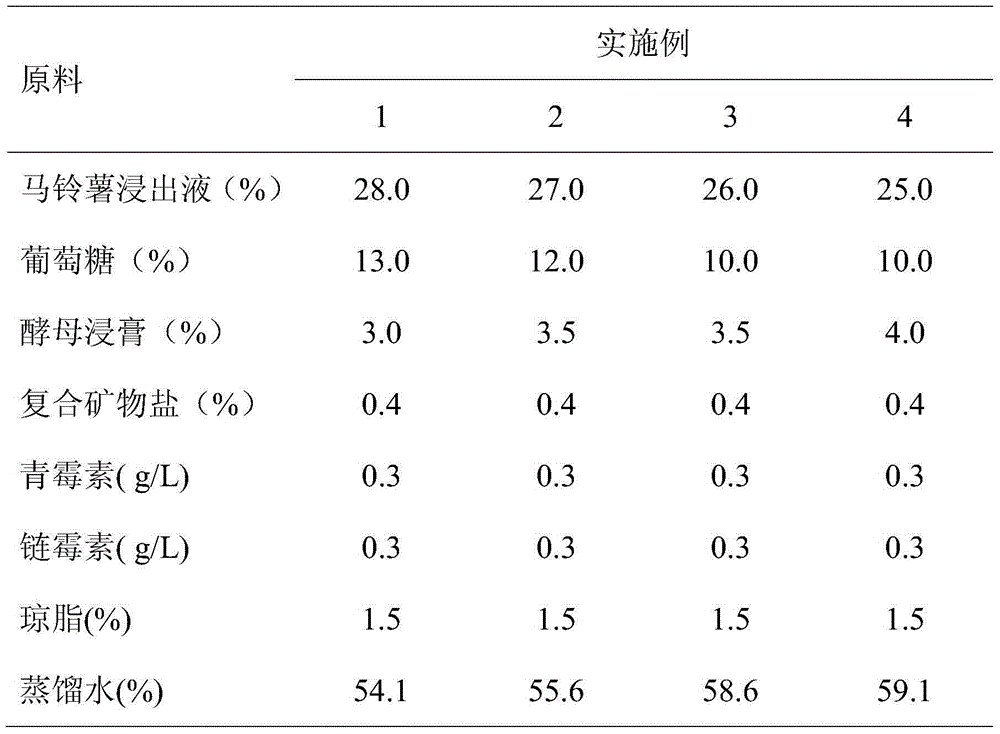
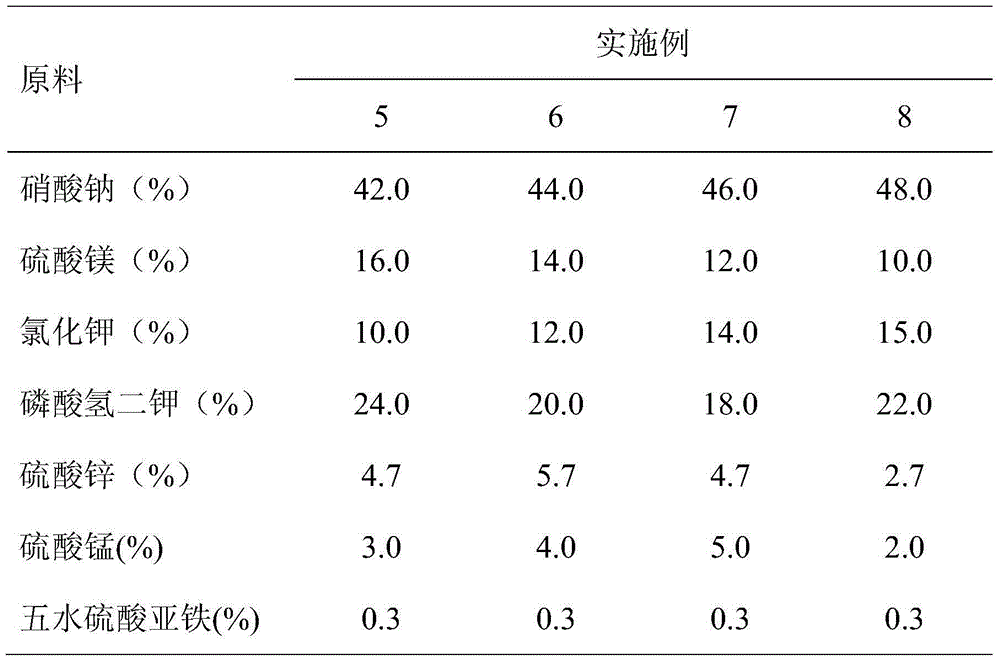
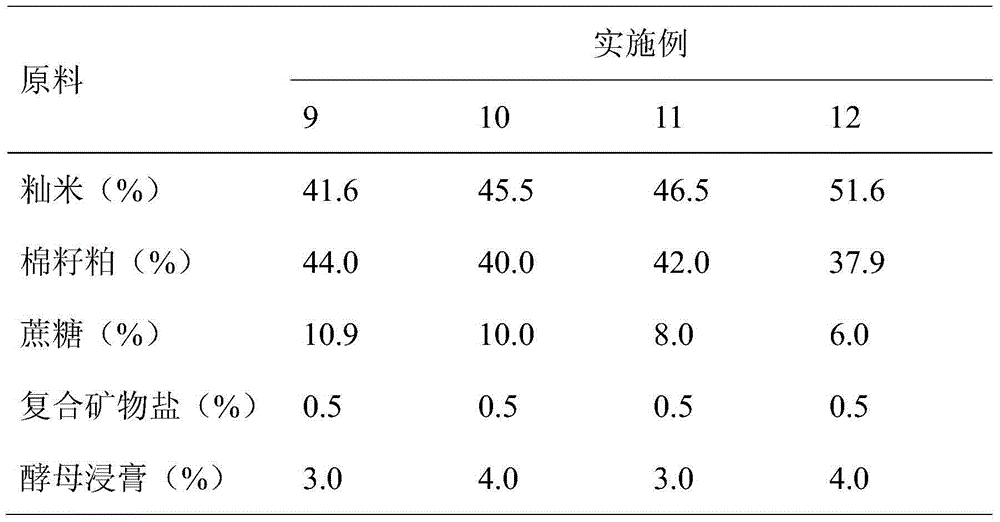
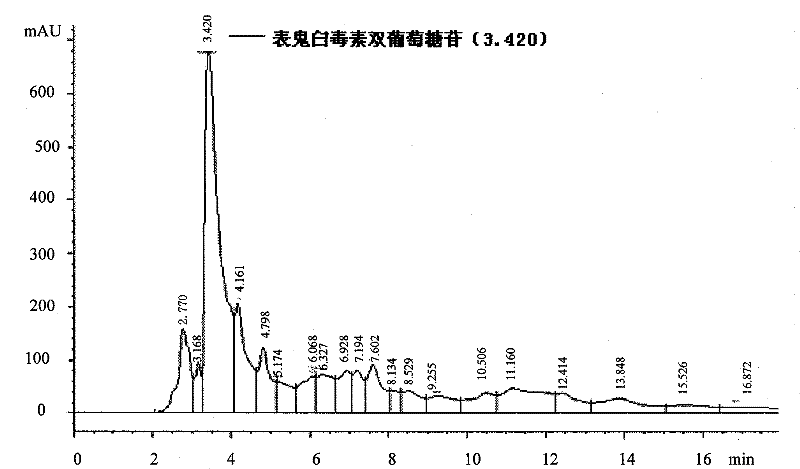
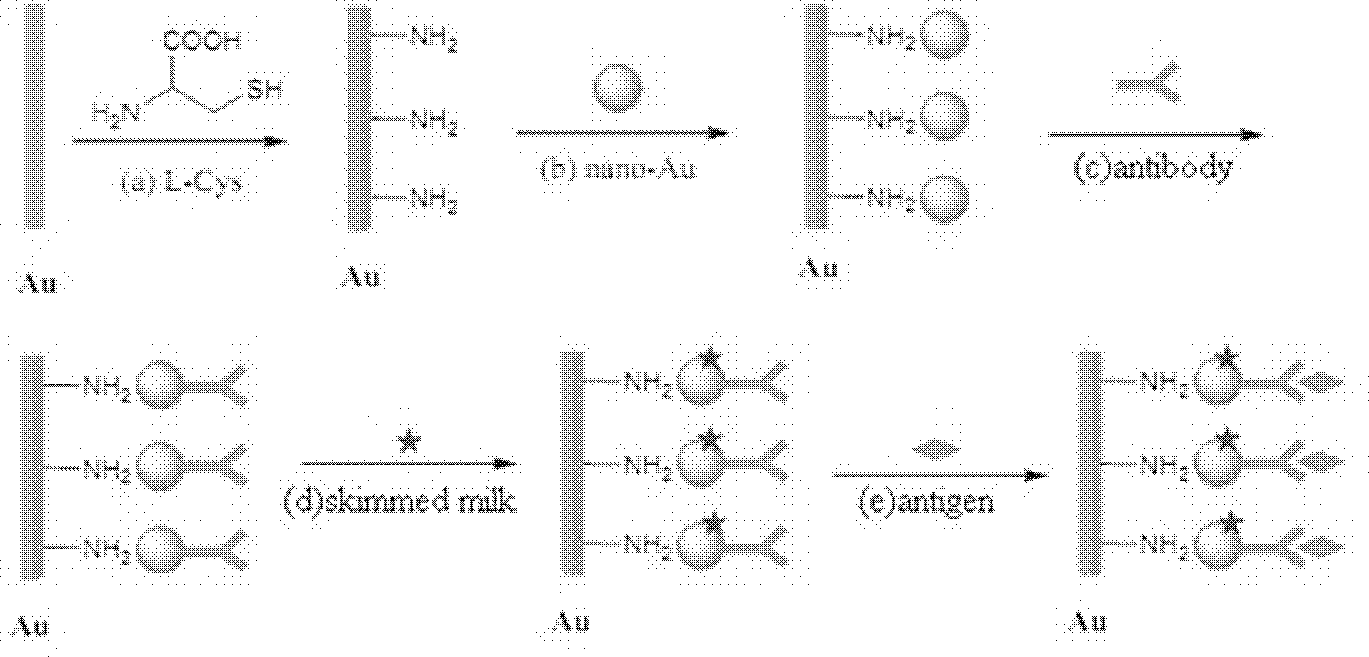Patents
Literature
37 results about "Aspergillus parasiticus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aspergillus parasiticus is a fungus belonging to the genus Aspergillus. This species is an unspecialized saprophytic mold, mostly found outdoors in areas of rich soil with decaying plant material as well as in dry grain storage facilities. Often confused with the closely related species, A. flavus, A. parasiticus has defined morphological and molecular differences. Aspergillus parasiticus is one of three fungi able to produce the mycotoxin, aflatoxin, one of the most carcinogenic naturally occurring substances. Environmental stress can upregulate aflatoxin production by the fungus, which can occur when the fungus is growing on plants that become are damaged due to exposure to poor weather conditions, during drought, by insects, or by birds. In humans, exposure to A. parasiticus toxins have potential to cause delayed development in children and produce serious liver diseases and/or hepatic carcinoma in adults. The fungus is also able to cause the infection known as aspergillosis in humans and other animals. A. parasiticus is of agricultural importance due to its ability to cause disease in corn, peanut, and cottonseed.
