Composition for intestinal delivery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
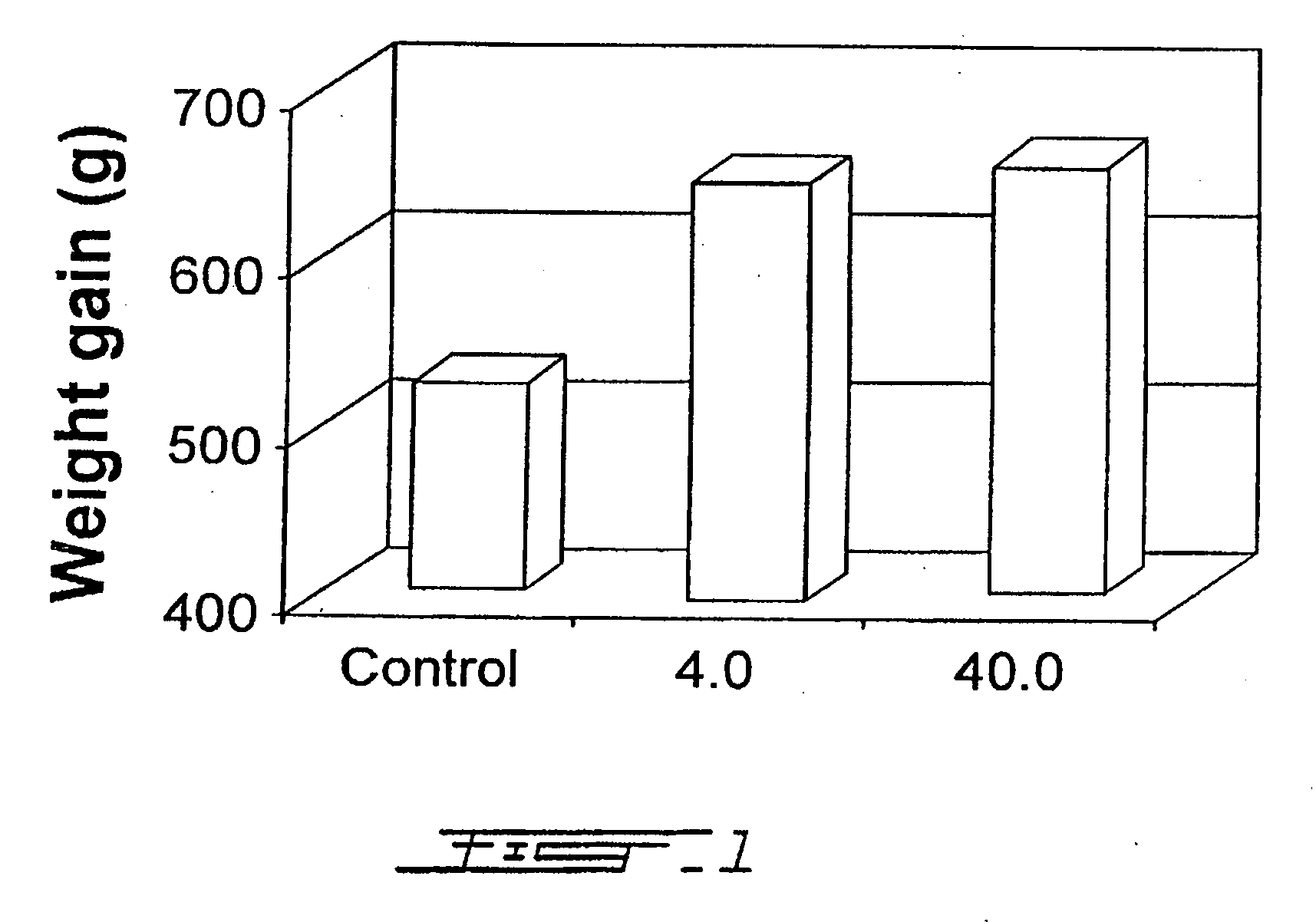
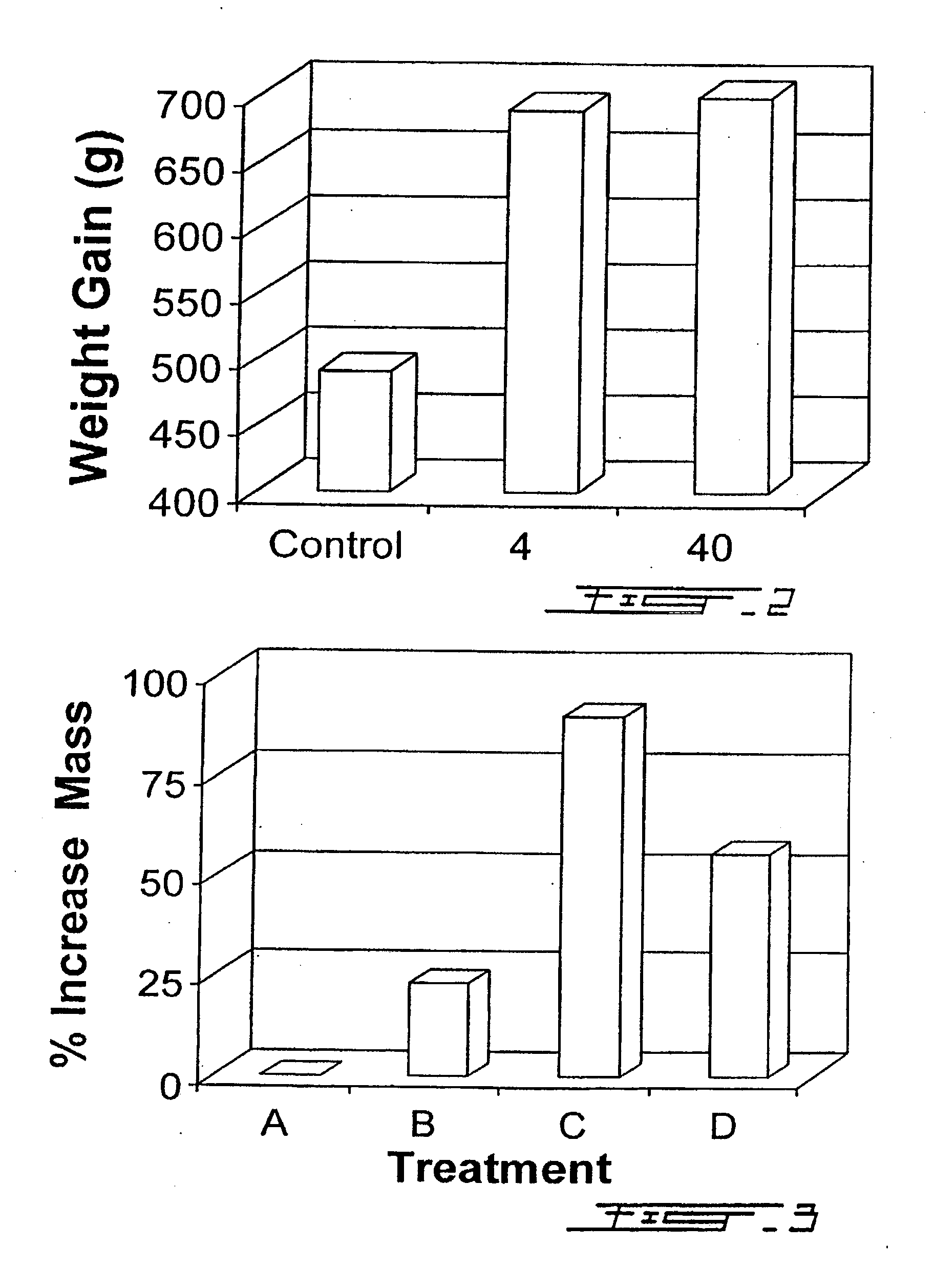
Growth Enhancement of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Brook Trout (Salvelinus fontinalis): Feeding of Recombinant Bovine Growth Hormone Using a Novel Delivery System
[0120] The aquaculture industry worldwide has undergone rapid expansion during the past 2 decades and currently represents the fastest growing agricultural segment. The sector has grown at an annual percentage rate of 10.9 since 1984, compared with 3.1 for terrestrial livestock meat production. The fastest growing livestock sector over the same period was chicken meat production with an APR of 5.3, followed by pig meat 3.4, mutton and lamb 1.4, and beef and veal 09. Aquaculture's contribution toward total world food fish landings has increased more than two fold since 1984 from 11.5% to 25.6% by weight in 1995. Projected increased demand for seafood products, coupled with decreased fisheries landings from wild stocks has, and will continue to contribute to the growth of the aquaculture industry.
[0121] The aquac...
