Catalysts for NOX reduction employing h2 and a method of reducing NOX
a technology of nox reduction and catalyst, which is applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal-oxide/metal-hydroxide catalysts, and separation processes, etc., can solve the problems of difficult construction of the supply network of hsub>2 /sub>, the use of ammonia to remove no/sub>x /sub>from diesel exhaust gas is very dangerous, and the urea-scr method is difficult to apply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Mixed Oxide Catalysts
[0035]Mixed oxide catalysts were prepared from oxides of A metals (Cu, Fe, Co, Ni) and B metals (Cr, Mn, Mo, V) through co-precipitation and mixing. The weight ratio of A metal oxide to B metal oxide was adjusted to 2, 1 and 0.5. As a precipitating agent, ammonia water or aqueous sodium bicarbonate was used, and pH of the mixed solution was adjusted to 6.0˜8.0. Any one A metal was reacted with any one B metal, thus preparing binary mixed oxide catalysts, and also, multicomponent mixed oxide catalysts were prepared using two or more kinds of these metals. The method of preparing some catalysts which are regarded as important is described below.
[0036]a) Cu—Cr Mixed Oxide Catalyst
[0037]A solution of 15.2 g of copper nitrate and 1.60 g of barium nitrate in 152 g of water was mixed with a solution of 15.4 g of potassium dichromate in 154 g of water, thus preparing a mixed solution. For sufficient mixing, the mixed solution was stirred for 30 min and th...
example 2
Preparation of Pt- or Pd-supported Mixed Oxide Catalyst
[0049]To evaluate NO2 reduction performance by a H2 reducing agent, Pt was supported in an amount of 0.1, 0.2, 1.0 and 2.0% by weight on the mixed oxide catalyst of Example 1. As a Pt precursor, hexachloroplatinic acid was dissolved in an amount of each of 0.1, 0.2, 1.1 and 2.1 g in 35 g of water, thus preparing a Pt solution, which was then added to 50 g of the mixed oxide catalyst. The catalyst reached equilibrium after 24 hours, and then dried in an oven at 80° C. and thus dewatered. The solution was burned in an electric furnace at 400° C. for 2 hours, placed in a quartz tube and then subjected to reduction treatment using a gas mixture containing N2 and H2 mixed at an equal ratio. The Pt-supported Cu—Cr catalysts and Fe—Mn catalysts were represented by Pt(0.1)-Cu—Cr, Pt(0.2)-Cu—Cr, Pt(1.0)-Cu—Cr, Pt(2.0)-Cu—Cr, Pt(0.1)-Fe—Mn, Pt(0.2)-Fe—Mn, Pt(1.0)-Fe—Mn, and Pt(2.0)-Fe—Mn.
[0050]On the other hand, Pd-supported mixed oxide c...