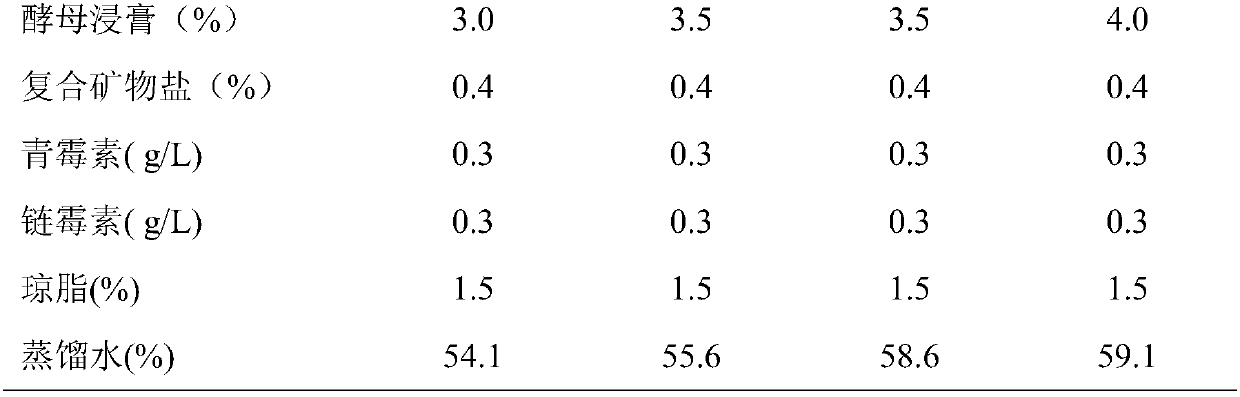
Preparation method and application of microbial agent composition for enhancing secondary fermentation of bean paste
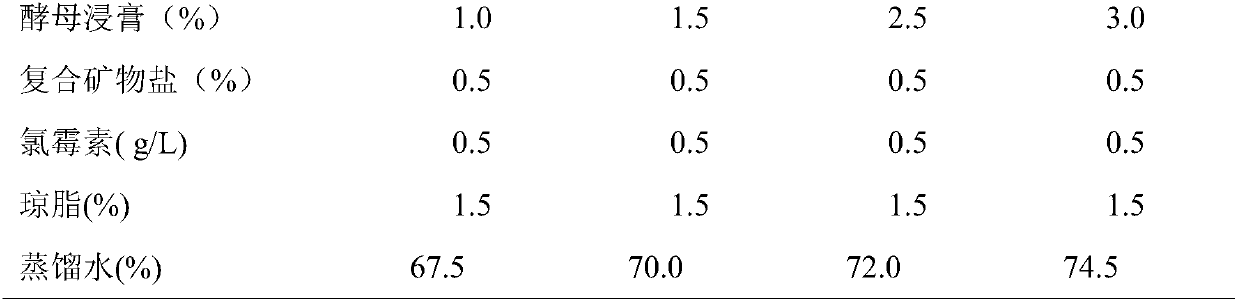
ActiveCN106520583AInhibit metabolismShorten the production cycleFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentSaccharomycetes
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering, in particular to a preparation method and an application of a microbial agent composition for enhancing secondary fermentation of a bean paste. The microbial agent composition consists of a saccharomycetes agent, an aspergillus oryzae agent and a pleospora agent; and the three microbial agents are prepared, and then the prepared microbial agents are mixed with the secondary-fermented bean paste, so as to promote the secondary fermentation of the bean paste. The whole process of the preparation method of the microbial agent composition provided by the invention is applicable to continuous industrial production; by-products (chili and radix platycodonis), from the production of Pixian bean paste, are comprehensively utilized; a production cycle can be shortened by 6 months, the content of amino nitrogen can be improved by 20% and the content of volatile aroma-producing components can be improved by more than 3 times (the contents of total ester, total acid and total aldehyde); by inoculating aflatoxin B1 with the saccharomycetes agent at a production peak (after being fermented for 30-60 days), an ester producing and aroma generating process can be enhanced, the metabolism of aspergillus flavus and partial aspergillus parasiticus can be competitively inhibited and the content of the aflatoxin B1 can be reduced, and the content of the aflatoxin B1 is lower than 0.5ppm, so that food safety is enhanced.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Rice processing method with essential oil mist spraying and pulse microwave action
InactiveCN109092398ALight in massReduce healthSeed preservation by irradiation/electric treatmentGrain millingPulse microwaveFatty acid
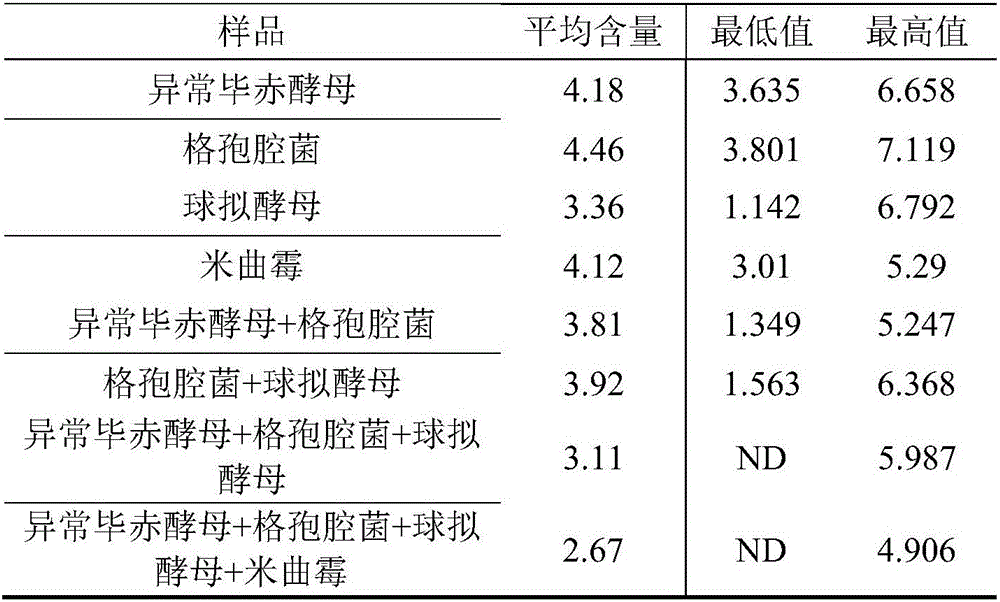
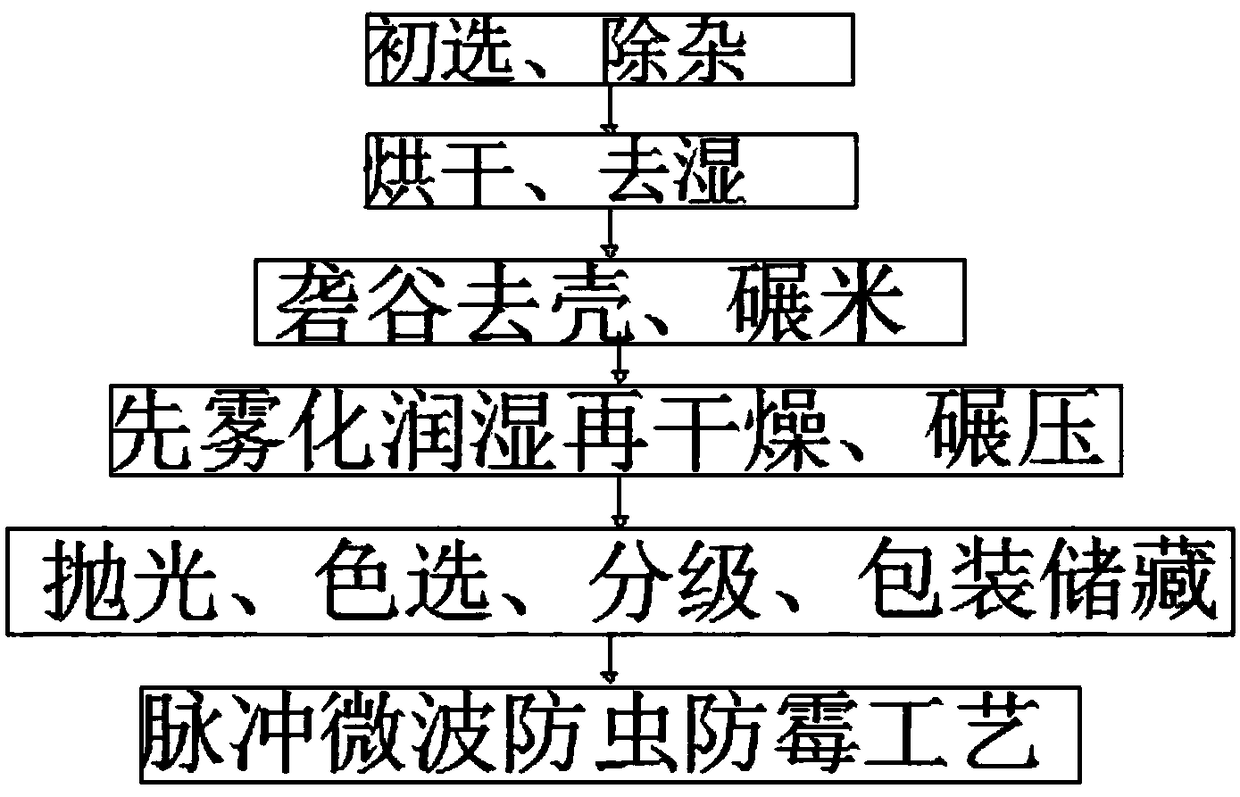
