Flash memory devices using large electron affinity material for charge trapping
a technology of electron affinity and charge trapping, which is applied in the field of field effect transistors, can solve the problems of difficult scaling down of dram cells, limited data retention capability of dram, and frequent refreshing of dram with attendant power consumption, and achieves high permittivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
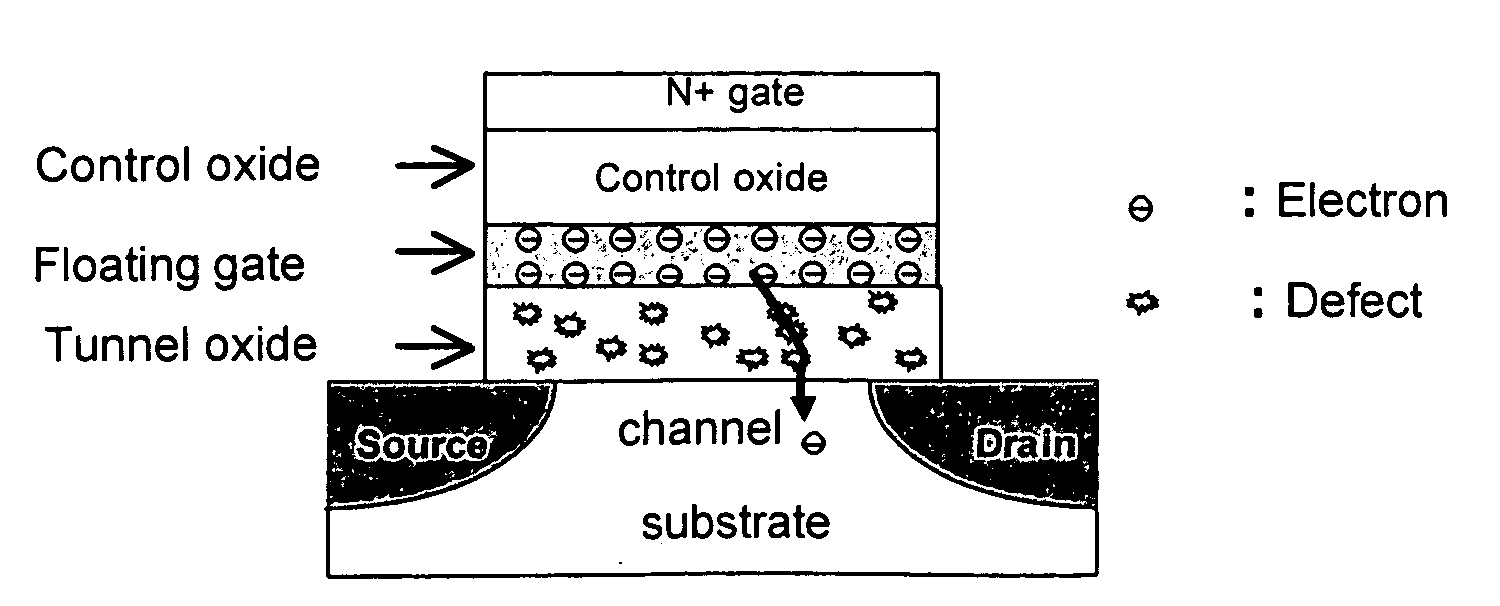
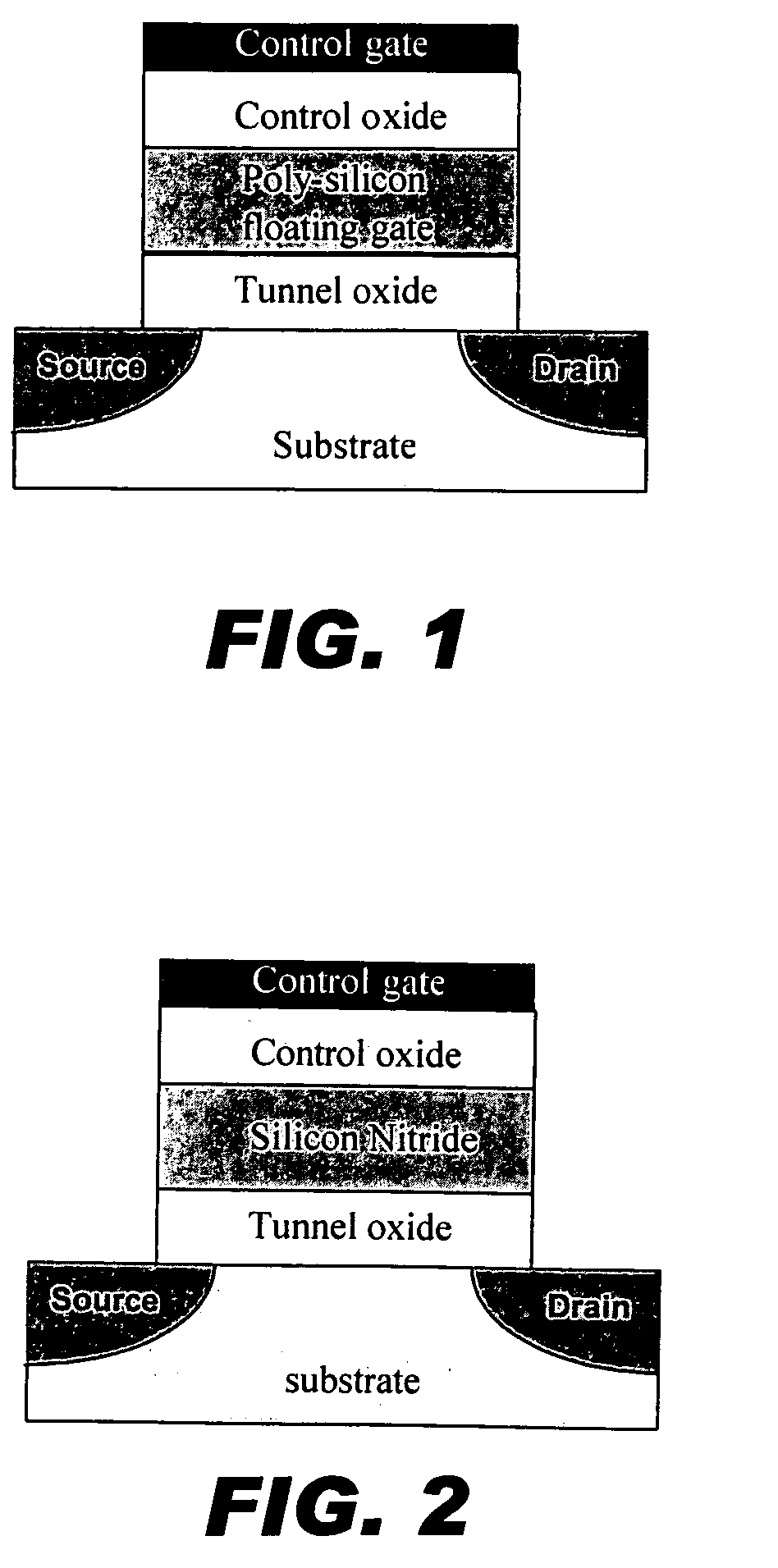
