Alkaloid that inhibits biosynthesis of mycotoxins and method for screening for mycotoxin inhibitors
a technology of mycotoxin and inhibitor, applied in the field of alkaloid compound, can solve the problems of crop and food commodity contamination by mycotoxin producing fungi, limited to a slight reduction in crop yield, and achieve the effect of inhibiting biosynthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
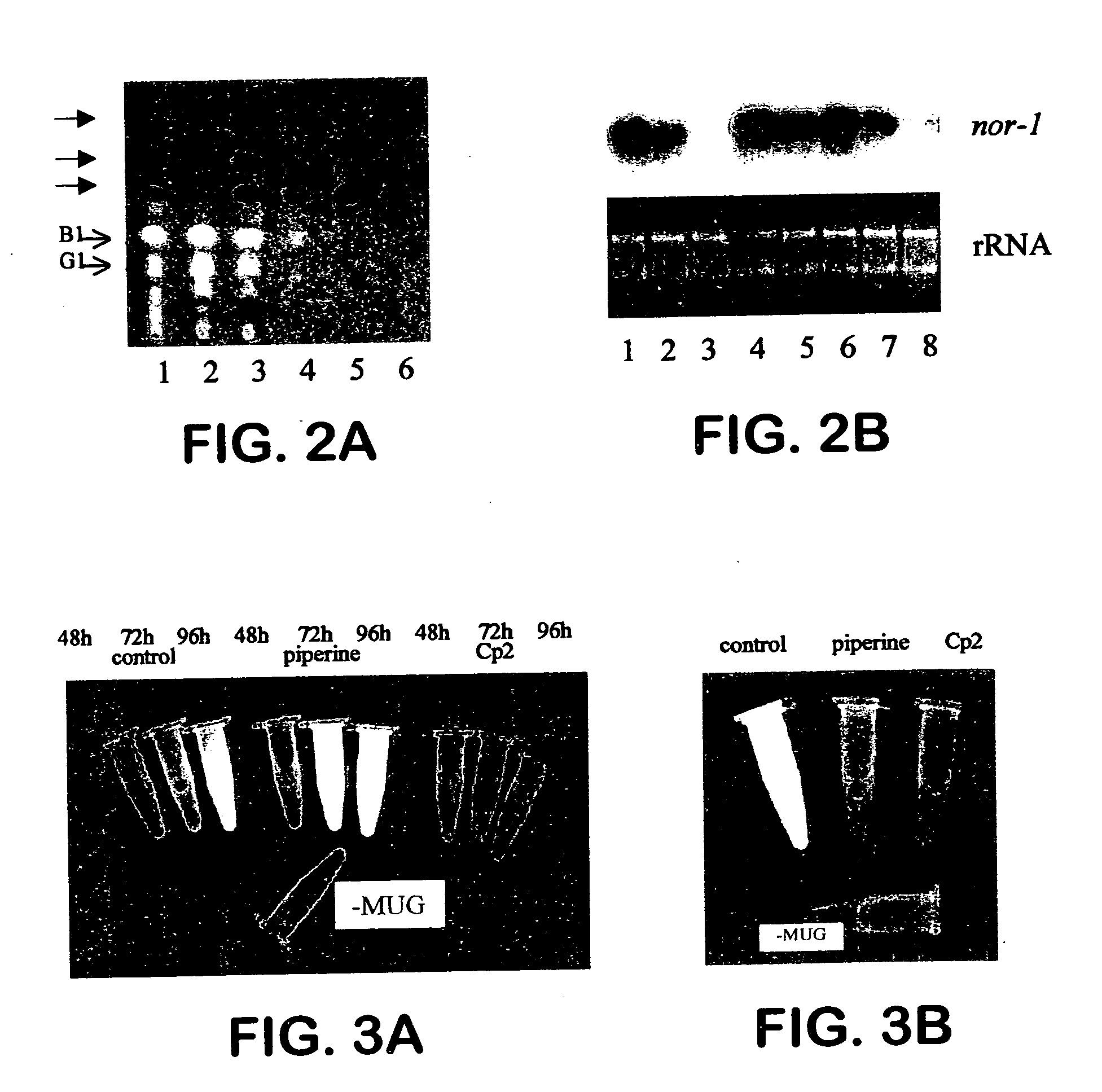
[0069] The method for identifying compounds that inhibit mycotoxin biosynthesis is illustrated using ground black pepper (Piper nigrum) extracts and assaying for compounds that inhibit aflatoxin biosynthesis.