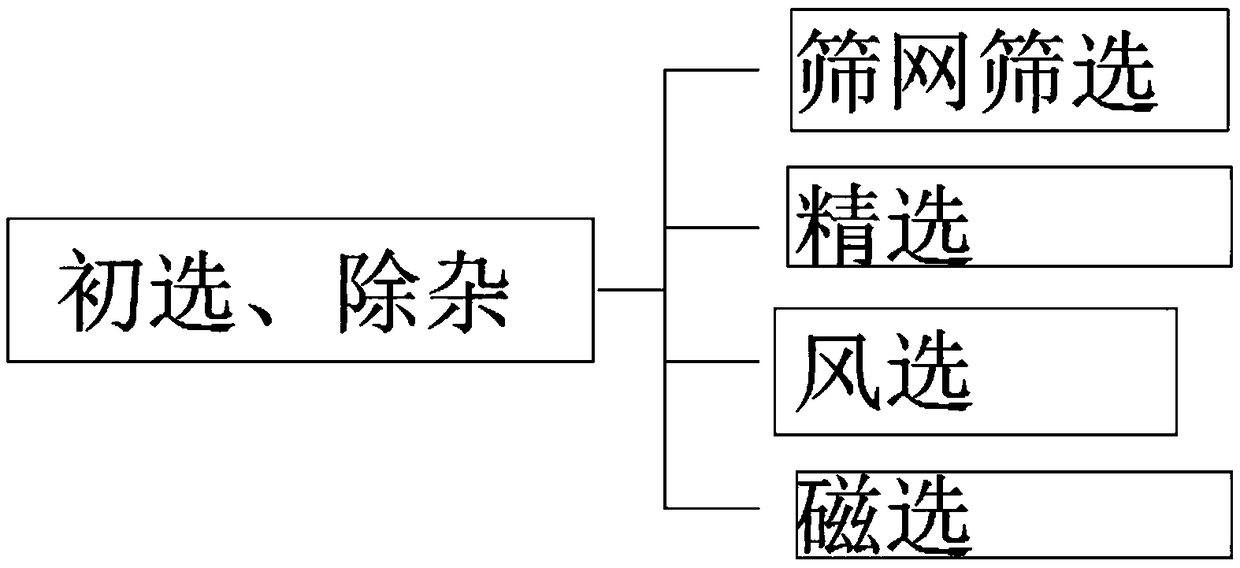
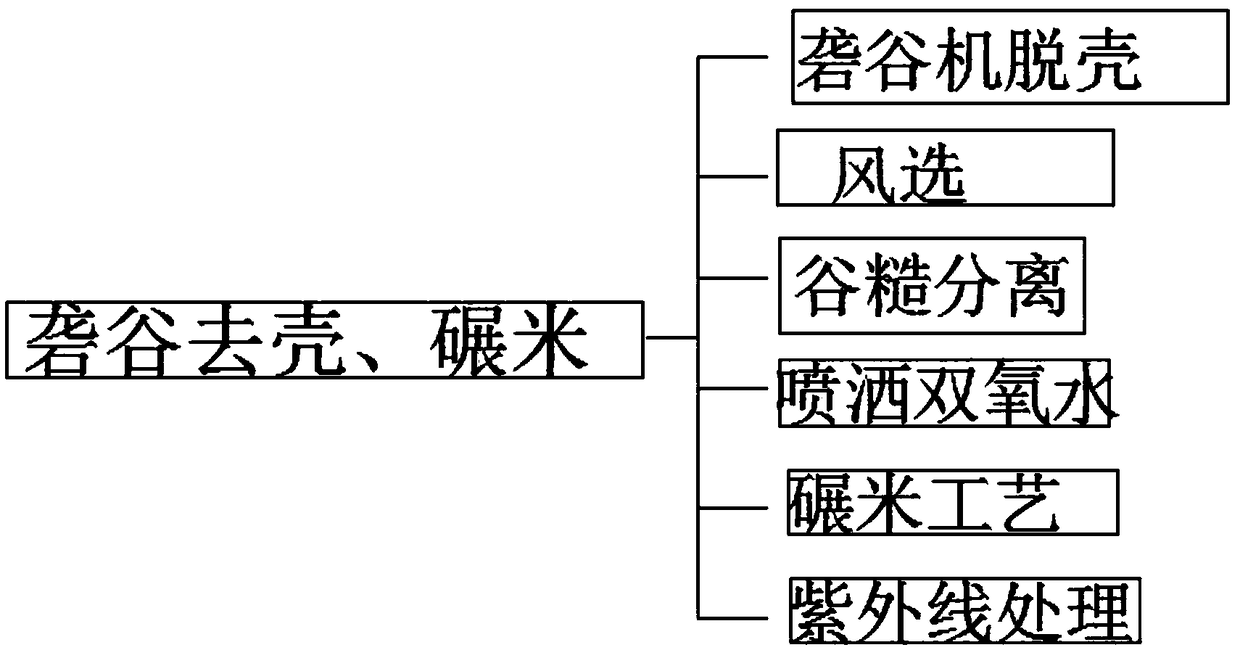
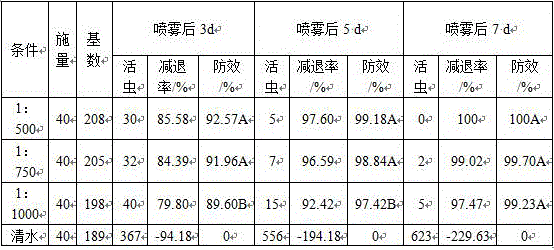
The invention discloses a rice processing method with essential oil mist spraying and pulse microwave action. The rice processing method comprises the following steps of preliminary screening, impurity removal, drying, dehumidification, husking shelling, rice milling, atomization and wetting and then drying, milling, polishing, color sorting, grading, packaging and storage and a pulse microwave anti-insect and anti-mould process, specifically, harvested rice is screened, firstly, a screening machine with appropriate sieve meshes is selected for screening out impurities with a different size from grains according to the different widths and thicknesses of rice and the impurities, then fine selection is performed, the rice is separated from the impurities according to the difference in lengths of the rice and the impurities, then air separation is continued to be performed, and the light impurities (such as chaff, rice straws and false grains) are taken away by wind force to be separatedfrom the rice in ascending or horizontal airflow. The rice processing method has good antibacterial and delay aging effects, can inhibit generation of colonies and formation of fatty acids in the rice and has a high fatality rate to pests and aspergillus parasiticus, and pulse microwave treatment reduces the hatching rate of pest eggs and reduces the viability of the pests.
Owner:江苏育龙粮油有限公司
Antifungal peptide and application thereof to inhibition of generation of aflatoxin
ActiveCN104059129AFlexible applicationInhibitionFood preservationPeptidesAspergillus parasiticusBiology
The invention provides an antifungal peptide and an application thereof to inhibition of generation of aflatoxin. The antifungal peptide has the amino acid sequence as follows: Ala-Asp-Leu-Pro-Val-Lys-Ser-Gly-Asp-Thr-Pro-Glu. The antifungal peptide provided by the invention is capable of effectively inhibiting the growth of aspergillus flavus and aspergillus parasiticus and the generation of aflatoxin, favorable and durable in inhibiting effect and suitable for large-scale production and application.
