Reduction of bioparticle levels of an organism
a bioparticle level and organism technology, applied in the field of cell biology, can solve the problems of unreliable fluids, unreliable methods, time-consuming, expensive, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing side effects, reducing costs, and reducing the number of stents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
rous Beads to Reduce Levels of Bioparticles in Biofluids
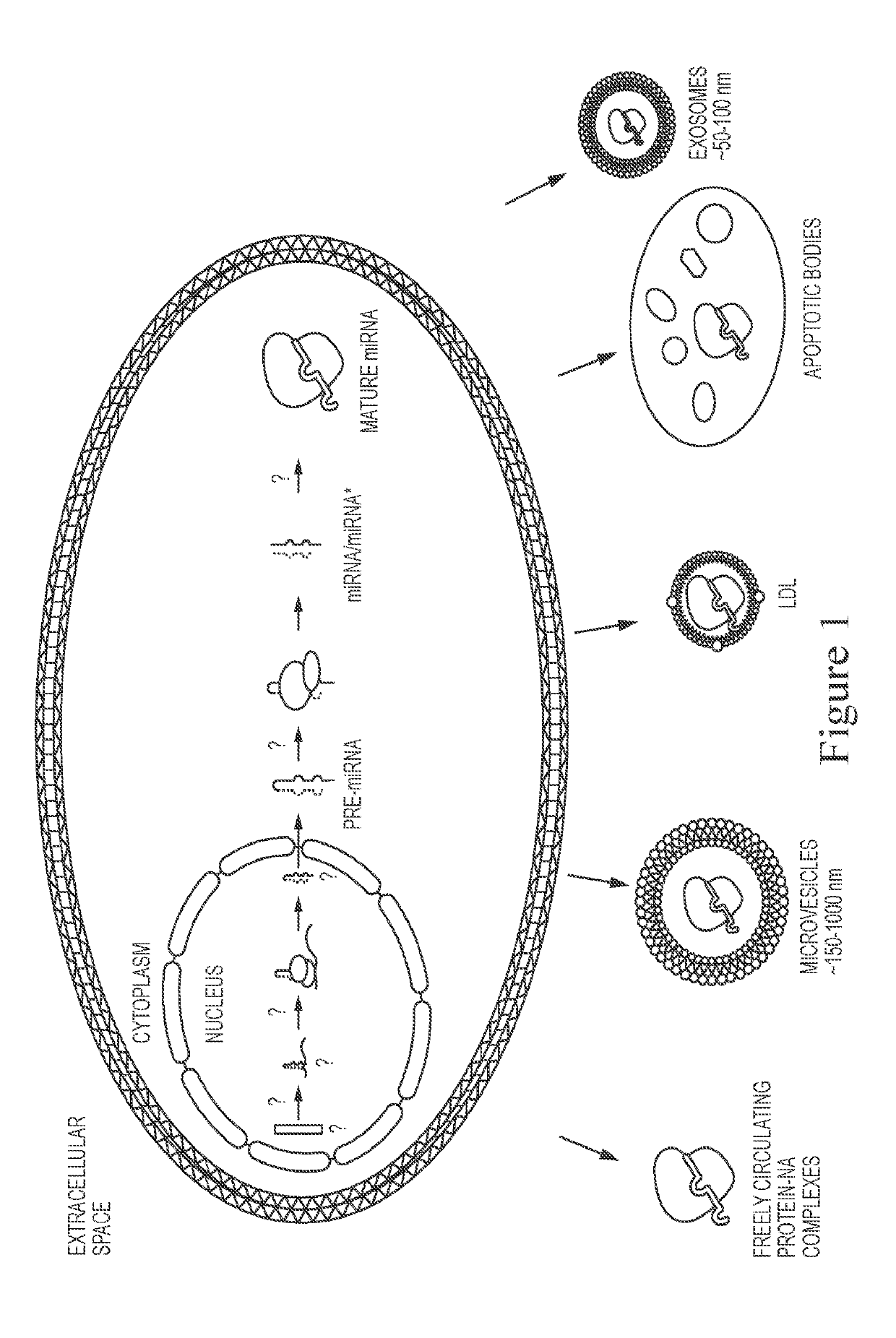
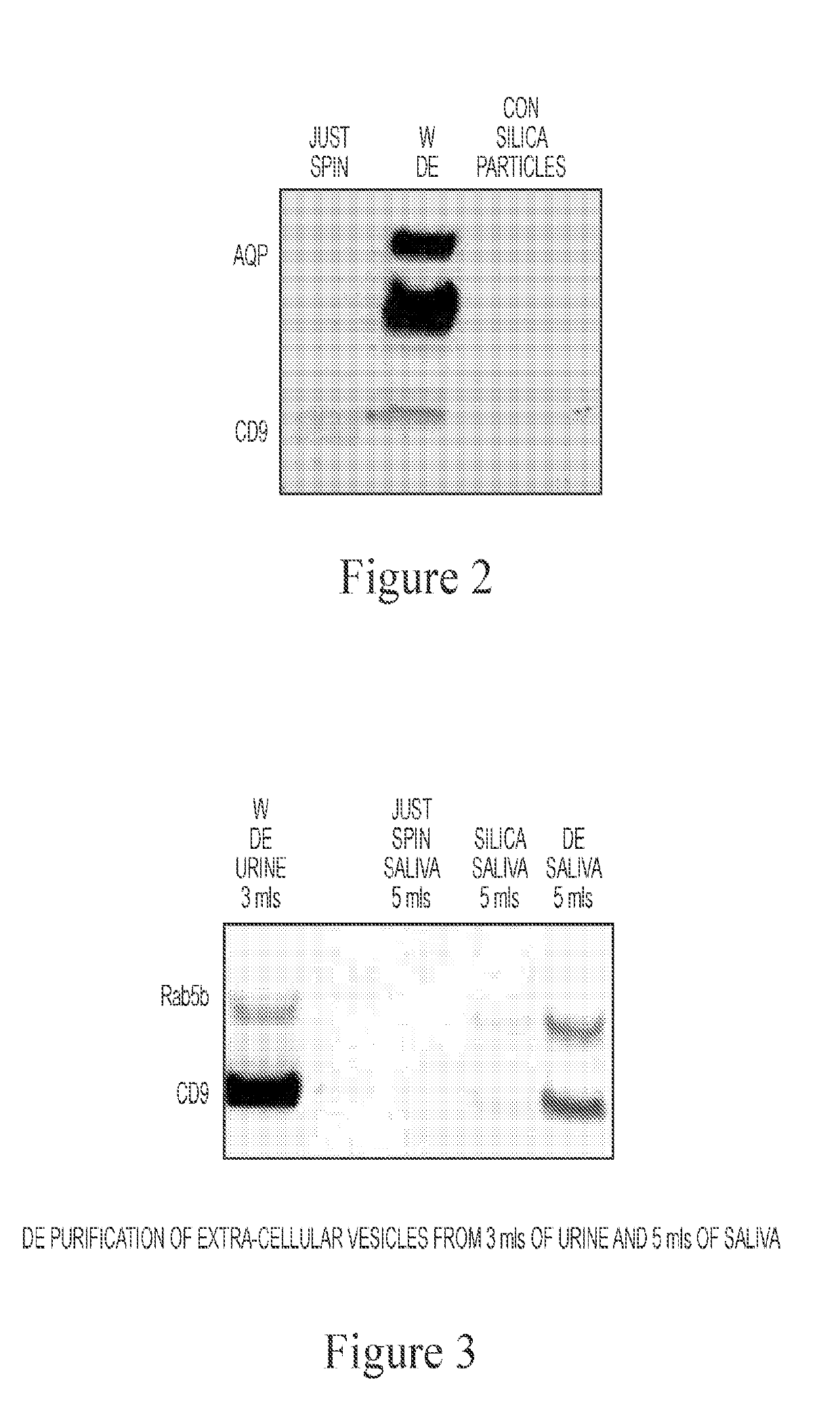
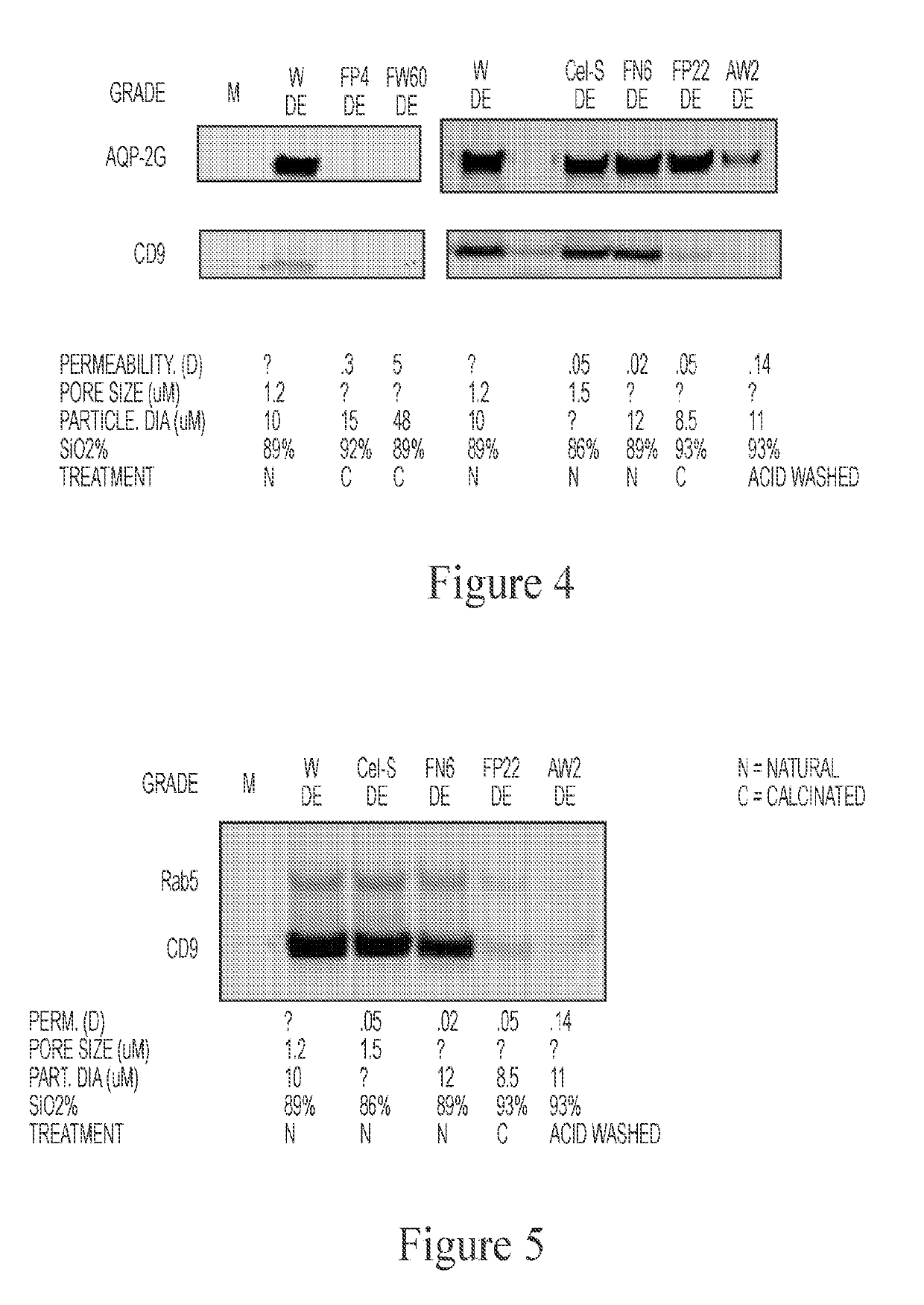
[0149]A broad range of biomarkers are secreted from cells, such as miRNA, proteins, lipids, glycoproteins, DNA, mRNA, tRNA, etc., which can exist in relatively stable form outside of cells, including but not limited to the following forms: protein-nucleic acid complexes, exosomes, microvesicles, LDL particles, and apoptotic bodies (FIG. 1). It was identified that Diatomaceous Earth (DE) isolated vesicle protein markers from urine, whereas control