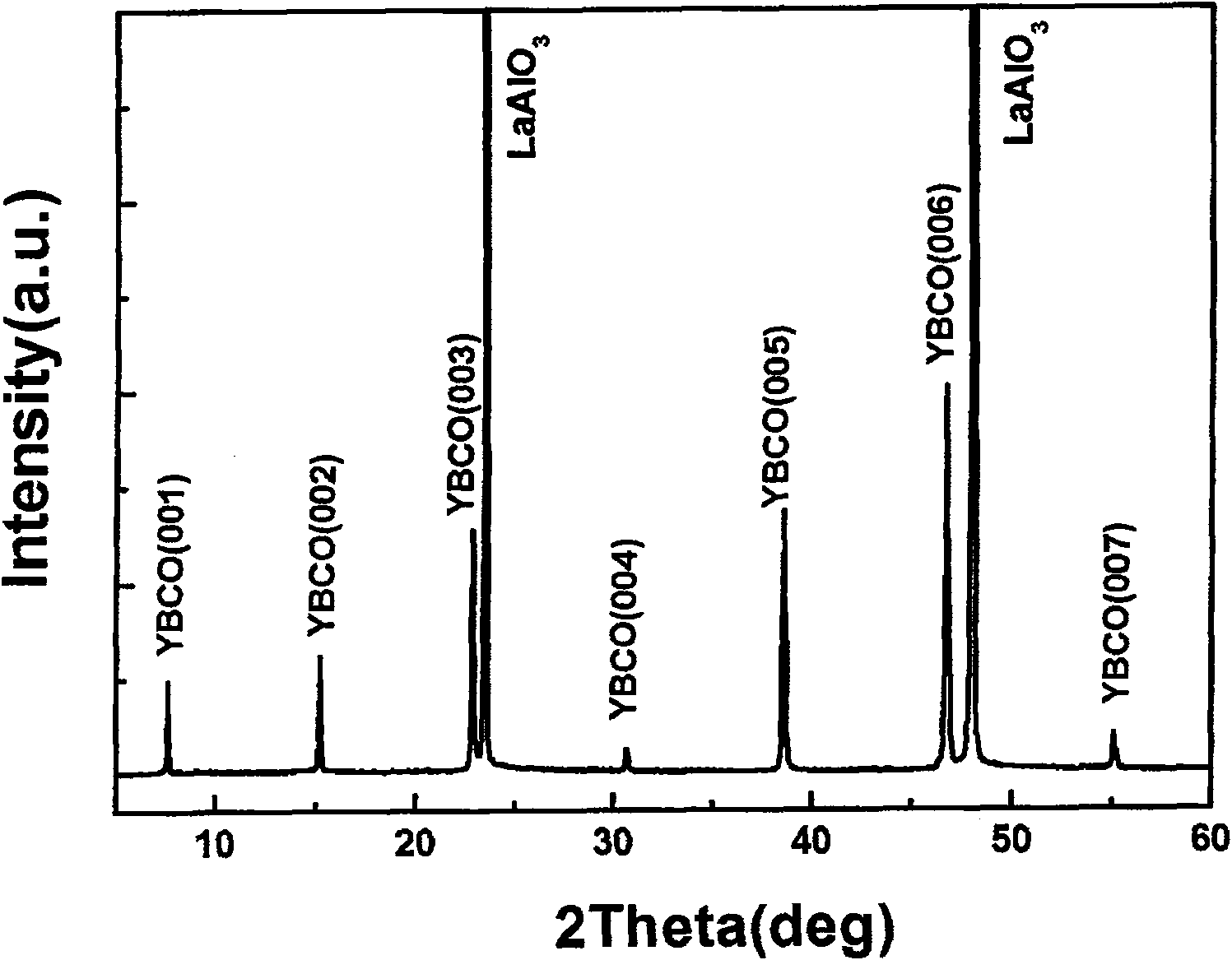
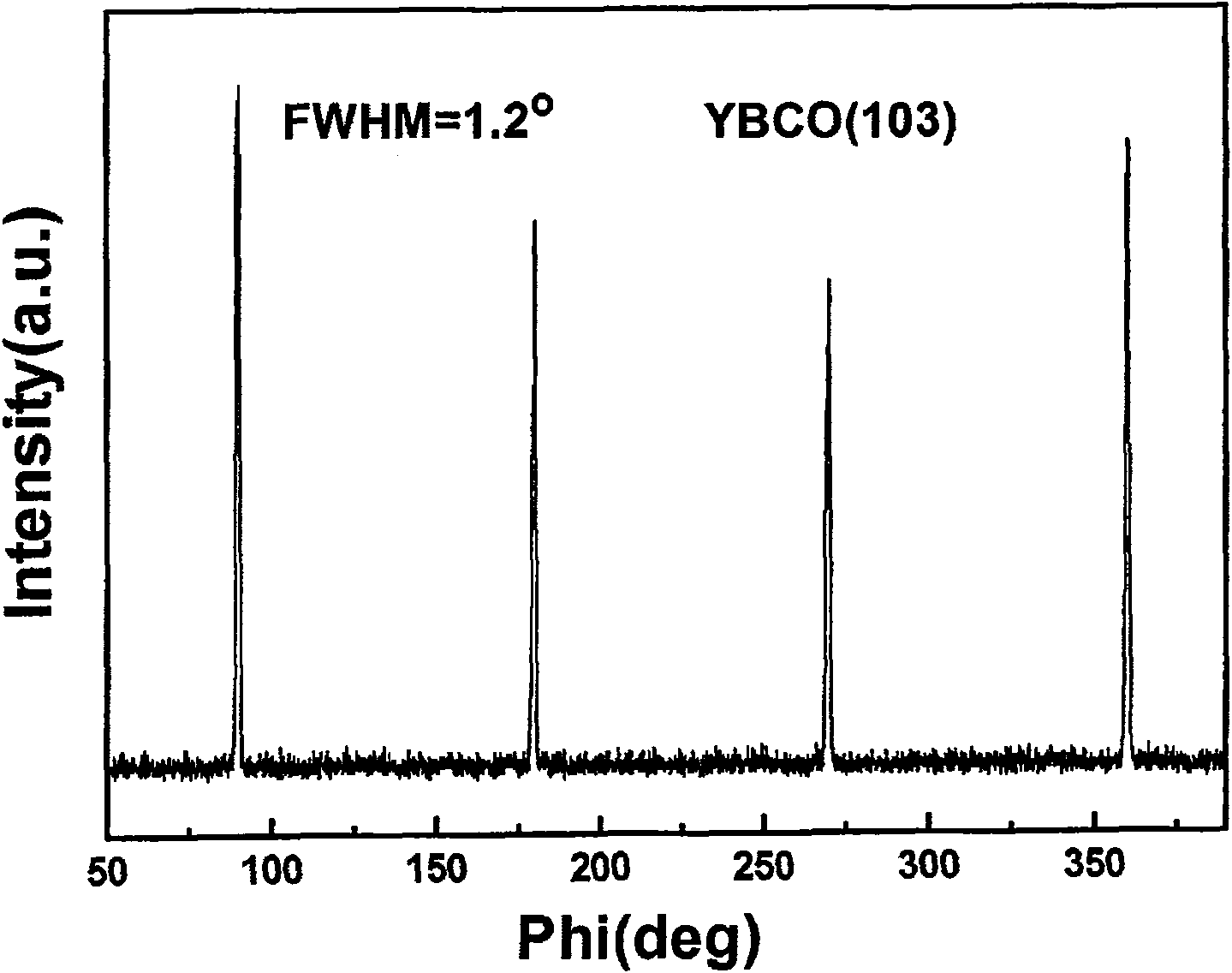
Method for polymer-assistant depositing high temperature superconducting coating conductor superconducting layer
A polymer-assisted, high-temperature superconducting technology, used in the manufacture/processing of superconductor devices, can solve the problems of expensive equipment, reduced film superconductivity, pores and micro-cracks, etc. Thick, inexpensive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0034] A kind of specific embodiment of the present invention is:
[0035] A method for polymer-assisted deposition of a high-temperature superconducting coating conductor superconducting layer, the specific method of which is:
[0036] a. Preparation of precursor solution: dissolving yttrium acetate, barium acetate, and copper acetate in propionic acid according to the stoichiometric ratio of rare earth: barium: copper in a ratio of 1:2:3 to obtain a precursor solution.
[0037] b. Preparation of coating colloid: In the precursor solution, add 3 parts of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) macromolecular additives and stir well to obtain a uniform and transparent coating colloid with a certain viscosity.
[0038]c. Colloid coating and drying: Spin coating is used for coating, that is, the colloid is dropped on the substrate and rotated with a coater to obtain a uniform coating film, and then dried at 100°C for 20 minutes.
[0039] d. Decomposition heat treatment: In a dry argon atmosphe...
Embodiment 2
[0043] This example is basically the same as Example 1, the difference is:
[0044] In the preparation of the precursor solution in step a, the rare earth acetate is dysprosium acetate.