Owner:BEIJING YUANSHENGYUAN SCI & TECH DEV
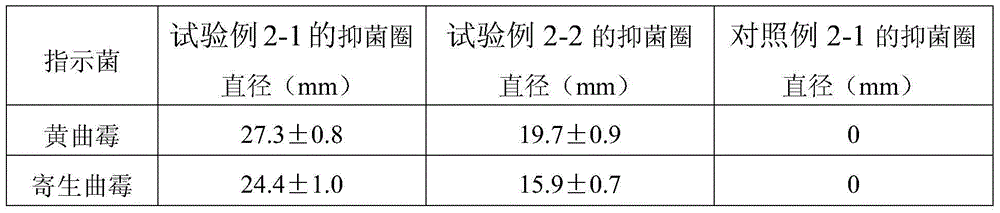
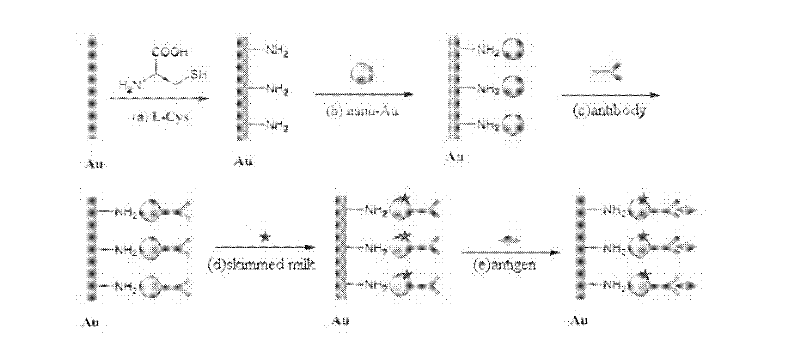
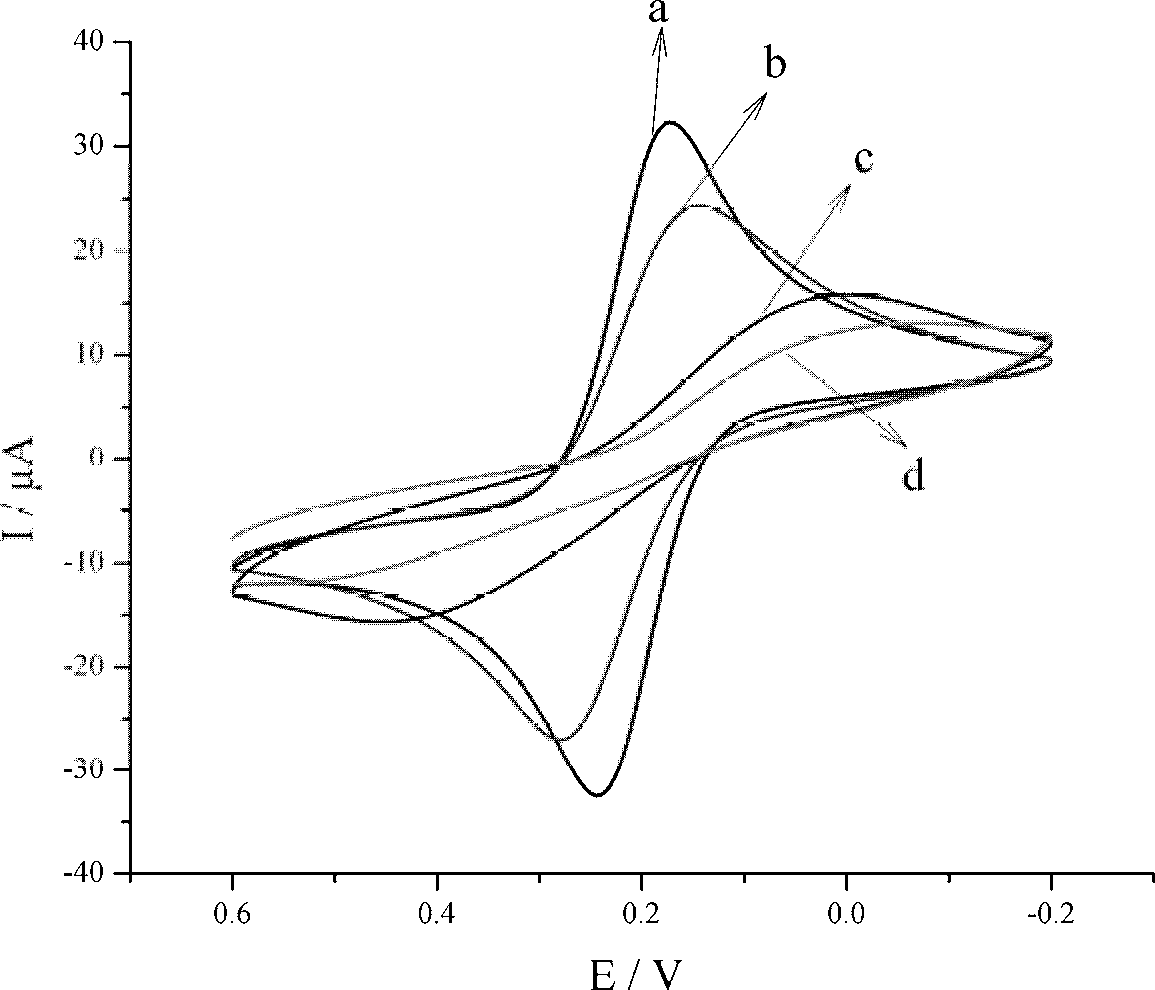
Immunosensor for detecting aspergillus parasiticus used for producing aflatoxin and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN102520168AFacilitates electron transferHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemistryChemical amplification
The invention discloses an immunosensor for detecting aspergillus parasiticus used for producing aflatoxin and a preparing method thereof. The immunosensor is obtained by the following step that: nano-Au, L- cysteine and aspergillus parasiticus polyoxin are self-assembled and modified on a gold electrode. According to the invention, the chemical amplification of the nano-Au and the specificity of the immunosensor are combined, and the advantages of the nano-Au and the immunosensor are also merged, so that the immunosensor simultaneously has the specificity of immune reaction and the quickness and sensitivity of electrochemistry analysis, and can accurately detect the low-content aspergillus parasiticus used for producing the aflatoxin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for preparing epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside and special strain used thereby
InactiveCN101603011AProtect ecological diversityEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyOperability
The invention discloses a method for preparing epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside and a special strain used thereby. The strain is aspergillus parasiticus TEQB with a preservation number of CGMCC No.3116. The strain of the invention can be used for preparing the epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside. The method for preparing the epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside in the invention has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, easy operation and short production period. The method of the invention provides a new way of preparing the epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside, avoids the limitations of other preparation methods in the prior art, has strong operability, is suitable for industrial large-scale production and has a great significant for the protection of the ecological diversity of plants at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Aspergillus parasiticus and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides aspergillus parasiticus which is Aspergillus parasiticus RWSF001-02 which is preserved in Guandong Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preservation number being GDMCC NO: 60080. The aspergillus parasiticus is screened from naturally dead aphids as a result of fungal parasitism. The aspergillus parasiticus and conidial powder containing the aspergillus parasiticus can be used for preparing an insecticide, and particularly has a relatively high preventing and treating rate on aphids, and the strain is good in production trait and fast to grow. The sporulation quantity of culture in a solid culture medium within 3-5 days can reach 8*10<8> / g.