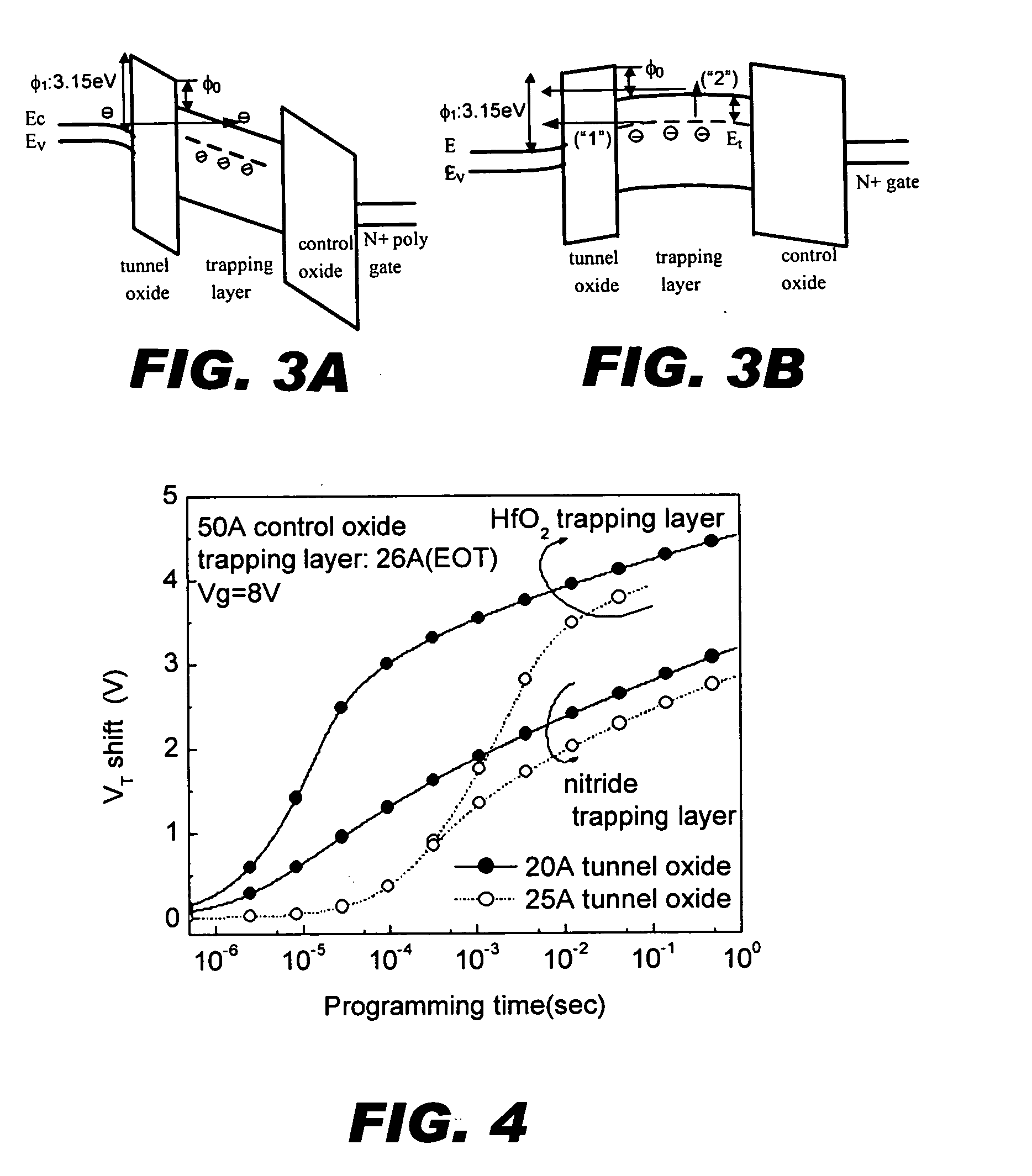
[0023] In order to improve the programming speed and / or lower the programming voltage of a SONOS-type memory device, it is desirable to use an electron-trapping material with a lower conduction band edge (higher electron affinity) to achieve a larger offset φ0, as well as to provide for programming by direct tunneling at low voltages. In accordance with the invention, a high-permittivity (“high-k”) dielectric material such as HfO2 or ZrO2 replace silicon nitride as the electron trapping material. Such materials have a lower conduction band edge than does silicon nitride. A comparison of dielectric material properties is given in Table 3. If HfO2 were to be used as the trapping layer, φ0 would be 1.65 eV, which is much better than the 1.03 eV barrier associated with a nitride-trapping layer. Thus, it is advantageous to use a high-k material as the trapping layer in a SONOS-type memory device, provided that it contains a sufficient density of deep trap states. In principle, the trap d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com