Methods For Preventing, Removing, Reducing, or Disrupting Biofilm
a biofilm and reducing technology, applied in the direction of hollow article cleaning, biological water/sewage treatment, compounding agent, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the life of materials, pathogenic problems in municipal water supplies, food processing, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing, reducing, or disrupting the biofilm on the surfa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
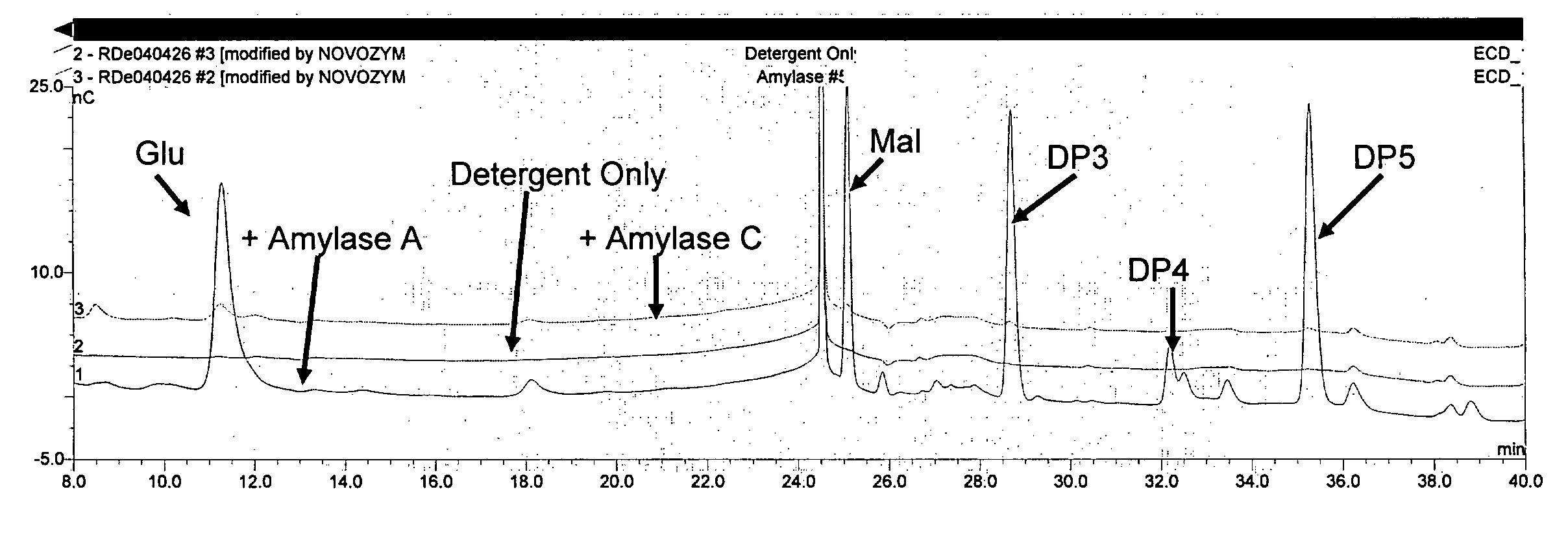
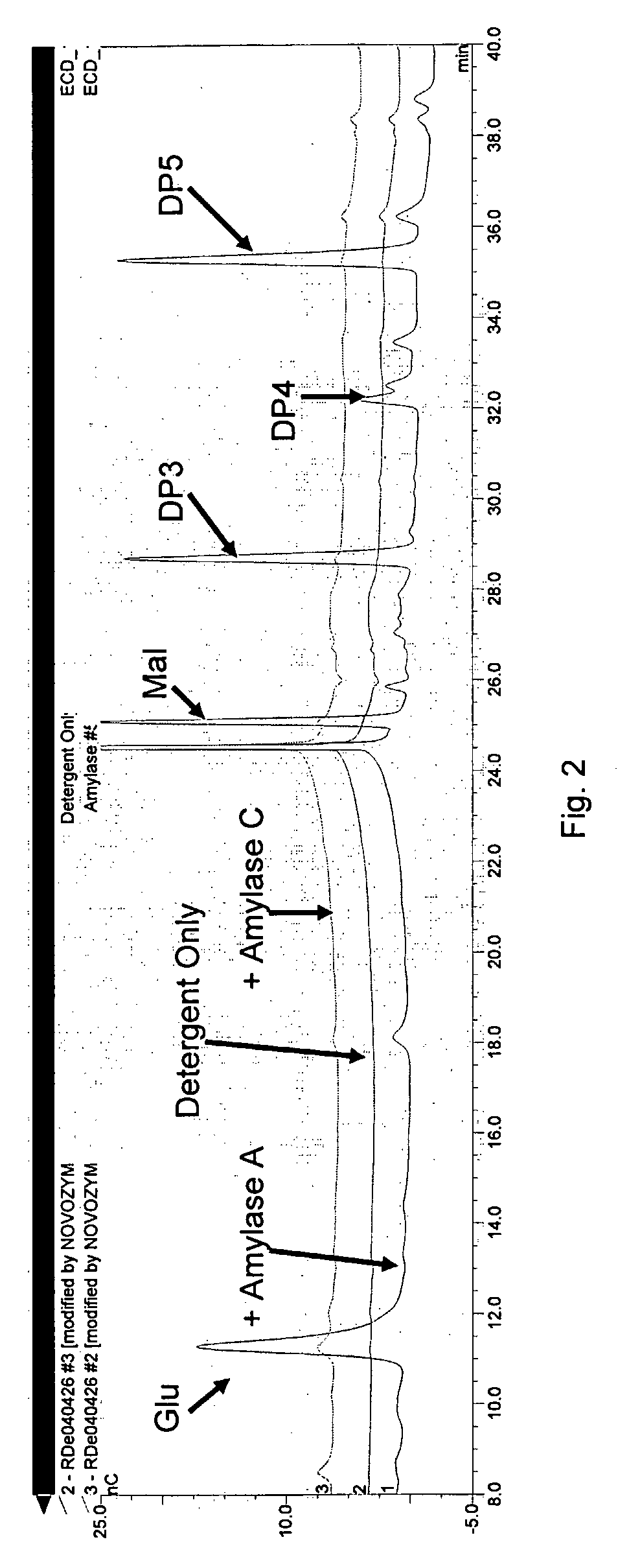
[0108]Biofilm Removal Using Alpha-Amylase A and Al pha-Amylase C
[0109]Biofilm reactors consisted of a 400 ml beaker, a magnetic stirrer, and 2 stainless steel coupons. The coupons are taped vertically to the sides of the beaker so that the bottom edge of the coupon rested on the bottom of the beaker. A stir bar is added and the beakers are covered with a circle of aluminum foil and autoclaved. 200 ml of sterile biofilm medium is added to each beaker. To prepare the inoculum, each bacterial strain (from Bacillus subtilis) is grown overnight at 28° C. on plate count agar. Using a sterile swab, each is suspended in sterile water to an OD686 