Owner:鹤壁市人元生物技术发展有限公司
Classification and identification upon 12 fungi by using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic technology
InactiveCN103217399APreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsMetrologyFourier transform
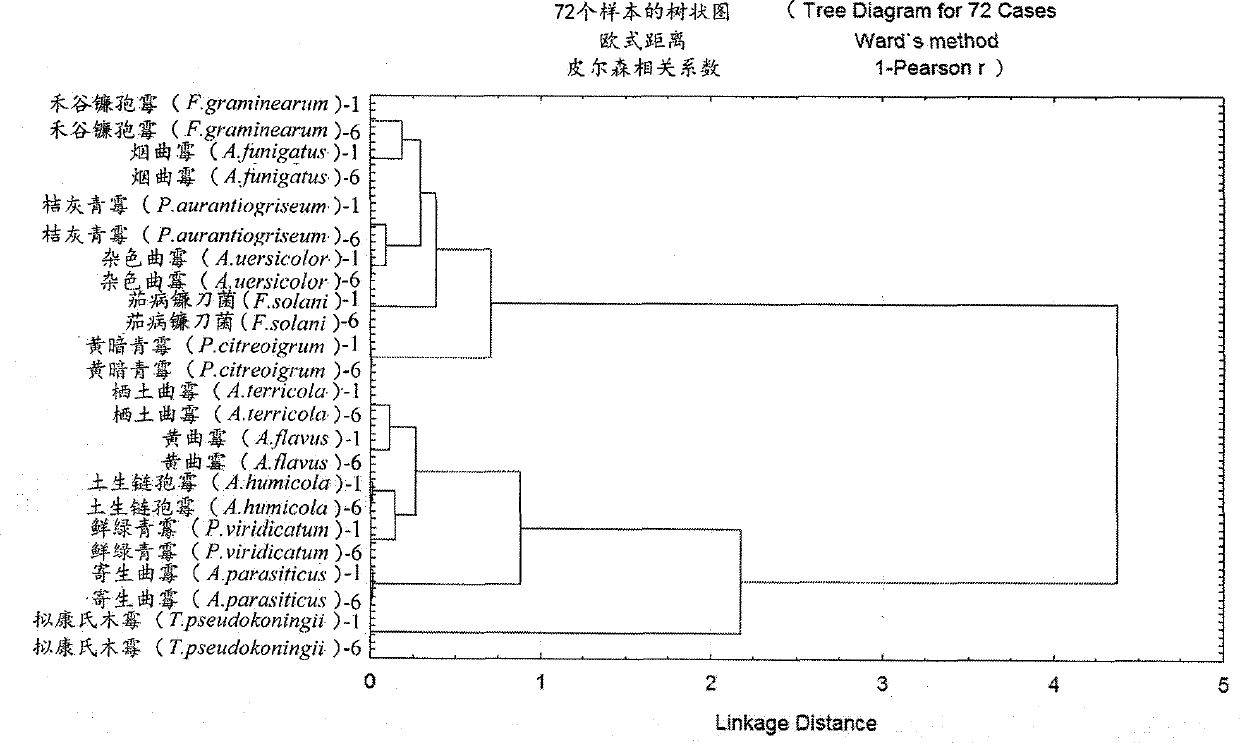
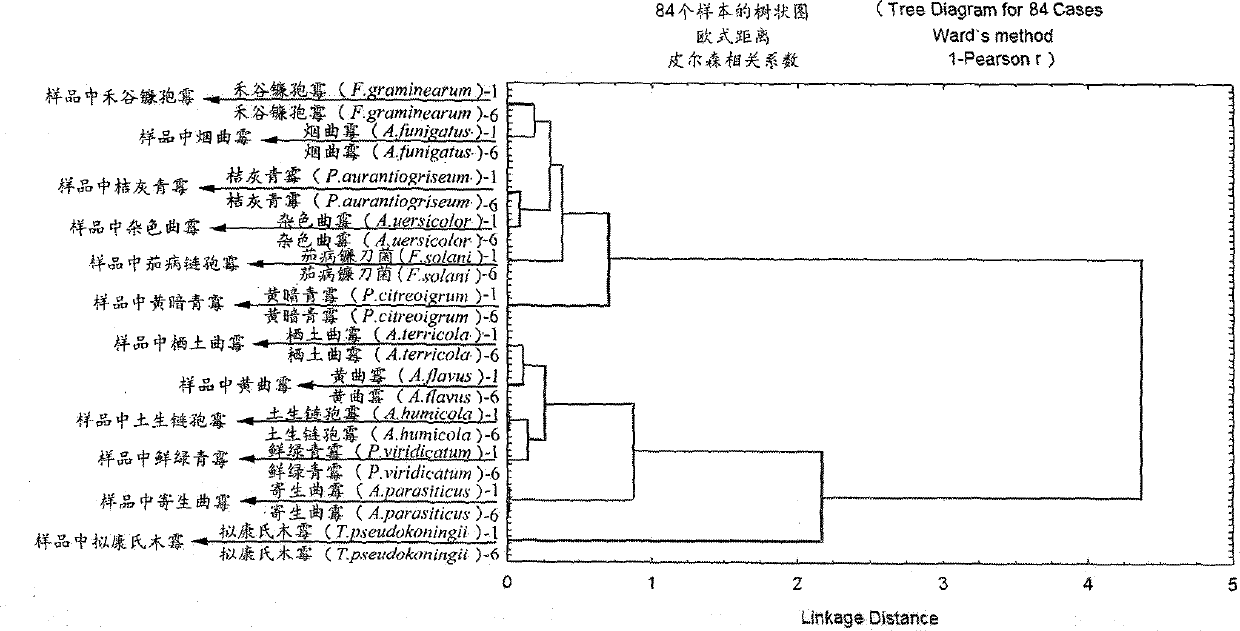
The invention belongs to a classification and identification method upon 12 common fungi, and specifically relates to a method for carrying out classification and identification upon 12 common fungi such as F.graminearum, A.terricola, P.citreonigrum, A.flavus, A.parasiticus, P.aurantiogriseum, T.pseudokoningii, A.humicola, P.viridicatum, A.funigatus, A.uersicolor, and F.solani by using a Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic (FTIR) technology combined with chemometric operation (hierarchical cluster analysis). The method comprises the steps of the establishment of a FTIR spectra information database of the 12 fungi, fungi culturing, ZnSe window manufacturing, spectral acquisition and preprocessing, and result determination by hierarchical cluster analysis. The method has the advantages of high resolution, high speed, simple operation, and low cost.
Owner:威海出入境检验检疫局检验检疫技术中心
Pu'er tea leaf endophytic bacillus and application thereof
ActiveCN111019866AMild conditionsEasy to controlBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
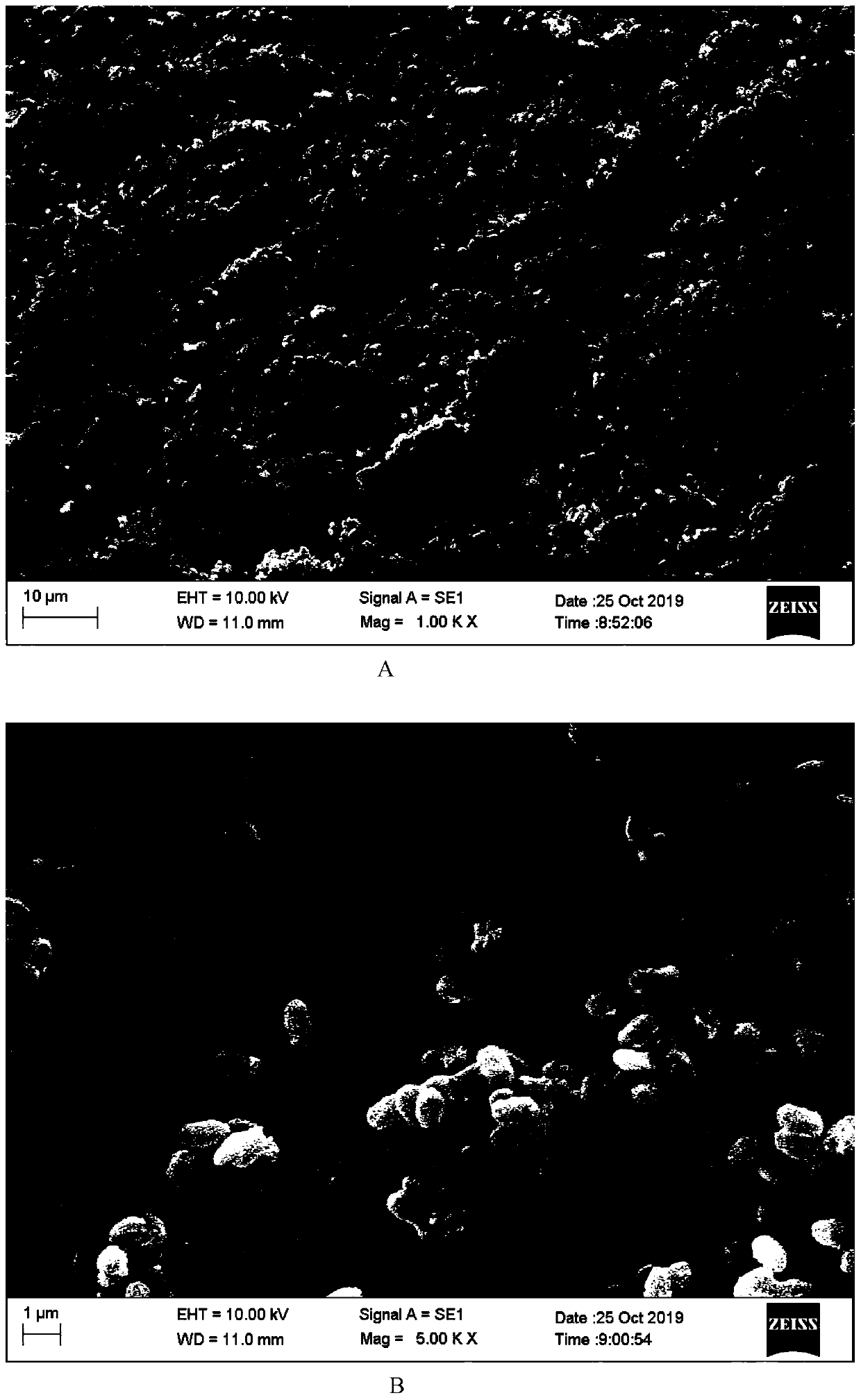
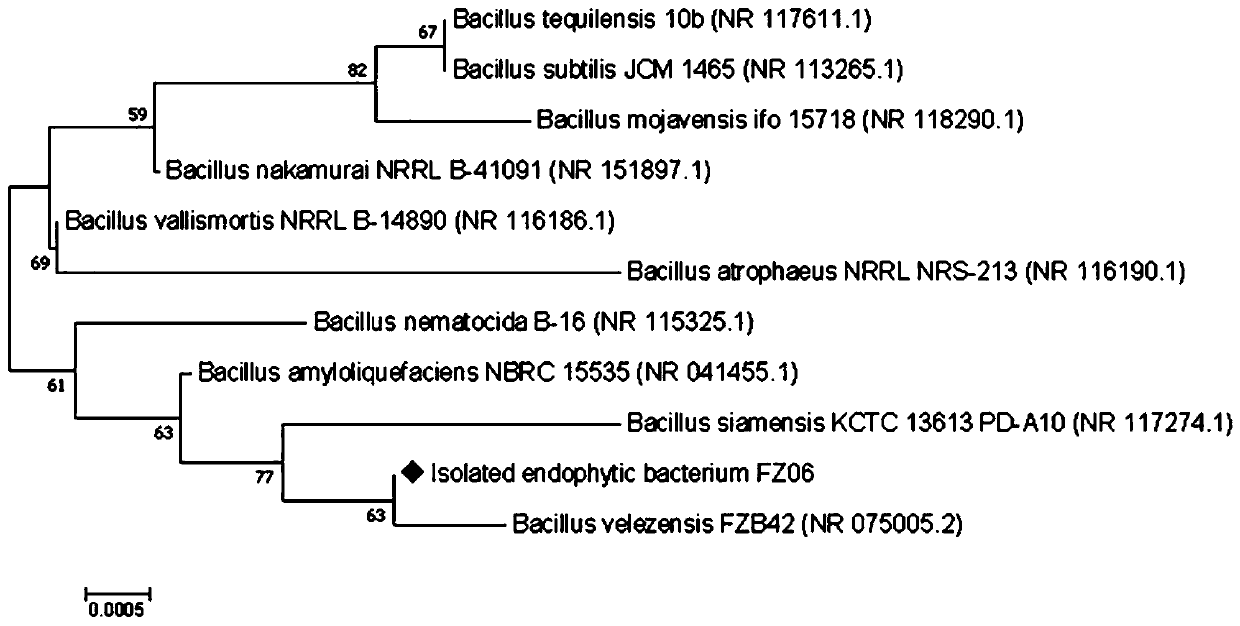
The invention discloses Pu'er tea leaf endophytic bacillus and application thereof. The name of the Pu'er tea leaf endophytic bacillus is FZ06 (Bacillus velezensis FZ06). The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University in Wuhan of China on October 25th, 2019, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2019854. Lipopeptide substances which can be produced bythe Bacillus velezensis FZ06 comprise 27 kinds of three categories, and the richness of the lipopeptide substances is higher than that of currently reported bacillus velezensis; the generated lipopeptide substances have obvious inhibitory activity on pathogenic bacteria such as escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella, aspergillus flavus and aspergillus parasiticus, and can be well applied to inhibition of the pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A kind of separation method for l-malic acid
ActiveCN108300739BIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation, and discloses a method for separating L-malic acid, which comprises the following steps: step 1) preparing Aspergillus oryzae seed liquid, step 2) preparing Aspergillus parasiticus seed liquid, step 3) fermenting, Step 4) Centrifugation, filtration and ion exchange. The invention has the advantages of high product yield and purity for separating L-malic acid from the fermentation liquid, simple operation process, low production cost and large-scale production.
