Tissue Cavitation Device and Method
a tissue cavitation and tissue technology, applied in the field of surgical devices and methods, can solve the problems of weakened bone prophylactic fixation in this manner, fractures under normal physiologic loading conditions, skeletal fractures, etc., and achieve the effect of minimal invasiv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
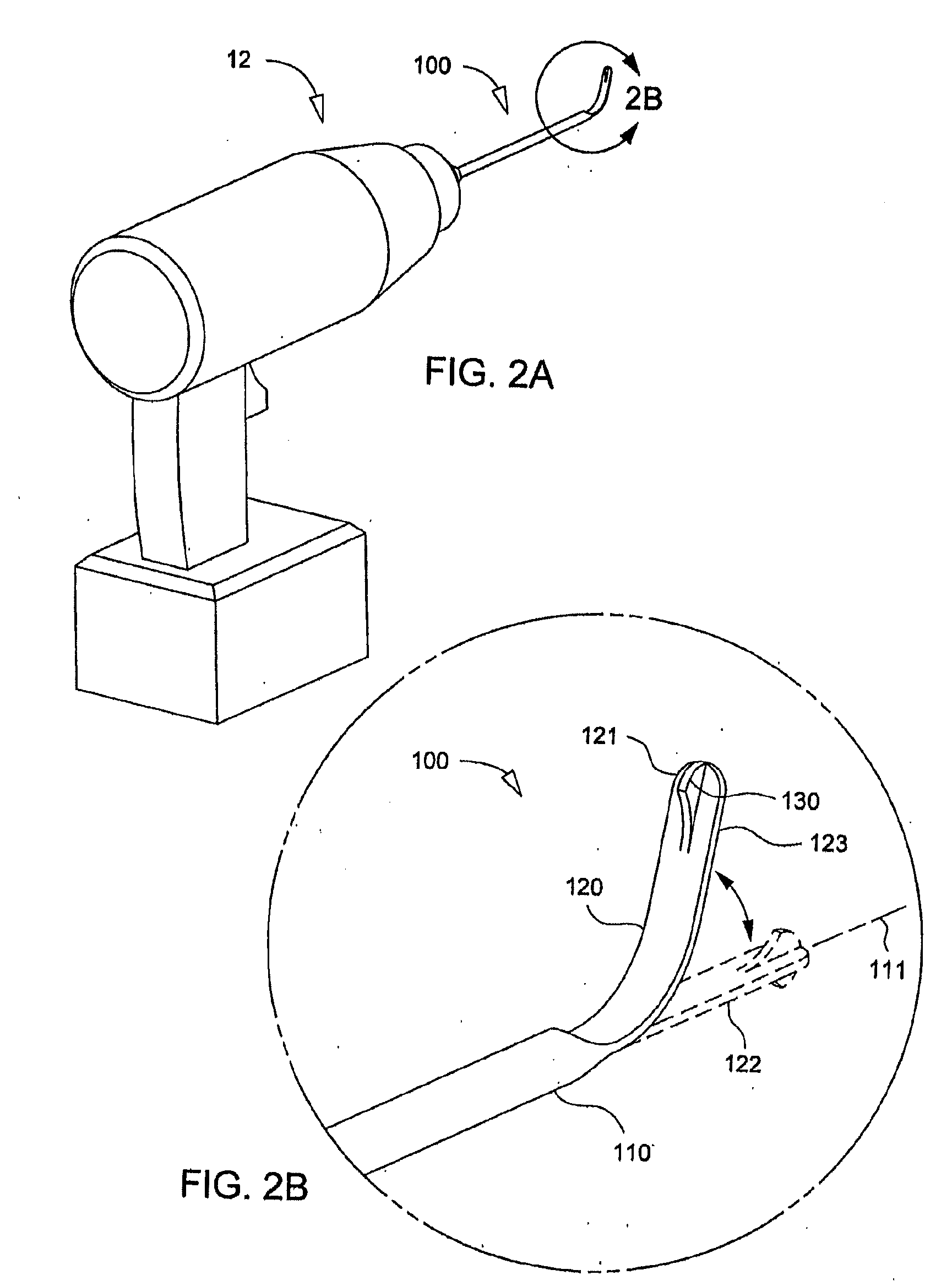
[0039]FIGS. 4A to 4C show the present invention, cavitation device 200, comprising rotatable shaft 210 and a flexible cutting element 220 having a free end 221 and a cutting tip 230. Flexible cutting element 220 is formed from a material, such as Nitinol, which is capable of shape change arising from thermal shape-memory behavior. Rotatable shaft 210 has a longitudinal axis 211. FIG. 4A shows cavitation device 200 at rest, with flexible cutting element 220 deformed below the transformation temperature to a first shape 222 in which flexible cutting element 220 is substantially colinear with longitudinal axis 211. When flexible cutting element 220 is in first shape 222, cavitation device 200 can be easily passed telescopically through the interior of an insertion tube 14, as shown in FIG. 4B. Referring now to FIG. 4C, as flexible cutting element 220 extends past distal end 15 of insertion tube 14, applied heat 24 activates the thermal shape-memory properties of flexible cutting elemen...
fifth embodiment
[0042]Another flexing means for biasing a flexible cutting element to move from a first shape toward a second shape is centrifugal force arising from rotational velocity of the shaft. Centrifugal force is the force that tends to impel a thing or parts of a thing outward from a center of rotation. FIG. 8A shows the invention, cavitation device 600, comprising rotatable shaft 610 with longitudinal axis 611 and flexible cutting element 620 having a cutting tip 630 and cutting flutes 632. Flexible cutting element 620 has a generally circular cross-section. FIG. 8B shows the cross-section of flexible cutting element 620 at the distal end of shaft 610 and illustrates that flexible cutting element 620 is a standard cable structure with a uniform helical arrangement of wires 622 concentrically stranded together. This type of cable structure has high strength and high flexibility. In additional, the cable structure has a naturally abrasive quality to aid in tissue cutting. Continuing to refe...
sixth embodiment
[0043]the present invention, cavitation device 700, is shown in FIGS. 9A and 9B. Referring to FIG. 9A, a plurality of flexible cutting elements 720 are generally colinear with the rotatable shaft 710 to form a first shape suitable for minimally invasive placement of the device within tissue. The proximal ends of flexible cutting elements 720 are rigidly attached to rotatable shaft 710, and the distal ends of the flexible cutting elements 720 are attached to a spindle 730. Referring now to FIG. 9B, when cavitation device 700 is rotated at a sufficient rotational velocity, flexible cutting elements 720 have a tendency to bow outward under the influence of centrifugal force. In this embodiment, the operator can also advance rotatable shaft 710 toward spindle 730 to assist in moving the flexible cutting elements 720 from the first shape toward a second shape, in which the flexible cutting elements extend outwardly from the axis of rotation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com