Materials for data storage
a technology of data storage and materials, applied in the direction of instruments, conductors, record carrier materials, etc., can solve the problems of loss of emission, change in the optical properties of materials, and formation of mesoporous materials, and achieve the effects of high resolution, positive contrast, and extraordinary photostability of oligo-atomics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation and Methods
[0141]Various methods for the production of metal ion exchanged molecular sieves are available in the art. A method similar to that described by Jacobs et al. (Jacobs, P. A. & Uytterhoeven, J. B., 1979, Journal of the Chemical Society-Faraday Transactions 175, 56-64) was used for incorporating silver ions in molecular sieves and creating silver clusters. However many parameters like loading percentage of the zeolites, exchange time, length of temperature treatment, initial, gradient and final temperature of the temperature treatment, presence of gasses during the temperature treatment (e.g. in vacuum, in presence of oxygen, in presence of oxygen and nitrogen, in presence of hydrogen, in presence of CO and / or CO2 gas) and the presence of moisture in the air influences the finally formed types of clusters, oxidation state of the clusters and distribution and polydispersity of the types of clusters formed.
[0142]A typical procedure goes as follows: Zeolite 3A (Uni...
example 2
Emission
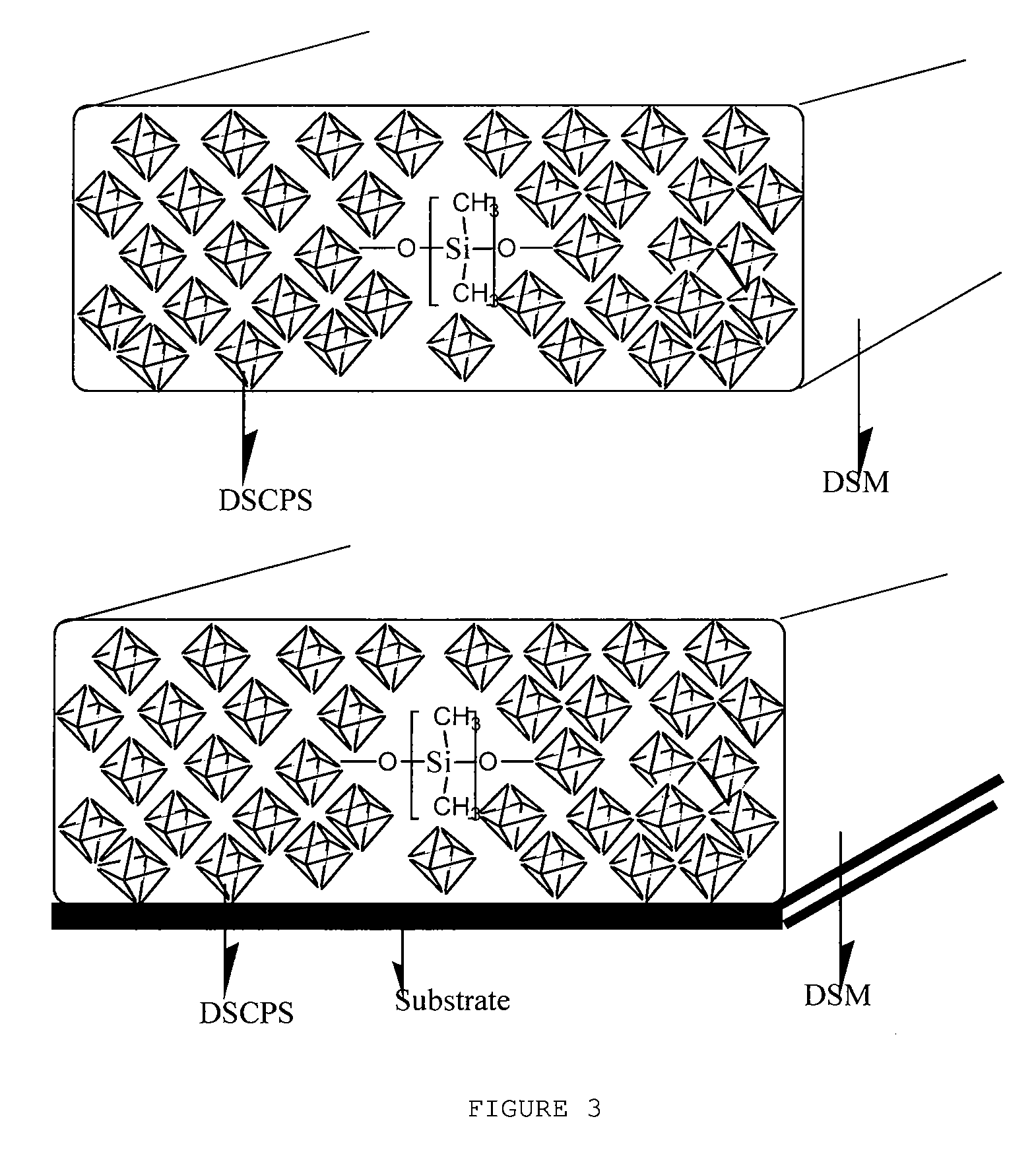
[0143]It was demonstrated that metal ion clusters especially silver in confined molecular sieves have a distinct and tunable emission throughout the VIS and NIR part of the electromagnetic spectrum while they are all excitable in the UV region. Thanks to the host matrix the confined metal clusters are prevented from aggregation with each other to form bigger non-emissive nanoparticles. Also they can be shielded from the outside environment (e.g., oxygen) if required by adding a silicon coating around the molecular sieves.