Owner:SHANDONG FUFENG FERMENTATION CO LTD
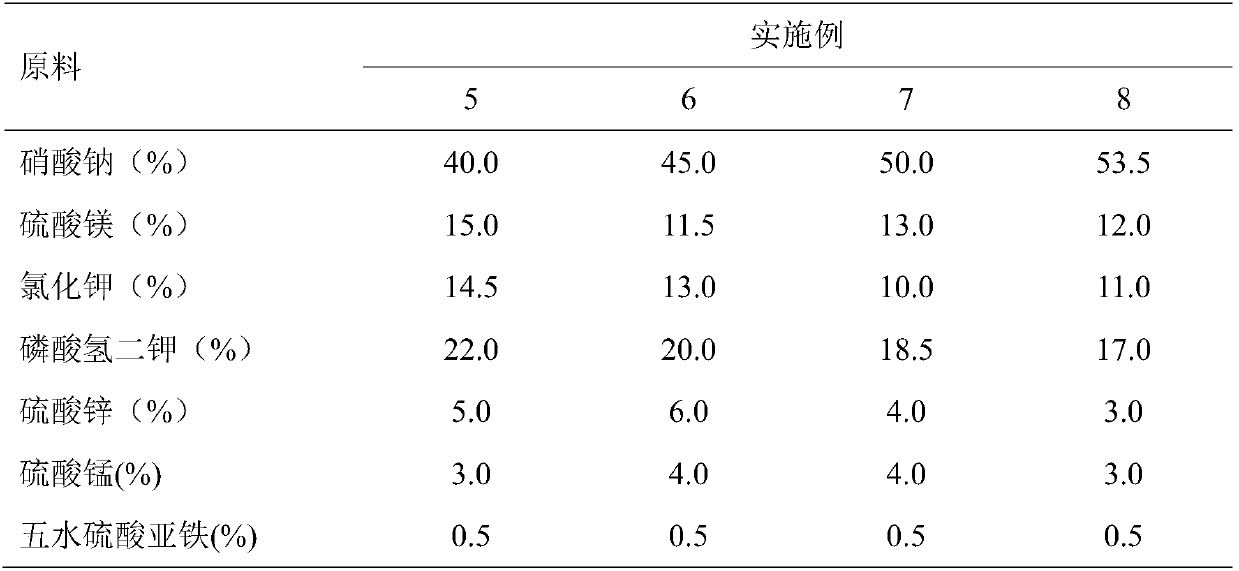
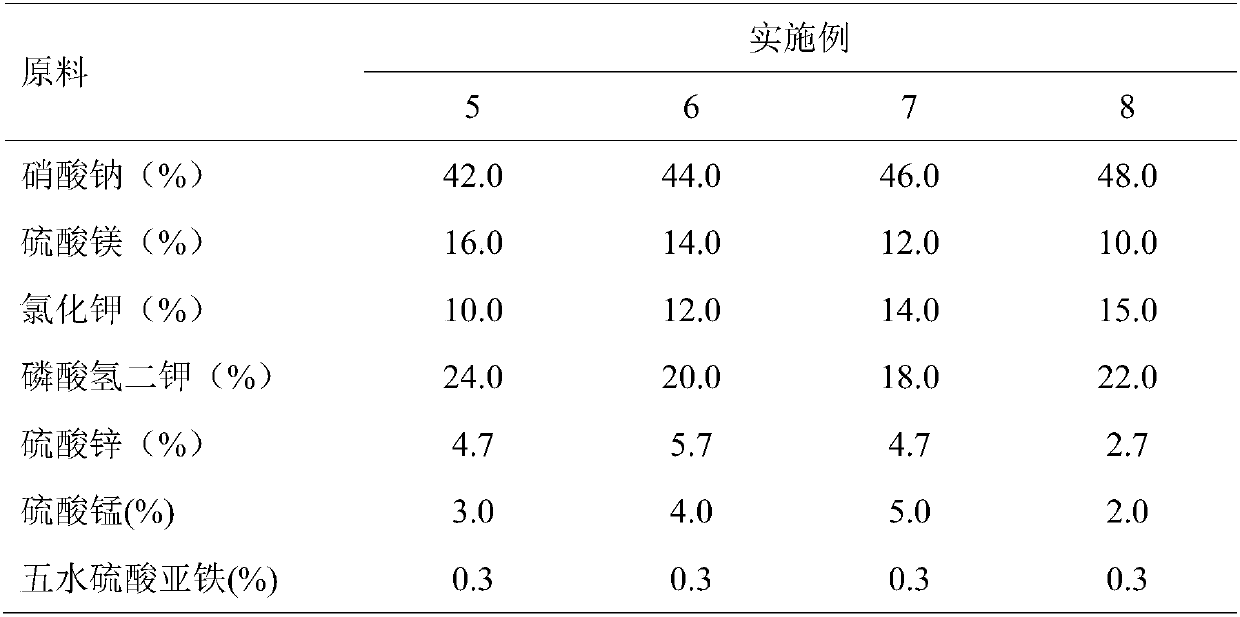
Serratia plymithica synthetic culture medium and method for preparing fermentation liquid of serratia plymithica synthetic culture medium
InactiveCN102634473AInhibition of Growth RequirementsReasonable collocationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSerratiaDipotassium phosphate
The invention relates to a serratia plymithica synthetic culture medium and a method for preparing fermentation liquid of the serratia plymithica synthetic culture medium. The formula (gram / liter) of the culture medium comprises the following components of 2 to 10 of colloidalchitin, 3 to 10 of beef extract, 5 to 15 of peptone, 6 to 10 of sodium chloride, 1 to 5 of ammonium sulfate, 1 to 3 of sodium citrate, 1 to 5 of dipotassium phosphate, 0.5 to 3 of magnesium sulfate and 0.01 to 0.05 of ferrous sulfate. The serratia plymithica high-yield fermentation liquid for producing a large quantity of active substances and chitinase which are used for suppressing aflatoxin can be obtained by continuously culturing on a table concentrator at the temperature within 28 and 35 DEG C and the speed of 140 r / min for 4 to 6 days according to the inoculation quantity within 1 to 10 percent. The activity of the chitinase in fermentation supernate is 2.04 to 5.36U / ml; the rate of suppressing the growth of parasitic aspergillus silk is 80.13 to 89.56 percent; and the rate of suppressing the aflatoxin is 90.22 to 98.31 percent. The culture medium is rational in component, and the preparation method is simple and reliable.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Method for synchronously extracting peanut oil and performing high-value utilization to cakes
InactiveCN104543373ARealize high-value utilizationPrevent pests and diseasesAnimal feeding stuffEdible oils/fatsRadix Astragali seu HedysariFermentation
The invention relates to a method for synchronously extracting peanut oil and performing high-value utilization to cakes, belonging to the field of deep processing and high-value utilization of peanuts. The processing method comprises the following steps: by taking high-quality peanuts as raw materials, performing high-temperature hot pressing, extracting with edible alcohol, filtering and evaporating, soaking Chinese herbal medicines, performing microbial fermentation, grinding, homogenizing, spray-drying and the like. According to the method, in the step of soaking the Chinese herbal medicines, herba portulacae, herba houttuyniae, fresh rhizoma phragmiti, skullcap, radix astragali seu hedysari, radix glycyrrhizae, acorus calamus and the like are added, and aspergillus parasiticus, aspergillus oryzae, saccharomyces cerevisiae and bacillus are adopted during microbial fermentation. Oil processed by utilizing the method is produced and eaten safely, the price of the peanut cakes is high, the protein solubility is good, the absorption utilization degree is high, the high-nutrition peanut hot-pressed cakes can effectively prevent various bred pest and disease damage as a feed, the cultured animals grow fast, the economic and social benefits are significant, and the high-value utilization of the peanut hot-pressed cakes can be realized.
Owner:青岛天祥食品集团有限公司
A method for producing malic acid by fermenting wheat bran hydrolysis sugar
InactiveCN103789359BIncrease hydrolysis rateQuick responseMicroorganism based processesFermentationLiquid glucoseHydrolysate
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Separation method for L-malic acid
ActiveCN108300739AIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismFiltration
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation, and discloses a separation method for L-malic acid. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparation of an Aspergillus oryzae seed liquid; 2) preparation of an Aspergillus parasiticus seed liquid; 3) fermentation; and 4) centrifugation, filtration and ion exchange. The L-malic acid product separated from a fermentationbroth has a high yield and a high purity, and the method has the advantages of simple operation process, low production cost and realization of large-scale production.
