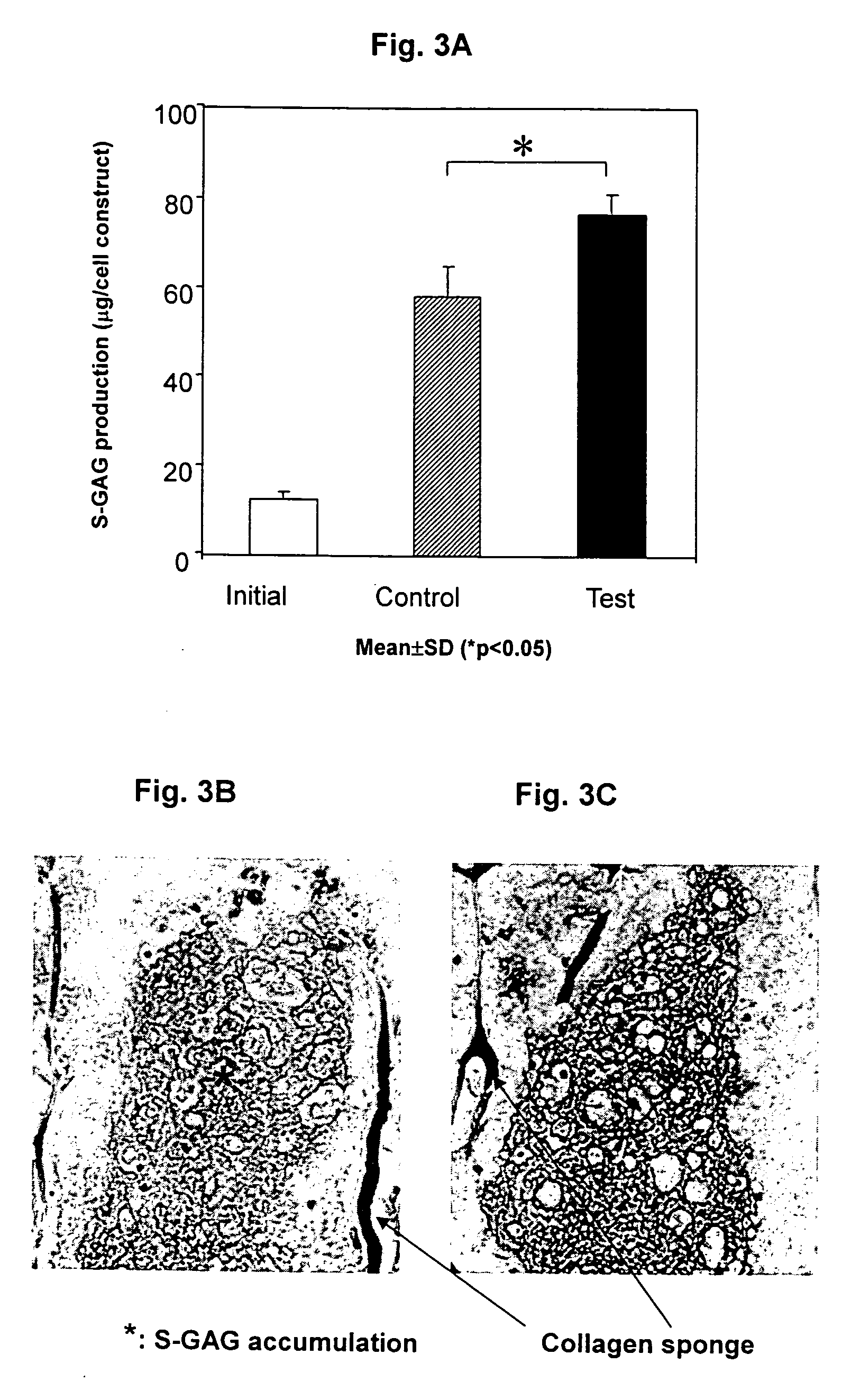
[0371] A cell suspension of 150,000 cells in 18 .mu.l of VITROGEN solution was seeded per matrix having an approximate volume of 19 .mu.l, with nine matrices per group. The seeded matrix (collagen sponge 4 mm in diameter and 1.5 mm in thickness) may be scaled-up to an increased volume, where approximately 1 .mu.l of the above described cell suspension is seeded in 1 .mu.l of matrix. The control group matrices were incubated in a 37.degree. C. incubator and the test group was incubated in the TESS.
[0372] In alternative set-up, isolated chondrocytes were incubated for a period of five days at 37.degree. C. in a standard incubator. Cells were then collected by trypsinization. A cell suspension of 300,000 cells in 18 .mu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com