Method of treating atherosclerosis or restenosis using microtube stabilizing agent
a technology of stabilizing agent and atherosclerosis, which is applied in the field of methods, can solve the problems of incalculable cost of human suffering and material resources, death and disability in the developed world, and afflicting the elderly, so as to and prevent or reduce the development of atherosclerosis or restenosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
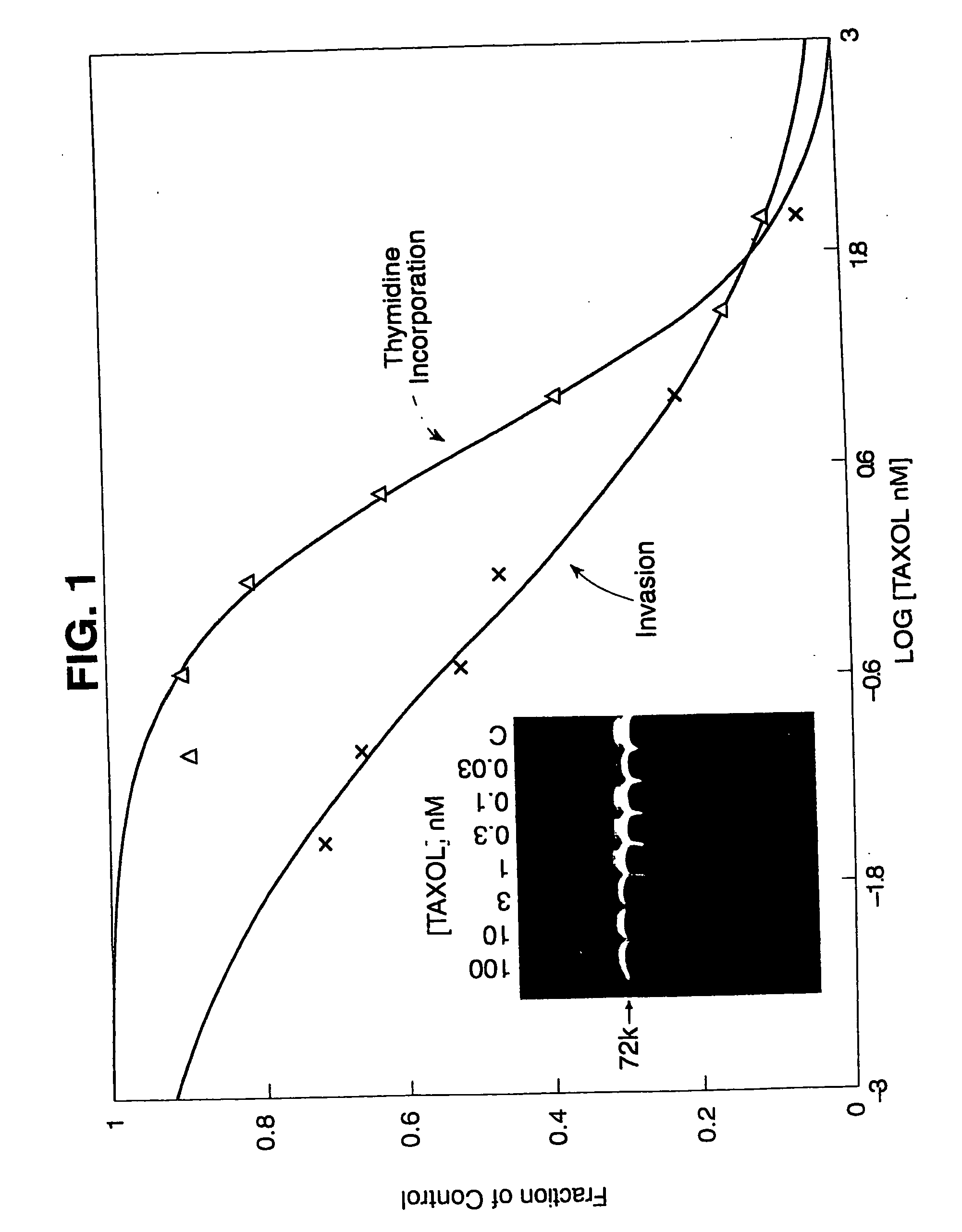
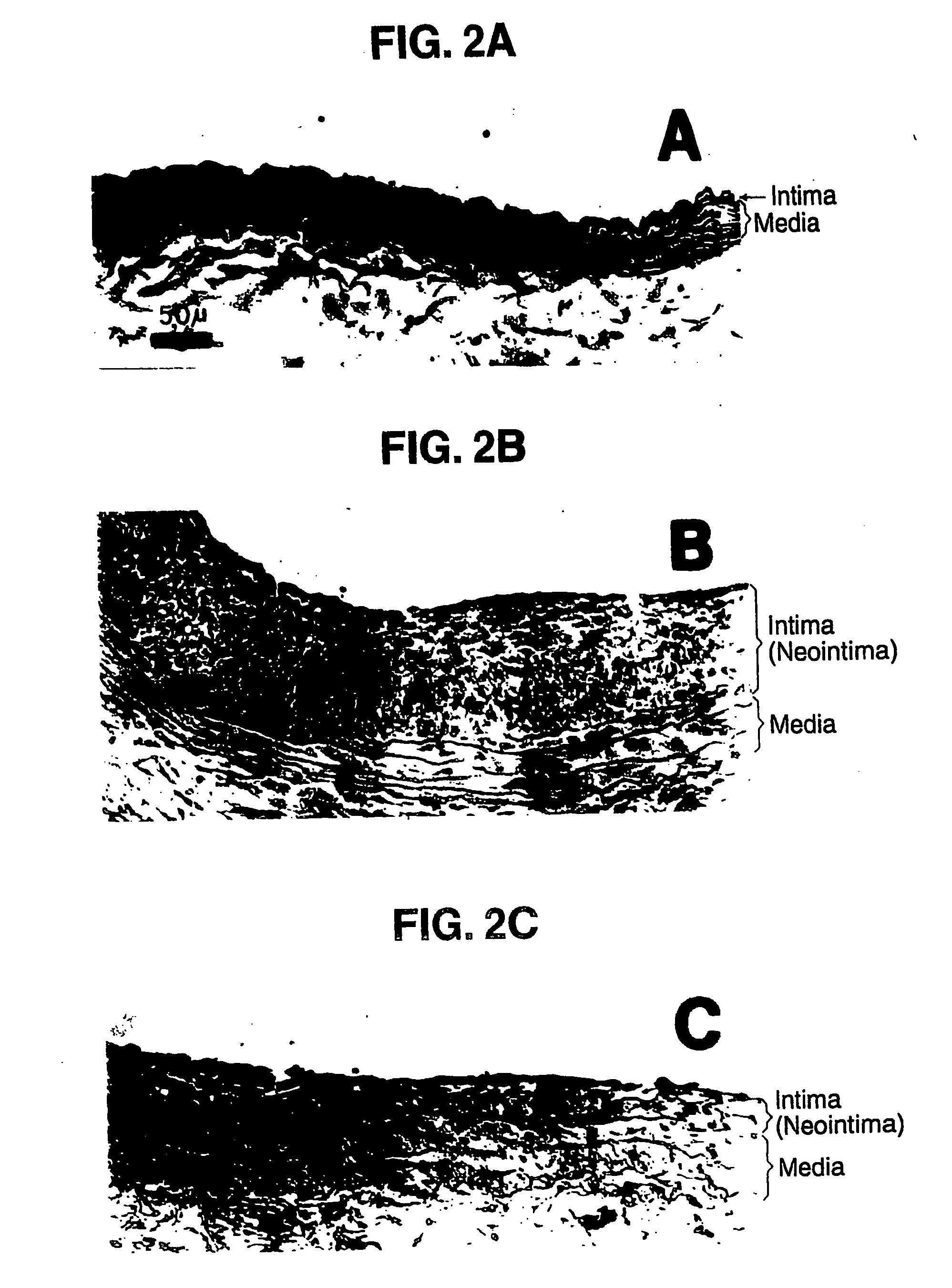
[0034] The in vitro ability of cultured VSMCs, pretreated with different taxol concentrations, to invade filters coated with reconstituted basement membrane proteins was tested to evaluate how taxol-induced microtubule bundling would impair cell processes necessary for in vivo neointimal formation.
[0035] Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMCs) were isolated by collagenase / elastase enzymatic digestion of the medial layers of the rat aorta obtained from 6 month old Wistar rats. The cells were maintained in culture with 10% fetal calf serum, high glucose DMEM, and amino acid supplement. Cell cultures were maintained at 37° C. in 5% CO2.
[0036] After 18-hour taxol pre-treatment in culture, cells were fixed in 3.7% formalin, permeabilized with 1% Triton X-100, and polymered tubulin was labelled with mouse anti-6-tubulin antibody (SMI 62 monoclonal antibody to polymerized 6-tubulin, Paragon Biotec, Inc., Baltimore, Md.). Secondary labelling was achieved with silver-enhanced, 1 nm gold-conju...