example 3
X-ray Diffraction Pattern of A-B Mixed Oxide Catalyst
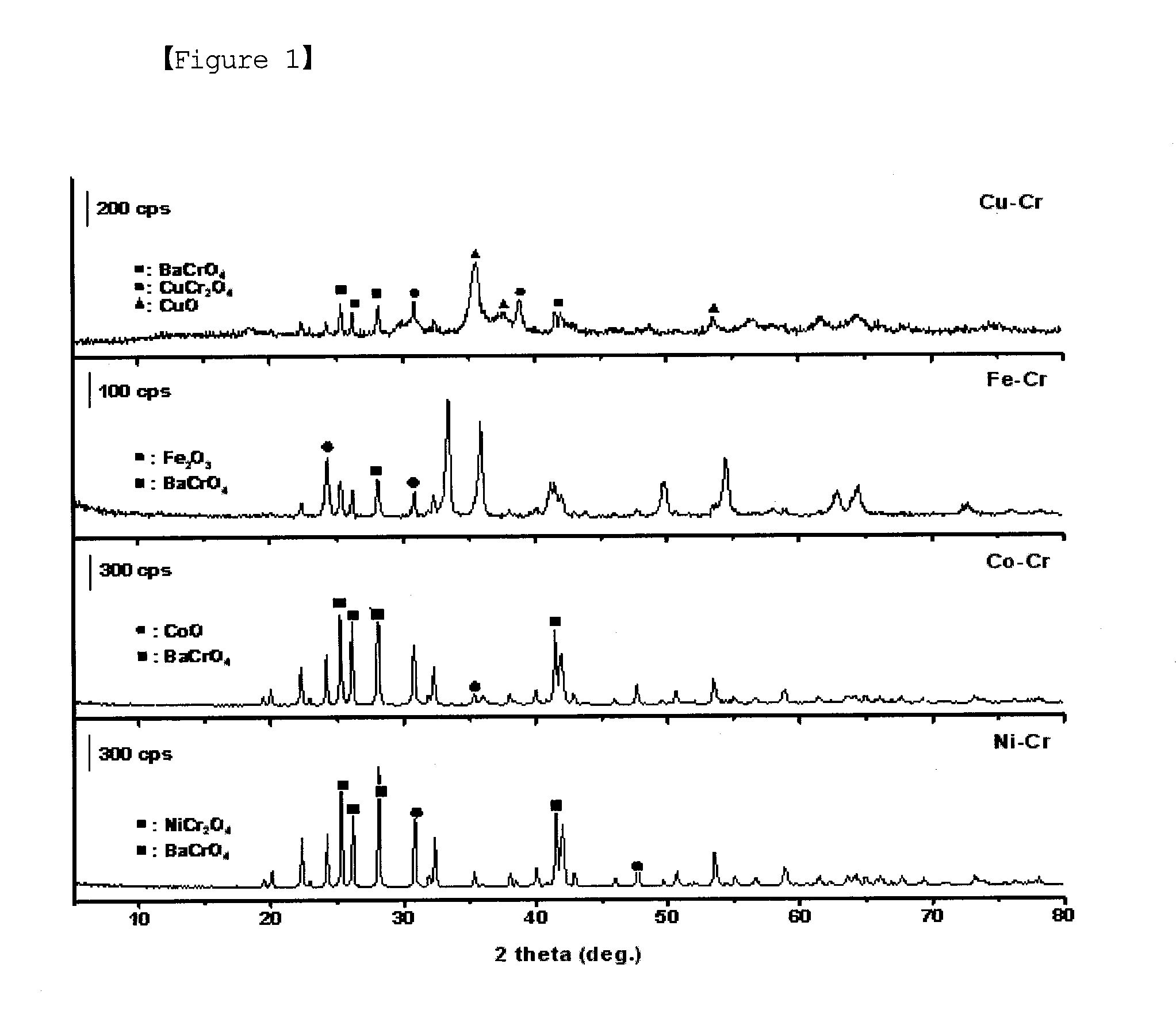
[0051]Among the A-B mixed oxide catalysts prepared in Example 1, the catalysts in which the B metal was Cr and the A metal was Fe, Co, Ni and Cu were burned, after which X-ray diffraction patterns thereof were measured. The results are shown in FIG. 1. The diffraction pattern of the mixed oxide catalyst was very complicated because the diffraction peaks of metal oxides alone and in combinations thereof coexisted. In the Cu—Cr catalyst, the diffraction peaks of CuO, CuCr2O4 and BaCrO4 were shown. In any catalyst, the diffraction peak of BaCrO4 added to improve structural stability of the catalyst was distinctly observed. In the Cu—Cr and Fe—Cr catalysts, the diffraction peak of CuO or Fe2O3 was strongly observed. In the Fe—Cr and Co—Cr catalysts, the diffraction peaks difficult to confirm were present, and thus the mixed oxide catalysts were seen to have a complicated structure.