[0070] Ground black pepper (500 mg) was extracted in 2 L cyclohexanol overnight under a fume hood with constant stirring. After 24 hours, the mixture was filtered through Whatman paper and the extracted pepper filtrate was removed and in a similar manner to the above, extracted with chloroform followed by absolute ethanol. The filtrates from each extraction were concentrated by rotary evaporation and analyzed by thin layer chromatography (TLC).
[0071] The extracts were separated on TLC plates using a solvent system consisting of chloroform:acetone:toluene (25:40:35 v:v:v). Afterwards, the TLC plates were dried in a fume hood to evaporate any solvents left on the plates, and then placed silica-side down on a UV transilluminator and UV absorbent spots were traced on an acetate sh...
example 2
[0075] The following is a procedure for isolating Cp2 from ground pepper extracts.
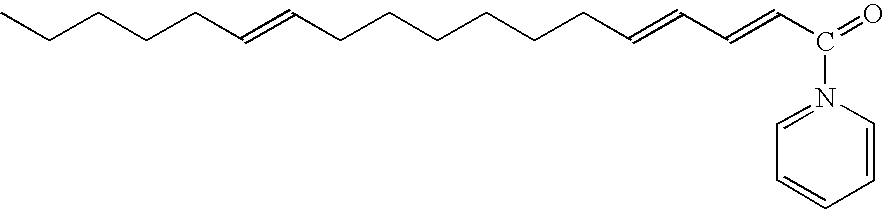
[0076] Black ground pepper was suspended in cyclohexane (1:2 w:v) with constant stirring overnight. The mixture was filtered and then reextracted with cyclohexane for an additional four hours. The filtrates were combined and concentrated by rotary evaporation under vacuum at 40° C. After rotary evaporation, the cyclohexane extract was observed to have two phases. These phases were separated yielding a phase readily soluble in cyclohexane and a less dense phase readily soluble in ethanol. Both phases were tested to determine which phase contained the bioactive compound indicated in Example 1. An amount consisting of 10 μl of both phases were loaded onto separate TLC plates and the plates were developed using a solvent system consisting of chloroform:toluene:acetone (25-40:35 v:v:v). After development, the plates were dried overnight. Then the GUS bioassay was performed as shown in Example 1. The bioact...