example 2
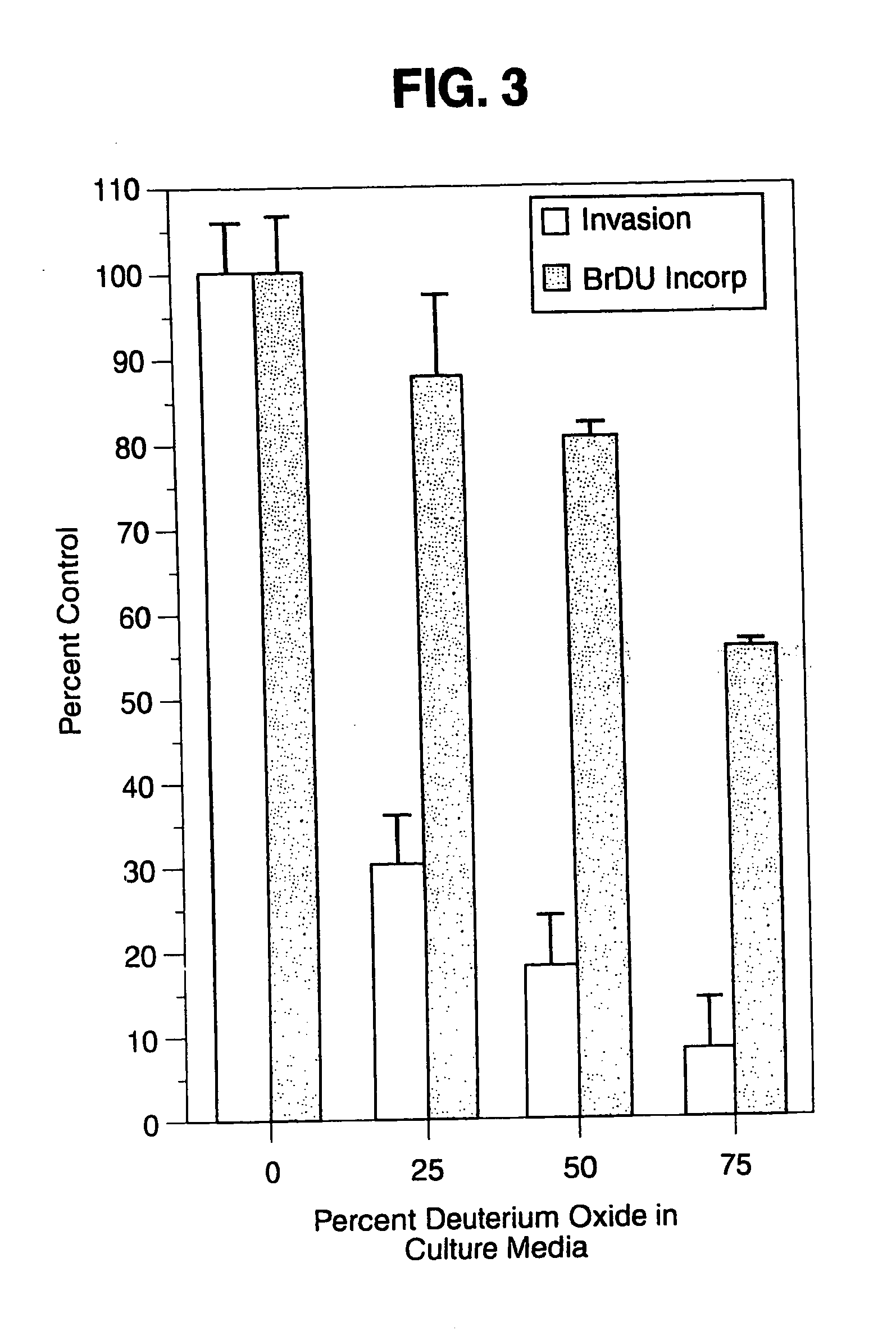
[0041] To confirm the fact that microtubule stabilization and hyperpolymerization is the critical and sufficient factor involved in taxol-inhibition of VSMC invasiveness, the chemoinvasion (Boyden chamber) assay was run with deuterium oxide (2H2O, heavy water). Deuterium oxide enhances microtubule / tubulin polymerization via a mechanism distinct from that of taxol. A combination of the isotope and solvent effects of deuterium oxide reversibly increases microtubule polymerization both by reducing the critical concentration for polymerization for α6-tubulin heterodimers via enhanced tubulin hydrophobic interactions (Itoh, T. J., et al. (1984) Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 800:21-27), and by converting a population of unpolymerizable tubulin to the polymerizable form (Takahashi, T. C., et al. (1984) Cell Struct. Funct., 9:45-52).
[0042] VSMC's were isolated by collagense / elastase enzymatic digestion of the medial layers of the rat aorta obtained from 6 month old Wistar rats. The cells were m...
example 4
[0049] Incorporation of the thymidine analog, bromodeoxyuridine (BrDU) was measured to determine the effect of deuterium oxide on VSMC DNA synthesis. VSMCs were plated at 4.5×104 on 24-well plates. Following 20 hr incubation in 10% FCS+DMEM at various 2H2O concentrations, 10 μM BrDU was added and the incubation continued for an additional 4 hr. Cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and fixed with 100% methanol (−20° C.) for 10 minutes. The cells were incubated for 2 hr with 1N HCl to denature the DNA, and subsequently washed 4 times in PBS. Mouse monoclonal BrDU antibody (Boehringer Mannheim) in 2% BSA-PBS was incubated with cells for 1 hr. After PBS wash, goat anti-mouse antibody conjugated with alkaline phosphatase was added. Cell nuclei containing BrDU substituted for thymidine stained red with alkaline phosphatase substrate, while all other nuclei stained blue. The fraction of BrDU-positive nuclei was compared between control (defined as 100%) and that of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com