example 3
Photoactivation of Individual Spots within an Individual Silver-Exchanged Zeolite Crystal
Writing Patterns Inside the Zeolite Crystals
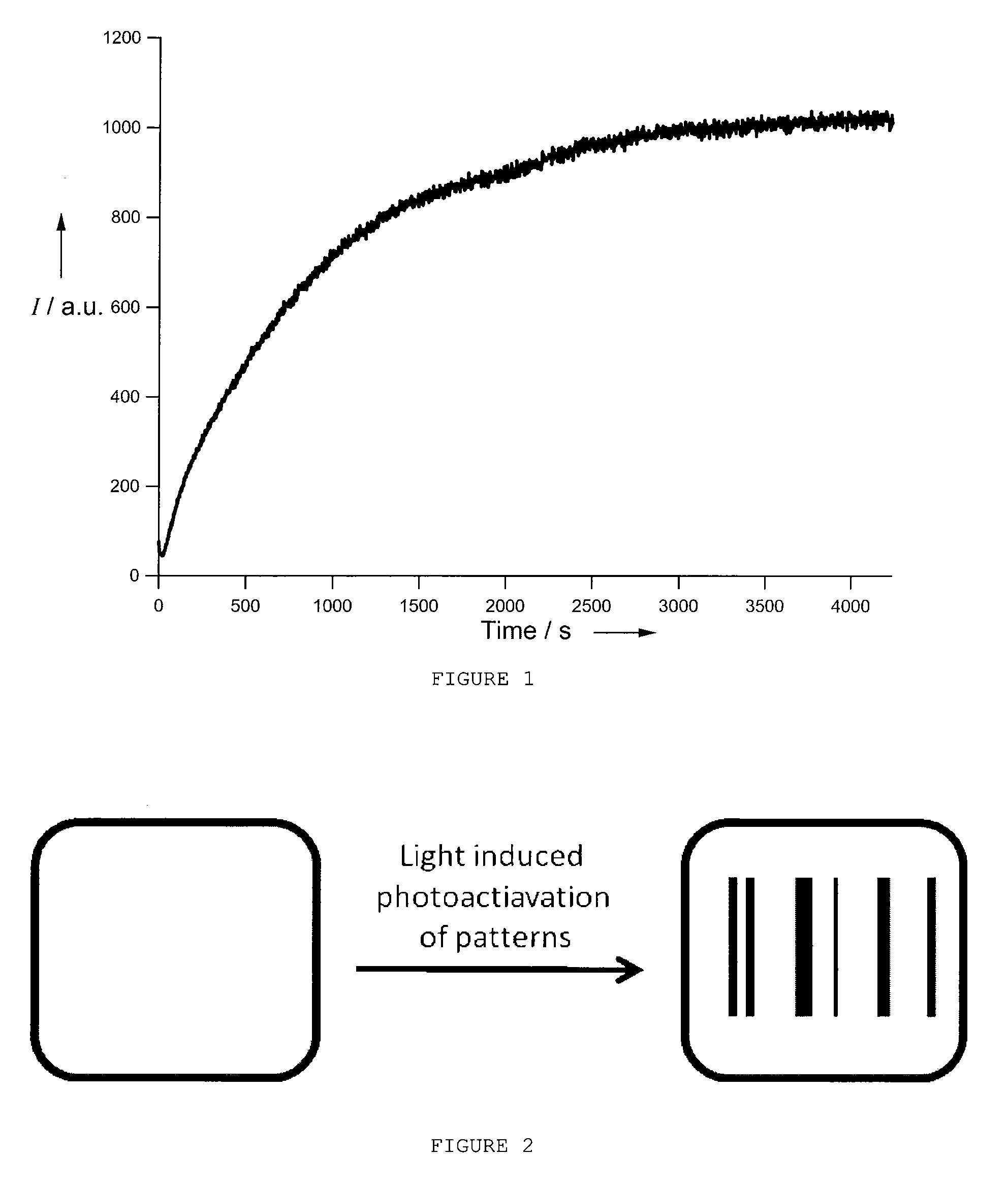
[0144]By irradiation with picoseconds pulsed 375 nm laser light of selected spots inside a silver-exchanged zeolite crystal, synthesized as described in example 1, using a confocal microscope setup, highly emissive silver clusters are formed inside a diffraction limited area, induced by the applied excitation source, giving rise to a strongly enhanced fluorescence (up to 200 times) from these selected spots. Typical irradiation powers for activation are 10 to 10,000 W / cm2 for photoactivation, whereas irradiation times vary from a 10 seconds for 10,000 W / cm2 to 1200 seconds for irradiation at 10 W / cm2.
[0145]By scanning the sample using a lower power (0.1 to 10 W / cm2), the photoactivated areas are easily recognized by their bright emission without further photoactivation during the scanning process.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com