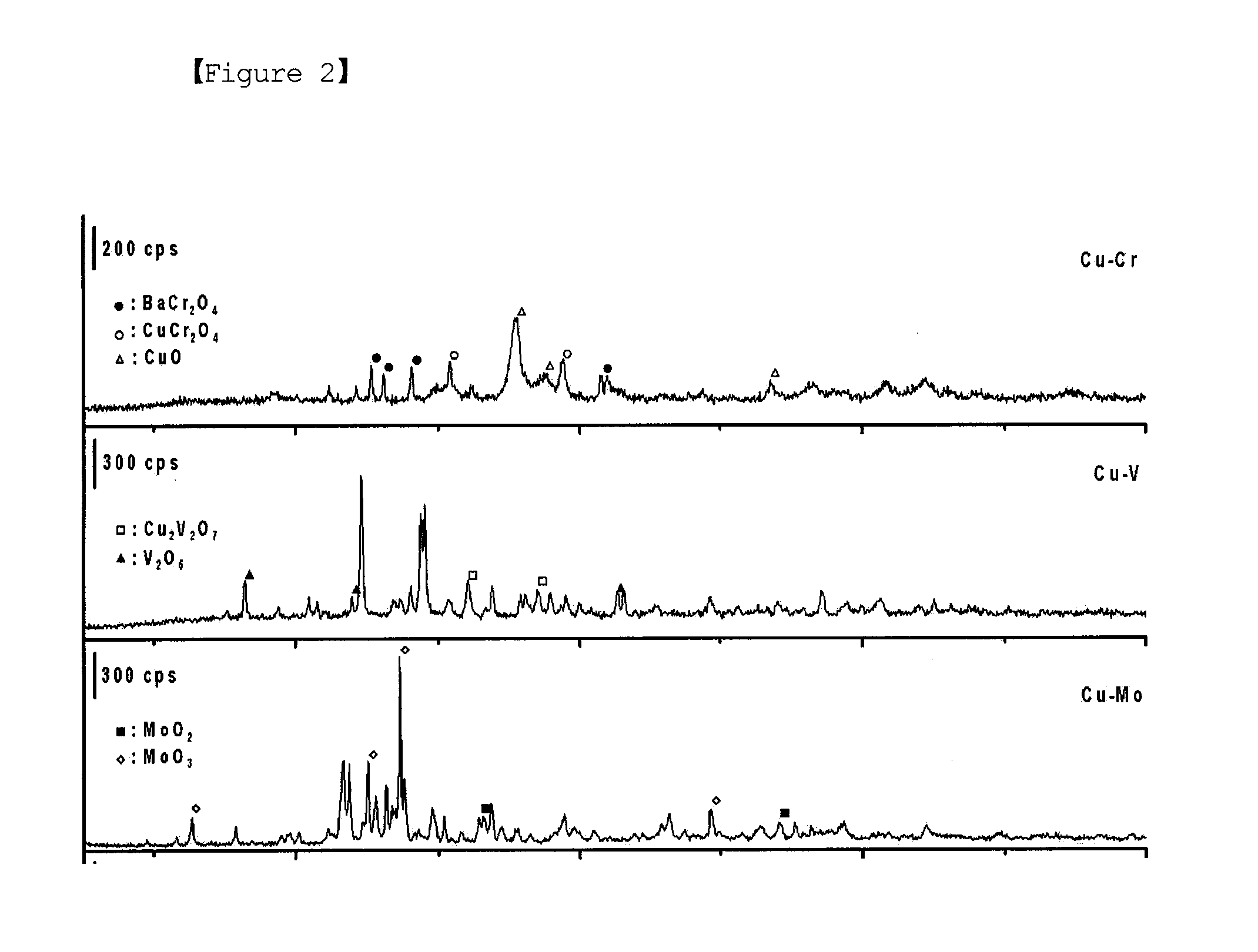
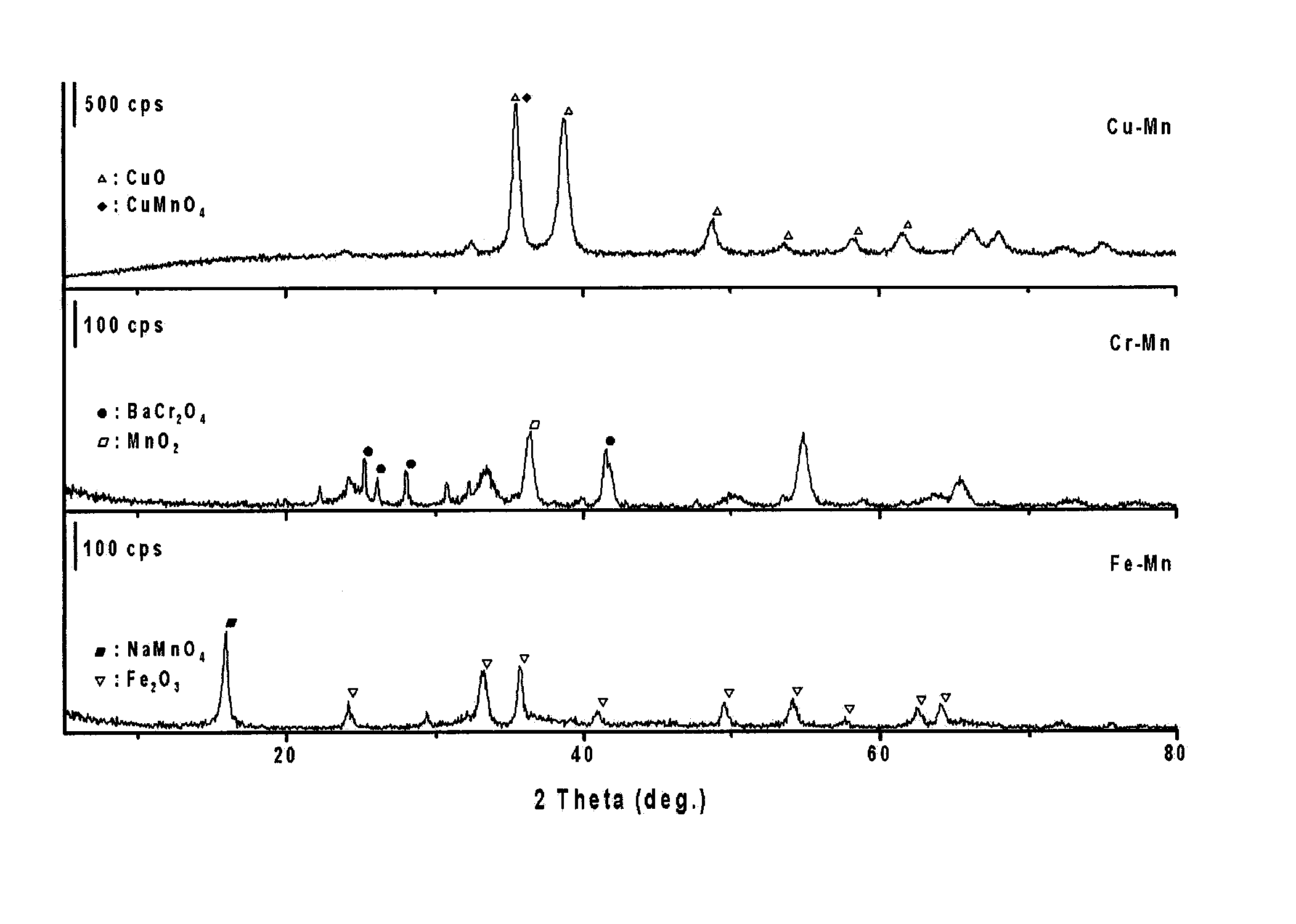
[0052]FIG. 2 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com