Method for combined sequential agent delivery and electroporation for cell structures and use thereof
a cell structure and sequential agent technology, applied in the field of combined sequential agent delivery and cell structure electroporation, can solve the problems of difficult transfer of all these compounds and particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
third embodiment
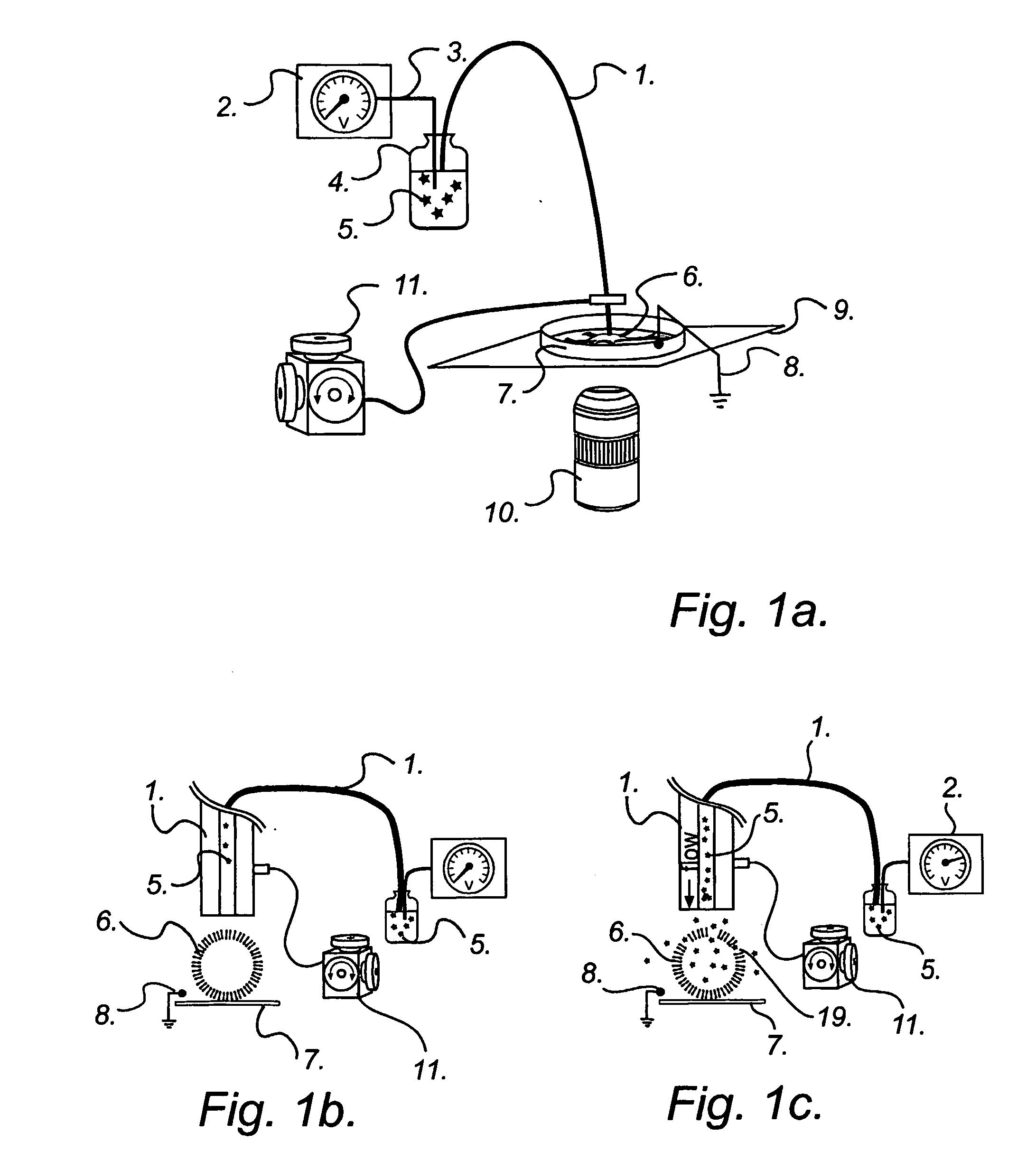
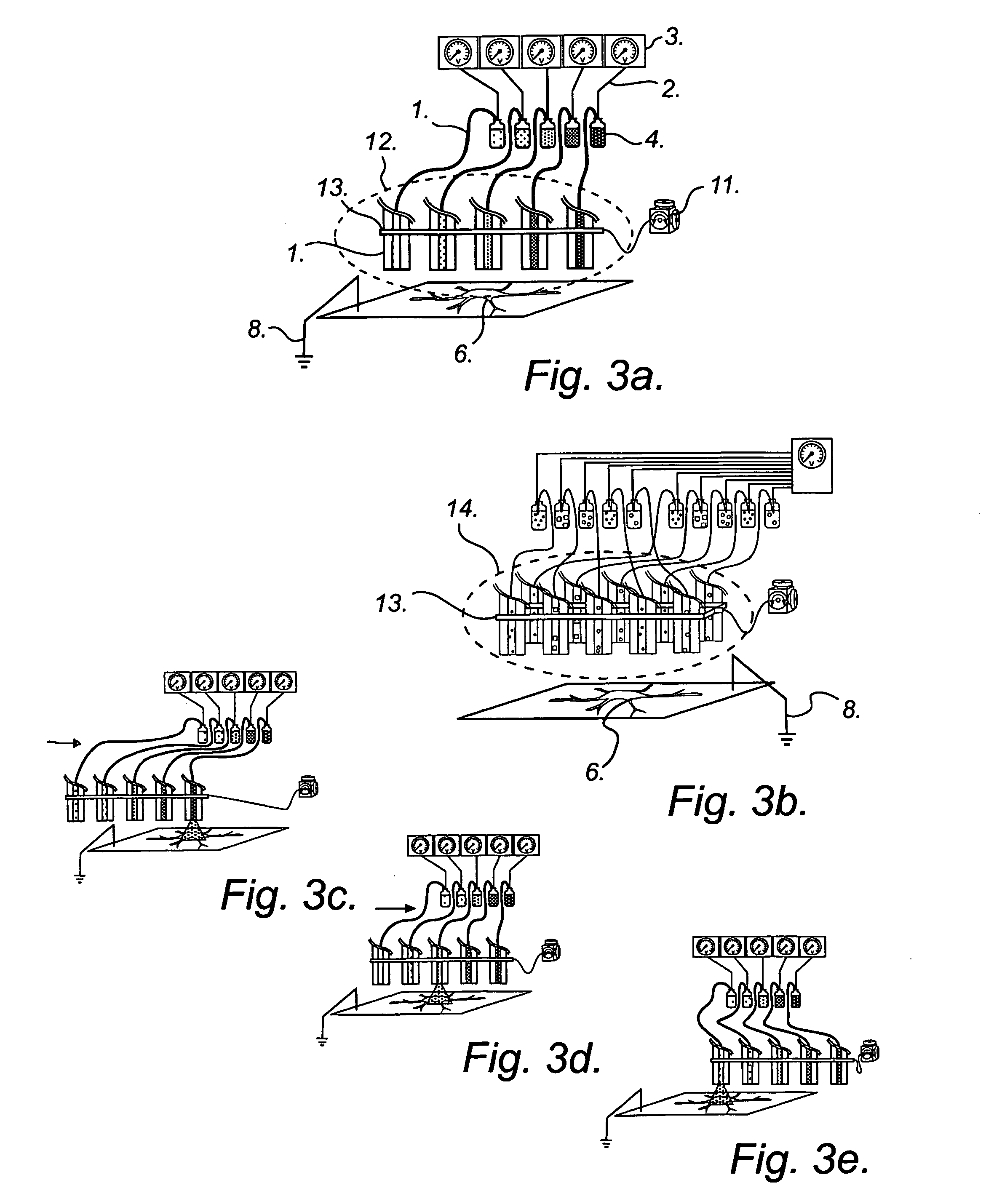
sequential delivery of multiple cell-loading agents is achieved by introducing a separation step while pumping the fluid through the EFC. When using electrophoretic pumping for delivery of reagents, all species present in the electrolyte solution is separated based on their charge-to-frictional drag ratio and will be delivered in a sequential manner at the cellular target. Analogously, sequential reagent delivery can be achieved by incorporating any separation technique applicable to the EFC format, for example, it is feasible to utilize chromatographic separation techniques.
The sequential delivery of cell-loading agents can be performed together with parallel delivery of cell-loading agents in a combinatorial fashion. Such combinatorial delivery may be achieved by selection of cell-loading agents to each EFC from a plurality of containers containing said cell-loading agents as shown in FIG. 3b. It may also be achieved by activating different EFCs in an array of EFCs where each EFC...
example 1
Detection of the Intracellular Receptor Ryanodine Type II
Fluo-3 AM ester was from Molecular Probes (Leiden, The Netherlands). Cyclic ADP ribose and the chemicals used for buffer solutions, were all of analytical grade and purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, Mo., USA). All solutions were made in distilled water from a Milli-Q system (Millipore).
