RTEF-1 variants and uses thereof
a technology of rtef-1 and variants, applied in the field of molecular biology, cell biology, clinical medicine, pharmacotherapy, oncology, can solve the problems of malignant phenotype, subsequence loss of function, excess tissue loss, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing vegf production and reducing the secreted vegf165 level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
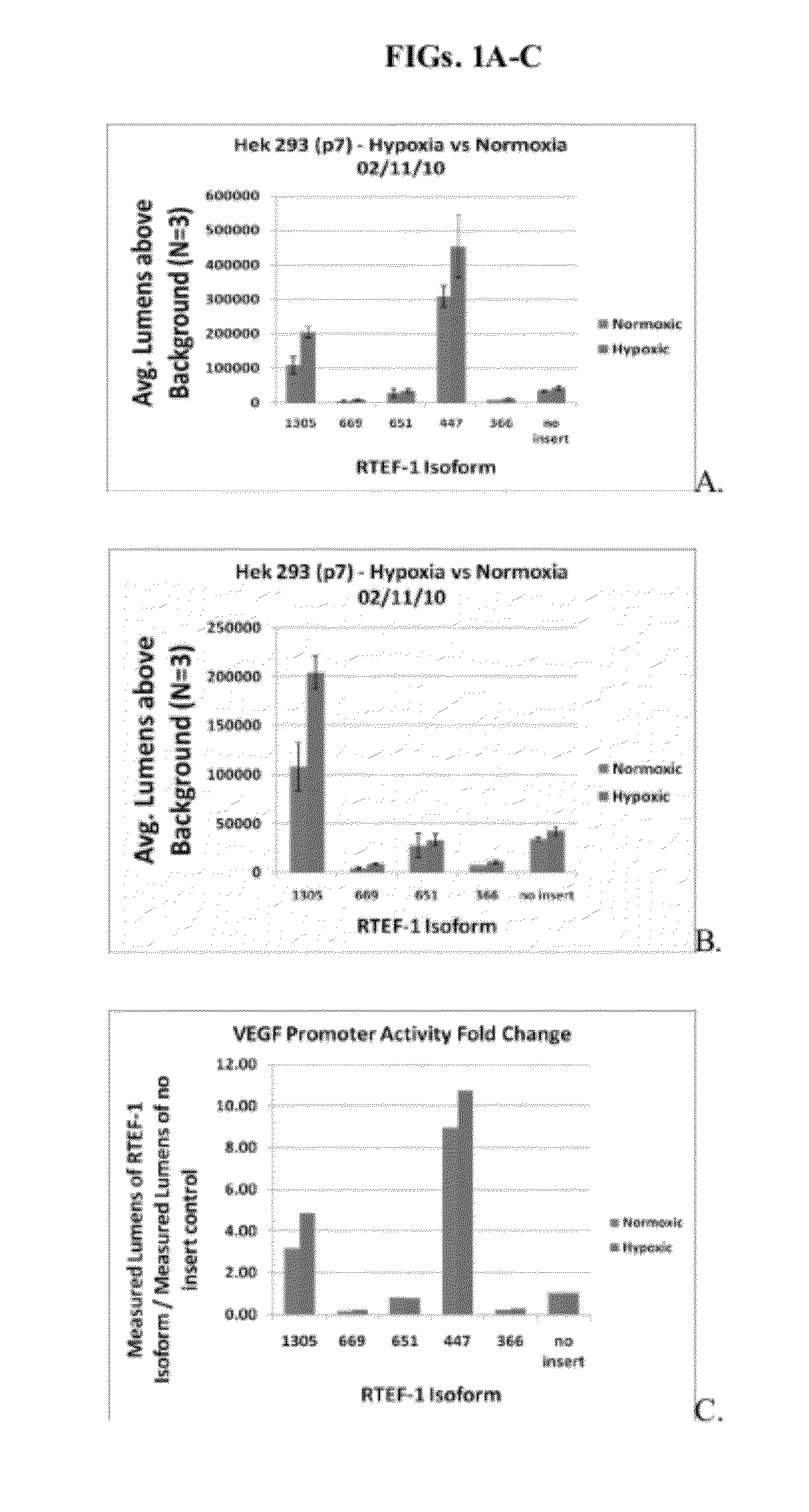
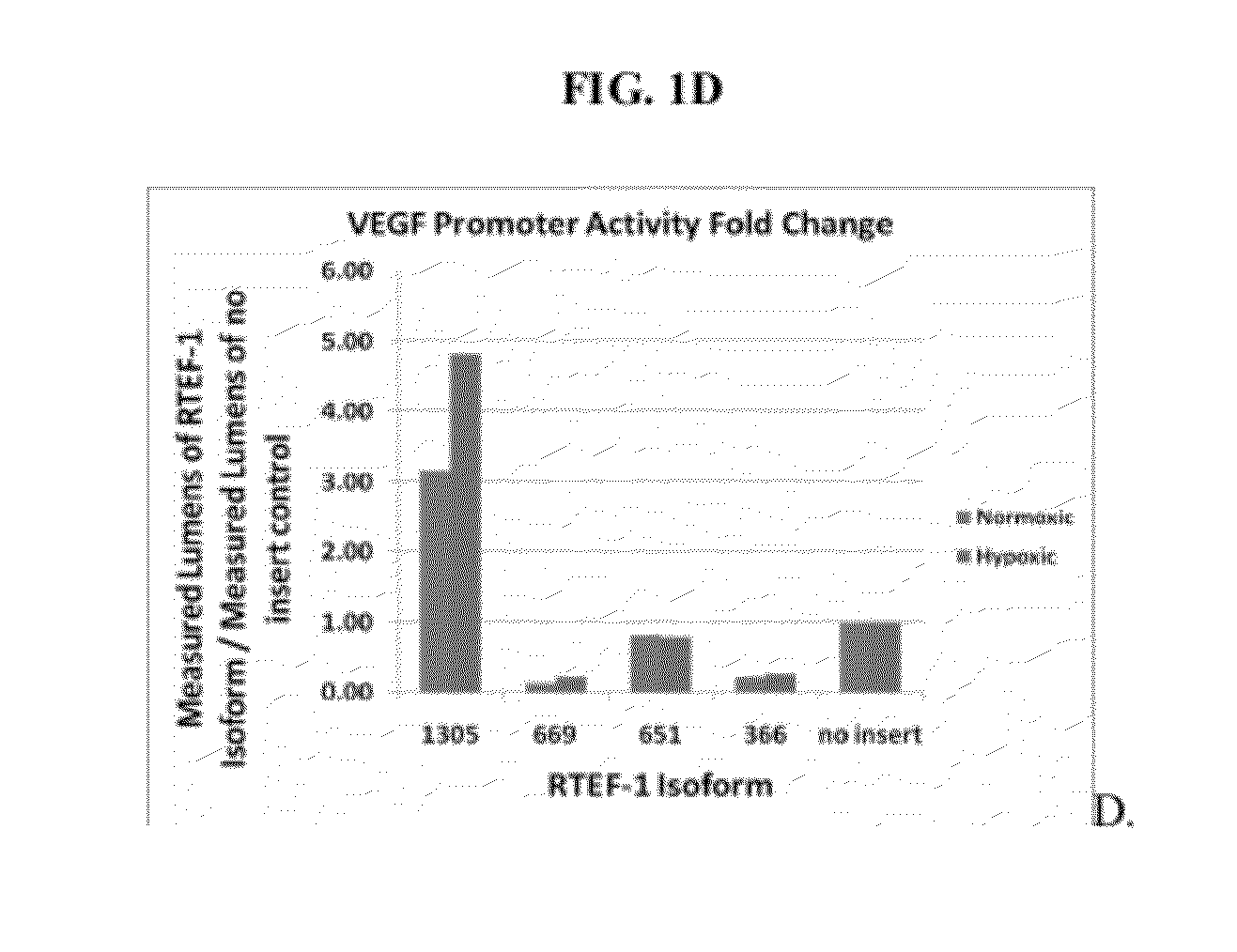
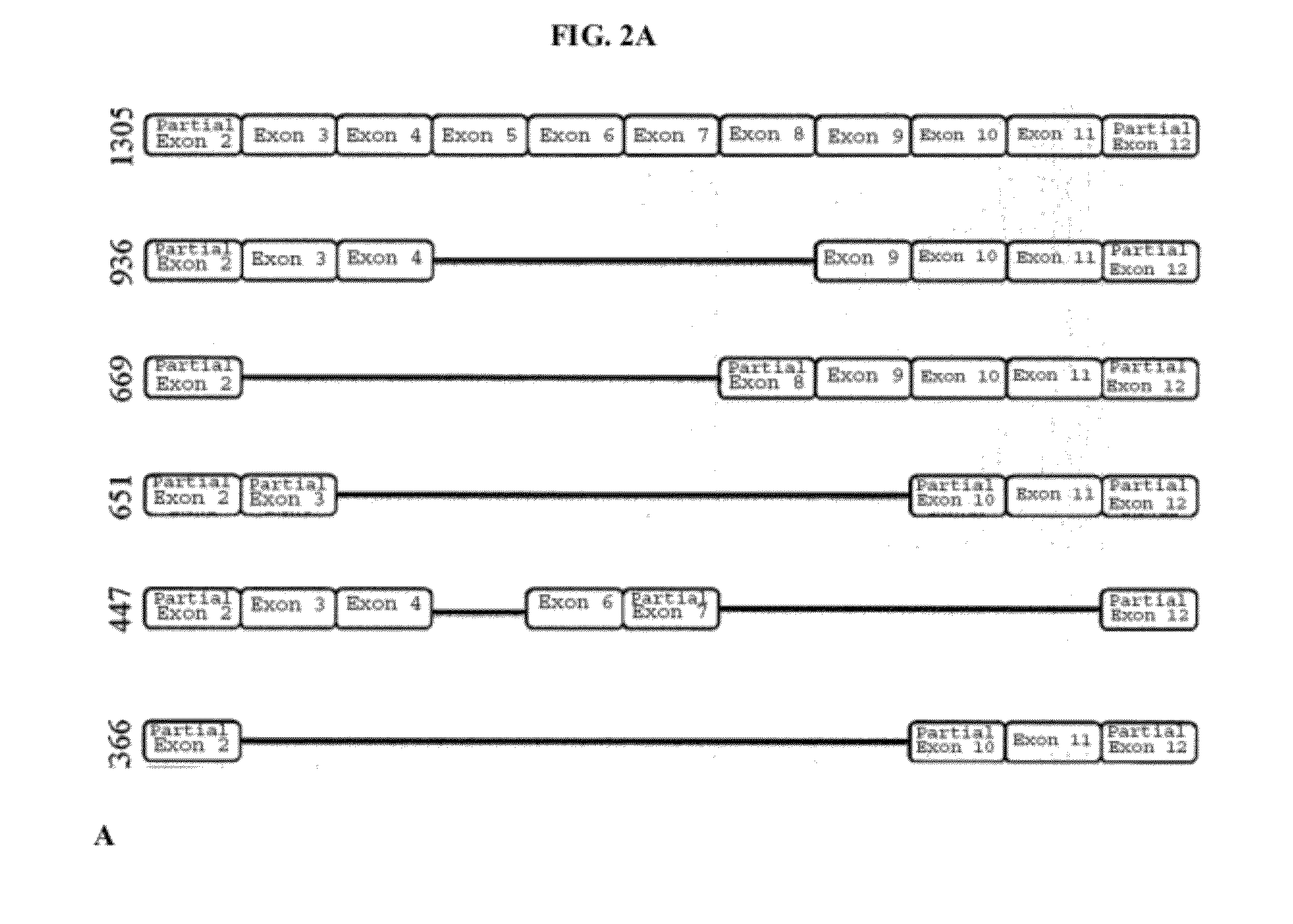
Relative VEGF Promoter Activity of Variant RTEF-1 Isoforms
[0196]Studies were conducted to examine the relative VEGF promoter activity of selected isoforms of RTEF.
[0197]The pSEAP assay is essentially a chemiluminescence assay in which two plasmids are electroporated into cells. One plasmid (pcDNA) contains a specific RTEF-1 isoform and the other plasmid (pSEAP plasmid) contains the VEGF promoter fused to the secreted alkaline phosphatase gene. Transcriptional activity on the exogenous VEGF promoter results in a secretable, thermo-stable, alkaline phosphatase (AP) protein. The abundance of AP protein can be measured by a luminescene assay. Thus, the measured lumens are indicative of the amount of AP in the media, which is a directly correlated to the activity on the promoter (human VEGF) driving the expression of the AP gene. Lumens measured from the ‘no insert’ control are indicative of the endogenous transcription factors (and cofactors) acting upon the exogenous VEGF promoter.
[019...
example 2
Expression of SRF, MAX, and YAP65 in Cell Lines
[0211]Materials and Methods
[0212]Hek293 cells were grown in 6-well plates with appropriate media to 80% confluency. The media was removed and the cells were washed with PBS. Cellular RNA was isolated using the RNAquous-4 PCR kit (Ambion®). Briefly, 300 μl of lysis buffer was added to the cells and incubated for 5 minutes at room temperature. The lysate was collected and an equal volume of 65% ethanol was added and mixed by inversion. The mixture was passed through an RNA collection filter by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm and washed three times with wash buffer (Ambion®) by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm. Filters were centrifuged once more to completely dry the filter. Elution buffer (Ambion®) heated to 75° C. was added to the column and centrifuged to elute the RNA. RNA was quantified by a UV spectrophotometer using a 260 nm wavelength. Total RNA at a concentration of 250 ng was used for reverse transcription using the Omni-script RT kit (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| 260 nm wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com