of 0.100 and then diluted additionally to 10−1. Each assay consisted of 4 control beakers without enzyme, 2 beakers with 50 mg of enzyme protein per liter of solution, and 2 beakers with 100 mg of enzyme protein per liter of solution. Beakers are first incubated at 37° C. overnight with stirring to grow the biofilm on the stainless steel coupons. Fo...
example 2
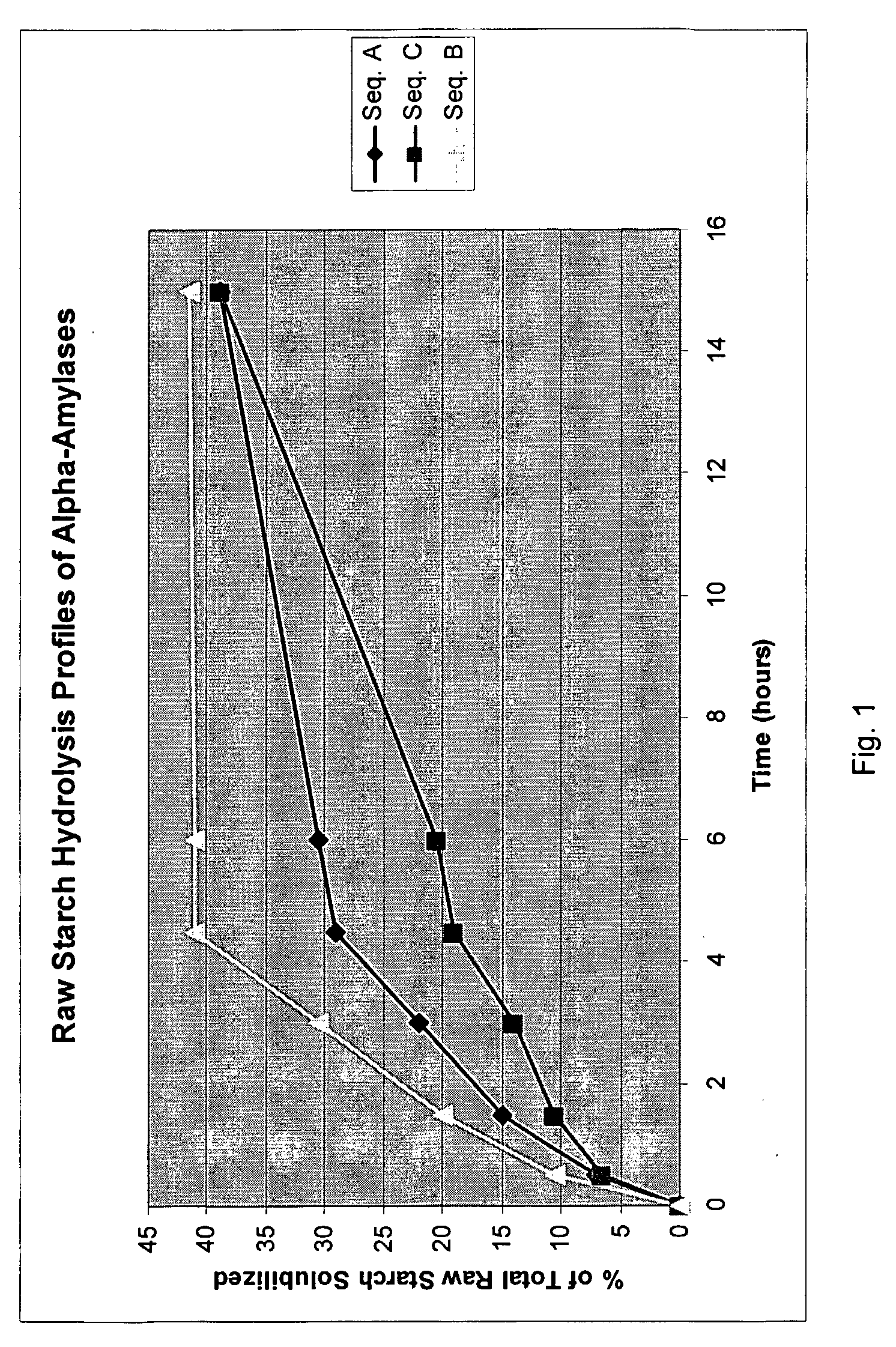
Raw Starch Solubilization Using Alpha-Amylase A, B, and C
[0110]The rate at which various alpha-amylases solubilize raw, unhydrated wheat starch was measured. Alpha-Amylase A, B and C, respectively, were used in the study.
[0111]Twenty five milliliters of a 1% raw wheat starch solution with pH 8 tris buffer and 15° dH was poured into a tube with lid and placed in a 40° C. water bath. The starting level of “reducing ends” was measured prior to addition of enzyme. The enzyme concentration used in the study was 3 mg enzyme protein per g raw wheat starch. One milliliter samples were taken out at different times. Twenty microliters of 1 M HCl was added prior to incubation at 99° C. for 10 minutes. The combination of acid and heat inactivates the amylase. Then 20 microL 1M NaOH was added to make sure the sample was no longer acidic. The sample was then diluted, incubated with color reagent (PHABH, potassium sodium tartrate, NaOH) at 95° C. for 10 minutes and finally centrifuged before measu...
example 3
[0113]Biofilm Removal Using Alpha-Amylase A and C in Combination with Protease E and Detergent
[0114]A mono-component biofilm of Escherichia coli (ATCC #11229) is grown on polycarbonate coupons in a pre-sterilized CDC biofilm reactor. At the start of the experiment, cultures of E. coli were grown on tryptic soy agar (TSA) overnight at 37° C. The next morning, a single colony was picked from the plate using a 1 microL sterile inoculation loop and added to a solution of 40 g TSB / liter of water. This solution was incubated at 37° C. overnight to grow up the culture. The following day, 1 milliliter of this culture was added to 400 milliliters of minimal media (0.30 g TSB / liter sterile water) contained in the CDC biofilm reactor. The solution was slowly stirred at 130 rpm and grown for 2 days at 22° C. in a non fed batch mode. After the 2 day growth period, the coupon holder rods and coupons were removed from the reactor, rinsed in sterile dilution water to remove planktonic cells, the co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com