NG108-15 cells were plated on no. 1 cover slips or in a Petri dish and allowed to grow for 1-3 days. Cell dishes were mounted in a circular polycarbonate holder and transferred to the stage on the microscope. Prior to experiments the culture medium was replaced by a HEPES buffer (NaCl 140 mM, KCl 5.0 mM, MgCl2 1.0 mM, CaCl2 1.0 mM, D-glucose 10 mM, HEPES 10 mM, pH was adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH).
The cells were stained with fluo-3 AM ester by incubating the cells for 30 minutes in dye solution (10 μM fluo-3 AM ester in HEPES buffer) at room temperature. To remove excess uncaptured dye, the cells were washed three times in HEPES buffer and sto...
example 2
Detection of Intracellular Enzymes I. Detection of Proteases
Casein BODIPY FL was obtained from Molecular Probes (Leiden, The Netherlands). The chemicals used for buffer solutions were all of analytical grade and purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, Mo., USA). All solutions were made in distilled water from a Milli-Q system (Millipore).
Cell culturing and preparations were made according to methods used in example 1 above, and apparatus and instrumentation was the same as in example 1.
Electroporation was performed as in example 1 and an EFC (30 cm long, 50 μm id., 375 μm o.d.) was used. Casein BODIPY FL was used in a concentration of 100 μg / ml and electroporated into cells using a 10 second pulse at 10 kV.
The results of detection of intracellular proteases using casein-BODIPY-FL is shown in FIG. 9. Specifically, the intracellular protease activity was investigated using a protein, casein, which was heavily loaded with the green-fluorescent molecule BODIPY FL, as enzyme substrate. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| close distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com