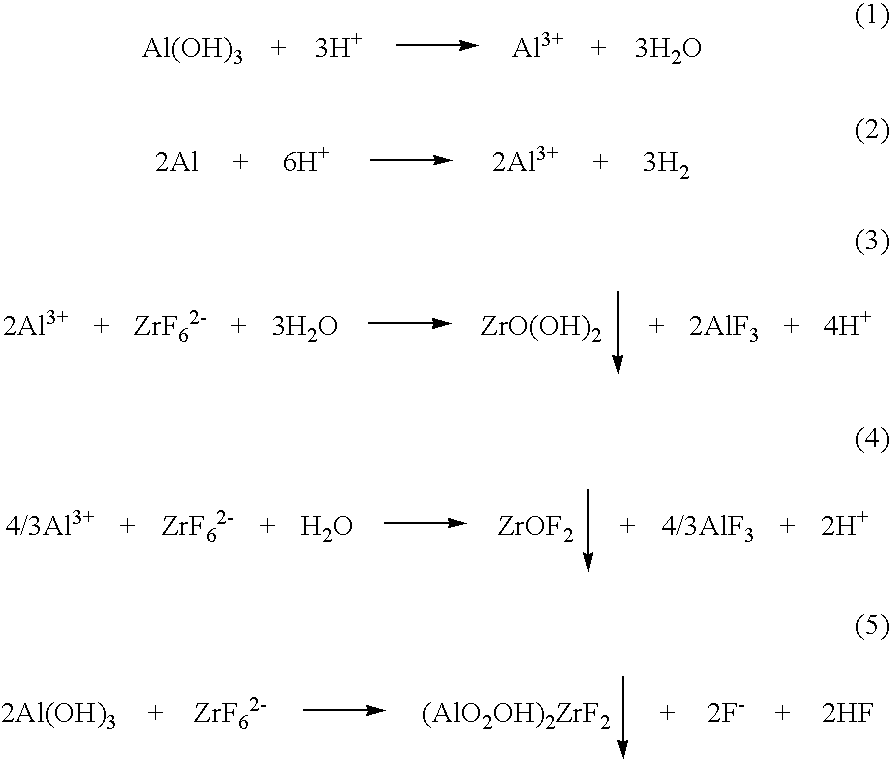Method of surface treating metal and metal surface treated thereby
a technology of metal surface and surface treatment, applied in the direction of electrolytic inorganic material coating, solid-state diffusion coating, coating, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient dense and uniform coating, deterioration of corrosion resistance, and difficulty in achieving uniform and dense protection coating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 22 to 23
[0093] Preparation of Chemical Conversion Treatment Agent
[0094] Chemical conversion treatment agents shown in Table 4 were prepared by mixing fluorozirconic acid and ammonium fluorozirconate as a zirconium-containing compound and a fluorine-containing compound, and .gamma.-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, and adding ion-exchanged water to the mixture.
[0095] Preparation of Test Sheet
[0096] Magnesium alloy AZ91D of 70 mm.times.150 mm.times.2.0 mm obtained by a thixomolding process was degreased by spraying at 50.degree. C. for 2 minutes using a 1% aqueous solution of an alkaline degreasing agent (SURF MAGDINE SF120 CLEANER manufactured by NIPPON PAINT Co., Ltd.). After rinsing by spraying with running water for 30 seconds, the metal sheet was acid-cleaned by spraying at 50.degree. C. for 2 minutes using a 1% aqueous solution of an acid cleaning agent (SURF MAGDINE SF400 manufactured by NIPPON PAINT Co., Ltd.). After rinsing by spraying with running water for 30 seconds, the metal sheet was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electric potential / voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Auxiliary magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com