example ii
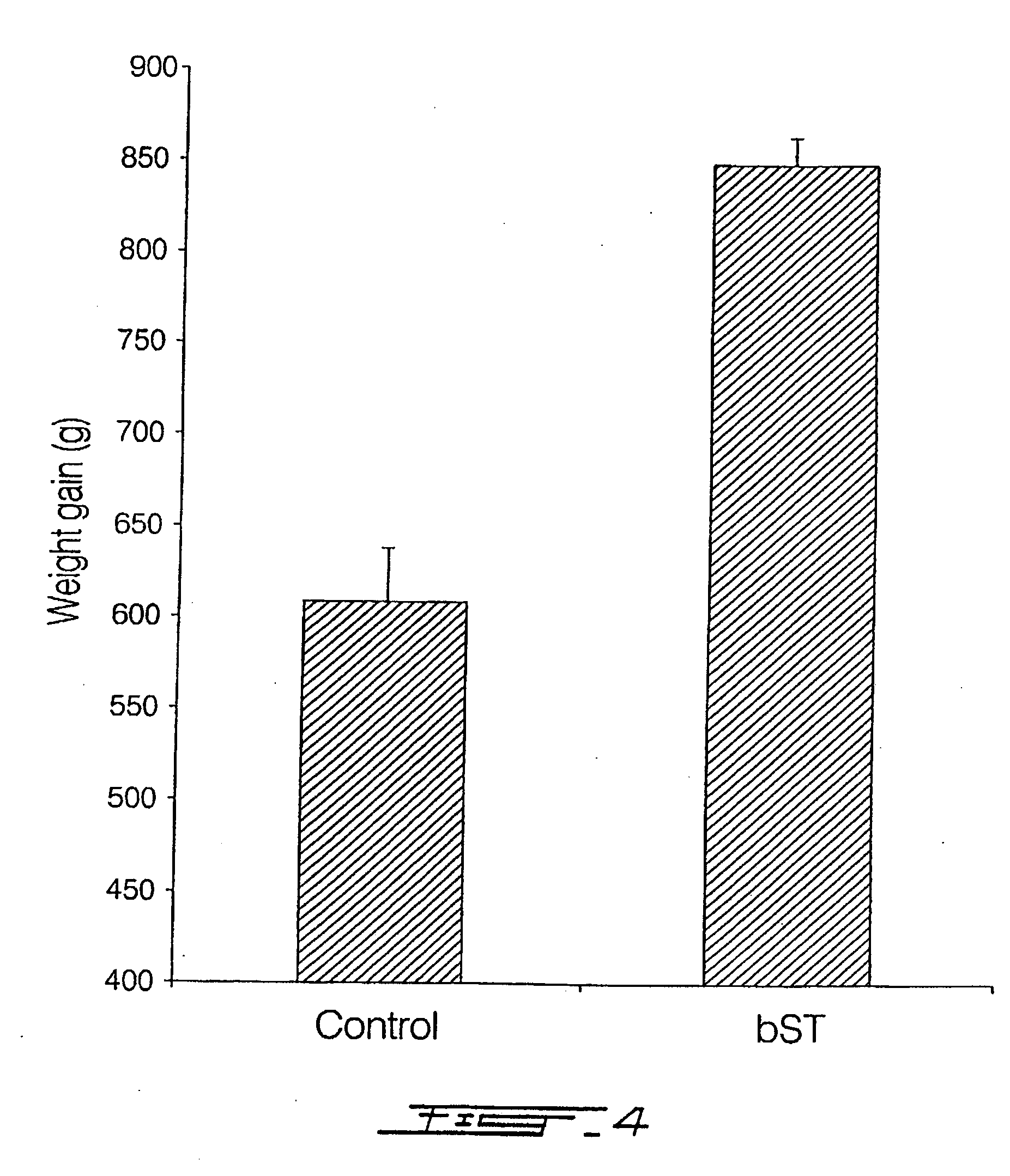
Growth Enhancement of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Intraperitoneal Injection of Recombinant Bovine Growth Hormone
Method
[0136] Intraperitoneal (IP) administration dose per fish weekly was 20 μg bST / g live body weight for 6 weeks.
Results
[0137]FIG. 4 illustrates that recombinant bST injected IP significantly induces increased body weight gain in rainbow trout.
example iii
Assessment of Proteolytic Enzyme Inhibitors Present in Feed Ingredients
Extract Enzymes Protocol
Materials
[0138] 1. Centrifuge Sorvall model [0139] 2. Bench-top blender [0140] 3. Dissecting material (scissors) [0141] 4. Centrifuge bottle [0142] 5. Disposable cuvettes for spectrophotometer [0143] 6. Microcentrifuge tubes 1,5 ml [0144] 7. Spectrophotometer [0145] 8. Vortexer [0146] 9. Microplates reader from Biorad [0147] 10. 50 mM Tris-HCl pH=7.5 [0148] 11. Commassie blue staining solution [0149] 12. BSA (1 mg\ml) standard solution [0150] 13. TCA 20% [0151] 14. Rainbow trouts pancreatic and duodenal tissues [0152] 15. 0.5% casein in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH=9 [0153] 16. 50 mM Tris-HCl+CaCl2 10 mM pH=7.5
Enzyme Extract [0154] 1. Rainbow trout were weighed and sacrificed. [0155] 2. Dissection was performed to remove the proximal small intestine from the fish. [0156] 3. After weighing, the tissues were homogenised in 50 mM Tris-HCl ph=7.5 (1:10 w\v). [0157] 4. Centrifuge at 16000×g for 30 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com