silica did not (FIG. 2). Diatomaceous Earth (DE) was also identified to isolate saliva exosomes (FIG. 3). DE (optionally non-calcinated (N) and low permeable / small pore size) also isolated EVs from urine (FIG. 4). Calcination and acid washing were identified to decrease DE's affinity for exosomes (FIG. 5). To examine the effect of pore size upon efficacy of isolation of bioparticles from biofluids, Perlite (Sil-Kleer) possessing smaller pore sizes / permeability that DE was examined, and...
example 2
in a Porous Container and Introduced to the Mouth of a Subject Isolated Exosomes
[0150]As shown in FIG. 9, Diatomaceous Earth placed in a porous cellulose bag, which was then held in the mouth of a subject for 30 minutes successfully and robustly sequestered exosomes, as evidenced by detection of the exosomal marker, Rab5b. A control Silica gel placed in the same type of container (cellulose bag) was meanwhile shown not to sequester this marker from saliva.
example 3
ic Reduction of Bioparticles in Urine of a Subject Having or at Risk of Developing Bladder Cancer
[0151]In an exemplary therapeutic method of the invention, a subject having or at risk of developing bladder cancer is identified. Porous beads, e.g., DE, are deposited in a porous, implantable membrane-bounded pouch or device. The implantable pouch or device is inserted into the bladder of the subject, optionally at or near a site of an existing tumor, and in contact with the urine of the subject. The device remains implanted in the subject for an appropriate period of time (e.g., ranging from a single day to a number of months or even years, noting the inert / non-toxic nature of both the implantable pouch or device and its contents (e.g., DE)). Growth, progression and / or metastasis of cancer (or markers of pro-cancer signaling) in the subject is assessed, using art-recognized methods, relative to an appropriate control subject or value, and the therapeutic efficacy of the implantable po...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com