Owner:SHANDONG FUFENG FERMENTATION CO LTD
Method for quickly and efficiently identifying aflatoxin producing strain
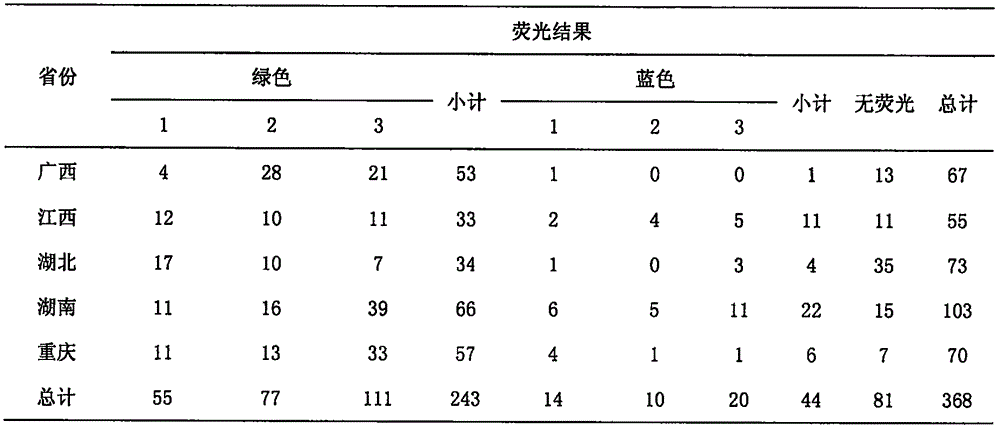
PendingCN106434836AFast identificationEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceBiology
The invention relates to an identification method and particularly relates to a method for quickly and efficiently identifying an aflatoxin producing strain. In gradient dilution screening, the asperigillus flavus and asperillus parasiticus in a sample are directly applied to a selective aspergillin agar base (AFPA) medium; according to the characteristic that the asperigillus flavus and asperillus parasiticus show bright orange color on the APFA medium, the asperigillus flavus and asperillus parasiticus can be separated from other fungi based on once separation culture; and then the type and content are identified with fluorescence. By adopting the method for identification, the process is simple, the identification is quick, and the specificity is very strong.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Aspergillus parasiticus and applications thereof in preparation of nitrite reductase, nitrite reductase gene and genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN104312925AReduce energy consumptionPromote degradationFungiMicroorganism based processesNitrite reductaseGenetically engineered
Aspergillus parasiticus and applications thereof in preparation of nitrite reductase, a nitrite reductase gene and a genetically engineered bacterium containing the nitrite reductase are disclosed. The accession number of the aspergillus parasiticus is CCTCC M2013662. The aspergillus parasiticus has characteristics of high efficiency, low energy consumption, good nitrite degradation effects, and rapid and reliable degradation is provided, and can be well applied in preparation of the nitrite reductase, preparation of the nitrite reductase gene and preparation of the genetically engineered bacterium containing the nitrite reductase.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
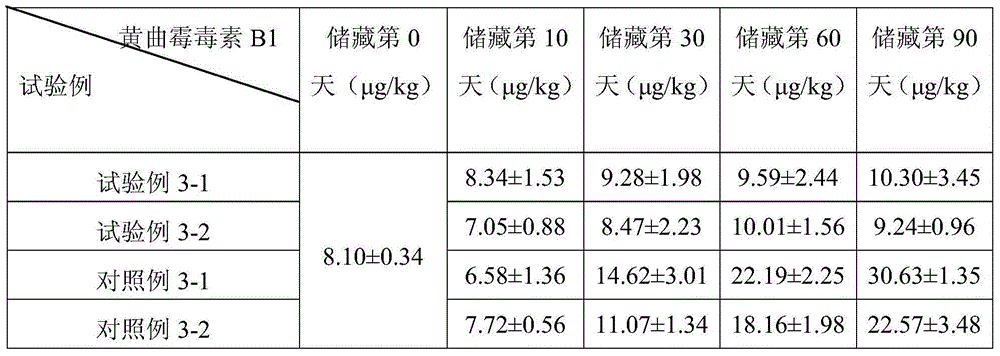
AFG1 (Aflatoxin G1) toxin-producing fermentation method of aspergillus parasiticus
ActiveCN107586799ASignificant progressImprove filtration efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationSporeMildew
The invention belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering and in particular relates to an AFG1 (Aflatoxin G1) toxin-producing fermentation method of aspergillus parasiticus. The AFG1 toxin-producing fermentation method of the aspergillus parasiticus comprises the following steps: a, carrying out reviving proliferation on aspergillus parasiticus spores by adopting an enrichment culture medium; b, carrying out solid fermentation culture by adopting a solid fermentation culture medium, wherein components of each of the enrichment culture medium and the solid fermentation culture medium contain yeast extract which accounts for 1 percent to 3 percent of the total amount of the culture medium. According to the AFG1 toxin-producing fermentation method provided by the invention, theproblems that AFG1 in grains which are naturally infected with mildew at present is low and not uniform and long time is consumed and the like are solved.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Immunosensor for detecting aspergillus parasiticus used for producing aflatoxin and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN102520168BFacilitates electron transferHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemistryChemical amplification
The invention discloses an immunosensor for detecting aspergillus parasiticus used for producing aflatoxin and a preparing method thereof. The immunosensor is obtained by the following step that: nano-Au, L- cysteine and aspergillus parasiticus polyoxin are self-assembled and modified on a gold electrode. According to the invention, the chemical amplification of the nano-Au and the specificity of the immunosensor are combined, and the advantages of the nano-Au and the immunosensor are also merged, so that the immunosensor simultaneously has the specificity of immune reaction and the quickness and sensitivity of electrochemistry analysis, and can accurately detect the low-content aspergillus parasiticus used for producing the aflatoxin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Fermented pig feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106615780AEasy to eatImprove palatabilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologySpore germination
The invention discloses a fermented pig feed and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing taken 10-20 parts by mass of corn flour, 10-20 parts by mass of wild jujube and 0.1-2 parts by mass of microorganism starter culture to obtain a mixture I, wherein the microorganism starter culture comprises lactic acid bacteria, saccharomycetes and bacillus; adding taken 50-200 parts by mass of sweet potato stems and leaves to the mixture I and mixing to obtain a mixture II; and putting the mixture II into a closed container and carrying out airtight fermentation for 2-6 days to obtain a fermented feed. Firstly, the fermented feed product has an acid fragrance, feeding of a pig can be stimulated and the feed intake is greatly improved; secondly, the digestion and absorption rate of the fermented feed is high, the nutrient value is high, and the digestion and absorption function of the pig can be improved after beneficial viable organisms contained in the fermented feed enter intestinal tracts of the pig; thirdly, growth and toxin production of mycete can be inhibited by the lactic acid bacteria and spore germination of aspergillus parasiticus can be inhibited by lactobacillus acidophilus; and fourthly, growth of the pig can be facilitated by the fermented feed.
Owner:湖南猪八戒生态农业科技开发有限公司
Transeliminase encoding gene and enzyme and preparation and application
InactiveCN111254154AEfficient degradationHigh activityFermentationGenetic engineeringHeterologousPentagalacturonic acid
The invention discloses a preparation and application of a transeliminase encoding gene derived from Aspergillus parasiticus, and an enzyme of the transeliminase encoding gene, that is, a gene of transeliminase is cloned to a pichia pastoris expression vector by using a technical method of gene engineering, then a pichia pastoris recombinant strain for heterologous expression of the enzyme can beobtained, the strain is capable of heterologously expressing the prepared transeliminase and efficiently degrading pectin polysaccharides and polygalacturonic acid (PGA). The transeliminase disclosedby the invention can be widely applied to fields such as agriculture, industry, foods, feed additives, medicines and pectin oligosaccharide preparation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Serratia plymithica synthetic culture medium and method for preparing fermentation liquid of serratia plymithica synthetic culture medium
InactiveCN102634473BInhibition of Growth RequirementsReasonable collocationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSerratiaDipotassium phosphate
The invention relates to a serratia plymithica synthetic culture medium and a method for preparing fermentation liquid of the serratia plymithica synthetic culture medium. The formula (gram / liter) of the culture medium comprises the following components of 2 to 10 of colloidalchitin, 3 to 10 of beef extract, 5 to 15 of peptone, 6 to 10 of sodium chloride, 1 to 5 of ammonium sulfate, 1 to 3 of sodium citrate, 1 to 5 of dipotassium phosphate, 0.5 to 3 of magnesium sulfate and 0.01 to 0.05 of ferrous sulfate. The serratia plymithica high-yield fermentation liquid for producing a large quantity of active substances and chitinase which are used for suppressing aflatoxin can be obtained by continuously culturing on a table concentrator at the temperature within 28 and 35 DEG C and the speed of 140 r / min for 4 to 6 days according to the inoculation quantity within 1 to 10 percent. The activity of the chitinase in fermentation supernate is 2.04 to 5.36U / ml; the rate of suppressing the growth of parasitic aspergillus silk is 80.13 to 89.56 percent; and the rate of suppressing the aflatoxin is 90.22 to 98.31 percent. The culture medium is rational in component, and the preparation method is simple and reliable.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
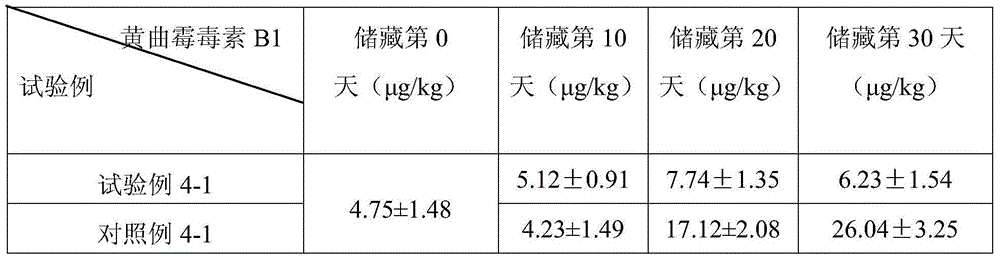
AFG2 toxin production fermentation method of aspergillus parasiticus
ActiveCN107557402ASignificant progressImprove filtration efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySpore
Owner:沭阳康源泰博生物科技有限公司
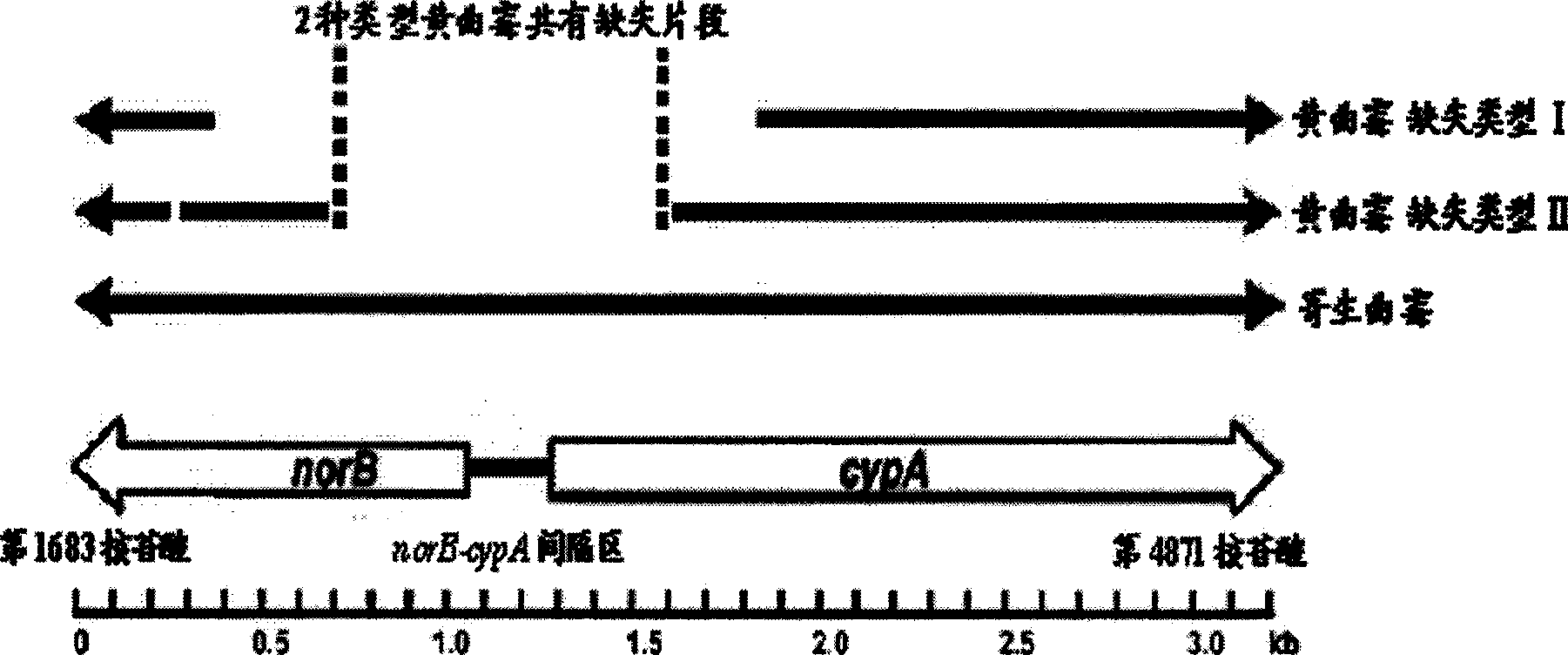
Primer sequence for identifying Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus flavus and identification method thereof
InactiveCN101376911BHigh sequence specificityImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerAspergillus welwitschiae
The invention discloses a primer sequence used to identify Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus flavus; the primer sequence comprises two sets of primers; the forward primer in the first set of primers is provided with the base sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table, and the reverse primer of the first set of primers is provided with the base sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence table;the forward primer in the second set of primers is provided with the base sequence of SEQ ID NO:3 in the sequence table, and the reverse primer of the second set of primers is provided with the base sequence of SEQ ID NO:4 in the sequence table. The primer sequence has high specificity, identities Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus flavus through PCR amplification with high speed and reliability, thereby laying theoretical foundation for researching the soil polluted by aflatoxin or the distribution and dynamic changes of two types of fungi in crops and providing scientific bases for thecontrol of aflatoxin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Easily digestible feed for pigs and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106578503AEasy to eatHas a sour smellFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSnow moldSpore germination
The present invention discloses an easily digestible feed for pigs and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1: 20-50 parts by mass of chicken manure granules are mixed with 0.1-2 parts by mass of a microbial fermentation agent to obtain first mixed materials and the microbial fermentation agent is EM (effective microorganisms); S2: 50-200 parts by mass of sweet potato vine leaves and 20-50 parts by mass of radish leaves are taken to be added into the first mixed materials to be mixed to obtain second mixed materials; and S3: the second mixed materials are subjected to an aerobic fermentation for 5-10 days to obtain the easily digestible feed for the pigs. The easily digestible feed for the pigs has a sour scent, can stimulate the pigs to eat, greatly improves the food intake amount, is high in digestibility and nutritional values, contains beneficial live bacteria, and can improve the digestion and absorption functions of the pigs. Lactic acid bacteria can inhibit the growth and toxin produce of molds, lactobacillus acidophilus can inhibit spore germinations of aspergillus parasiticus, and the easily digestible feed for the pigs can promote pig growth.
Owner:湖南猪八戒生态农业科技开发有限公司
A strain of Aspergillus parasiticus and its preparation method and application
The invention provides a strain of Aspergillus parasiticus, which is Aspergillus parasiticus RWSF001‑02, which is preserved in the "Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center" with a preservation number of GDMCC NO: 60080. The Aspergillus parasitica is selected from aphids that died naturally due to fungal parasitism. The Aspergillus parasitica and the spore powder containing the Aspergillus parasitica spores can be used to prepare insecticides, especially for aphids with a high control rate, and the strain has good production properties and rapid growth. After 5 days, the sporulation amount can reach 8×108 / g.
Owner:鹤壁市人元生物技术发展有限公司
A preparation method and application of a composition for strengthening watercress post-fermentation bacteria
ActiveCN106520583BInhibit metabolismShorten the production cycleFungiMicroorganism based processesSaccharomycesAldehyde
Owner:四川省郫筒酱园有限责任公司
A strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with high fungal inhibitory activity and its application
ActiveCN104988091BInhibition protectionEnhanced inhibitory effectBacteriaFood preservationMetaboliteAntifungal protein
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Primer probe combination and kit for detecting aflatoxin-producing fungi in food
PendingCN113930542AQuick checkNo cross reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideFluorophore
The invention provides a primer probe combination and a kit for detecting aflatoxin-producing fungi in food, the aflatoxin-producing fungi comprise aspergillus flavus and aspergillus parasiticus, the primer probe combination is characterized in that the primer comprises an upstream primer and a downstream primer, the nucleotide sequence of the upstream primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, the sequence of the downstream primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, the probe is shown as SEQ ID NO.3, the 5' end of the probe sequence is modified with a fluorophore, and the 3' end of the probe sequence is modified with a fluorescence quenching group. The fluorophore is FAM, and the fluorescence quenching group is BHQ1. According to the primer probe combination and the kit provided by the invention, the test method is high in specificity, high in sensitivity, rapid and environment-friendly, and is suitable for rapid detection of main toxin-producing fungi in food in basic laboratories.
Owner:GONGBEI CUSTOMS TECH CENT
Toxigenic medium of AFG2, and AFG2 toxigenic fermentation method of Aspergillus parasiticus
ActiveCN104531800AReduce research costsSignificant progressFungiMicroorganism based processesYeast cell extractAspergillus parasiticus
The invention relates to a toxigenic medium of AFG2, and an AFG2 toxigenic fermentation method of Aspergillus parasiticus. The medium contains 3-5wt% of yeast extract, and a fermentation medium comprises an enrichment medium and a solid fermentation medium. The toxigenic medium of AFG2 solves the problems of low concentration of the AFG2 in present cereal naturally infecting molds, non-uniformity and long time.
Owner:南京金桔饲料有限公司
Method for preparing epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside and special bacterial strain thereof
InactiveCN101603011BProtect ecological diversityEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesEpipodophyllotoxin glucosideOperability
The invention discloses a method for preparing epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside and a special bacterial strain thereof. The strain is Aspergillus parasiticus TEQB, and its preservation number is CGMCC No.3116. The bacterial strain of the present invention can be used to prepare epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside. The method for preparing epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside of the present invention has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, easy operation and short production cycle. The method of the present invention provides a new way for preparing epipodophyllotoxin diglucoside, avoids the limitations of other various preparation methods in the prior art, has strong operability, is suitable for industrialized large-scale production, and simultaneously It is of great significance to protect the biodiversity of plants.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
LAMP primer for detecting Asperillus Parasiticus, and kit including primer
InactiveCN105368918AQuick checkSpecific detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLoop-mediated isothermal amplificationOperability
The invention relates to an LAMP primer for detecting Asperillus Parasiticus, and a kit including the primer. The LAMP primer comprises inner primers FIP and BIP, outer primers F3 and B3, and loop primers LF and LB; and the kit comprises the LAMP primer, a Bst DNA polymerase, a reaction buffer solution containing dNTPs, and deionized water. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology is used to rapidly detect Asperillus Parasiticus in the invention, so the Asperillus Parasiticus can be rapidly, accurately and conveniently detected, and the LAMP primer and the kit are of great significance to prevent and detect Asperillus Parasiticus pollution. A detection method also disclosed in the invention has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, lower detection limit reaching 1*10<-12>g / [mu]L, short reaction time, strong operability, no need of expensive apparatuses, convenient product detection, realization through macroscopic observation, and very high practical values.
Owner:黄耀江 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com