example 3
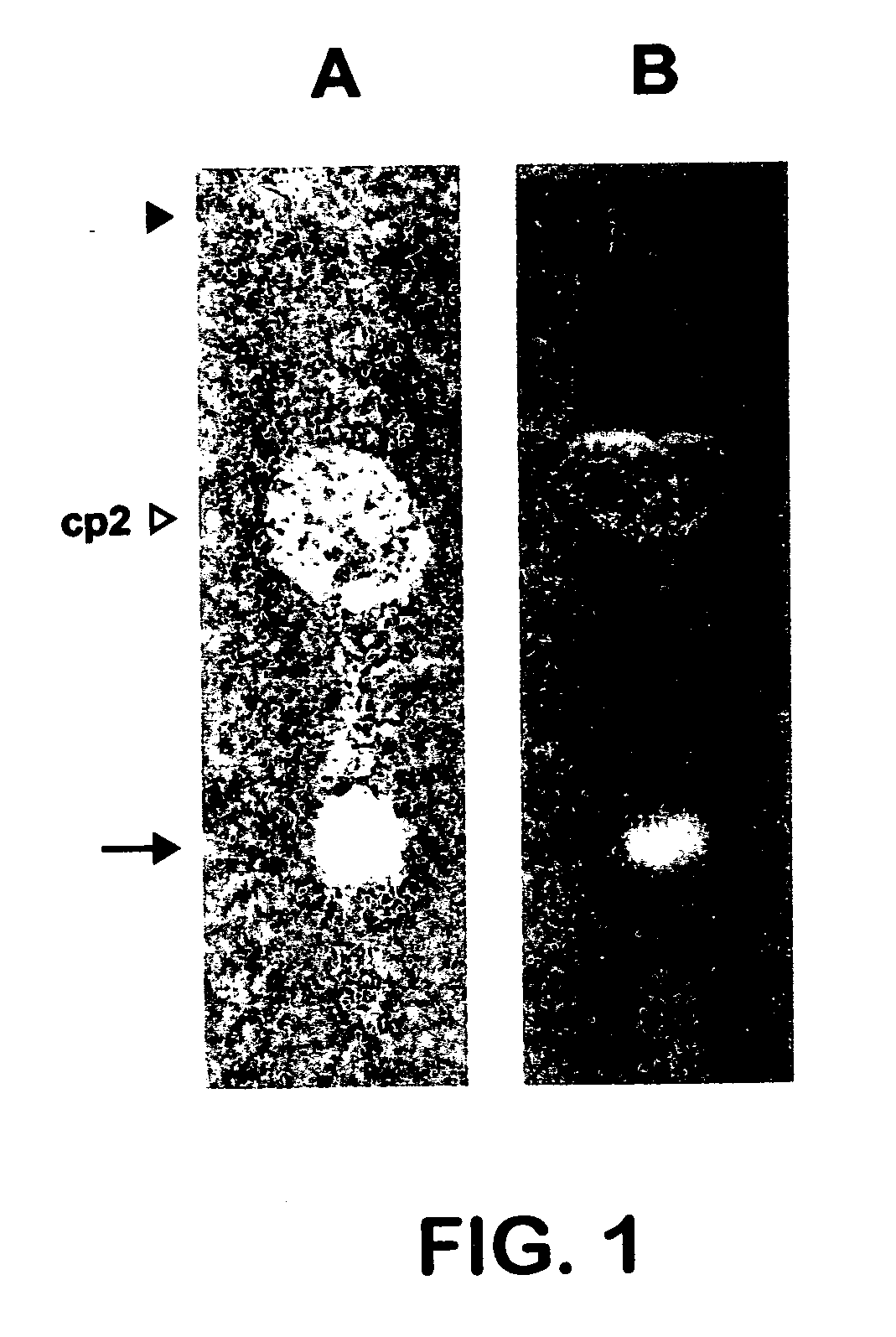
[0079] Cp2 has a demonstrable effect on aflatoxin biosynthesis and nor-1 transcription. This example used Aspergillus parasiticus SU-1, a wild-type aflatoxin producing isolate, and consisted of analyzing aflatoxin biosynthesis by TLC and aflatoxin mRNA transcription by Northern analysis.
[0080] A nutritional shift protocol (Skory et al., Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 3315-3320 (1990)) was used with the modifications below to determine the effect of Cp2 on expression of the nor-1 gene and aflatoxin biosynthesis. Six cultures of fungi were incubated in PMS (peptone mineral salts), a medium that does not induce biosynthesis of aflatoxin. After 48 hours, the mycelium from each culture were separately transferred to GMS (glucose mineral salts), a medium that induces biosynthesis of aflatoxin. At the same time Cp2 was added to five of the six cultures to provide cultures having a final concentration of 2.6 μg / ml, 26 μg / ml, 39 μg / ml, 52 μg / ml, and 78 μg / ml, respectively. Thirty-six hours l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Freezing point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com