[0045] In the d-step decomposition heat treatment process, the temperature is raised from room temperature to 135°C at a rate of 3°C / min in a dry argon atmosphere, and then water vapor with a dew point of 20°C is introduced into the furnace, and argon gas is introduced at the same time to form moist argon At this time, the temperature was raised to 450°C at a rate of 1°C / min, and the temperature was kept for 0.75 hours.
[0046] In the phase-forming heat treatment of step e, water vapor with a dew point of 30°C and argon gas are introduced into the tube furnace in the upward step to form a humid argon protective atmosphere, and the furnace temperature is rapidly raised at 25°C / min To 840°C, keep warm for 5 minutes; then cool down to 775°C at 7°C / min, keep warm for 1 hour, and finally drop to...
Embodiment 3
[0049] This example is basically the same as Example 1, the difference is:
[0050] In the preparation of the precursor solution in step a, the rare earth acetate is gadolinium acetate.
[0051] In the preparation of the coating colloid in step b, 5 parts of polyethylene glycol (PEG) was added to the precursor solution as a polymer material additive.
[0052] The drying in step c is 150° C. for 15 minutes.
[0053] In the d-step decomposition heat treatment process, the temperature is raised from room temperature to 125°C at a rate of 2°C / min in a dry argon atmosphere, and then water vapor with a dew point of 15°C is introduced into the furnace, and argon gas is introduced at the same time to form moist argon At this time, the temperature was raised to 470°C at a rate of 0.25°C / min, and kept for 1 hour.
[0054] During the phase-forming heat treatment in step e, water vapor with a dew point of 35°C and argon gas are passed into the tube furnace in step d to form a humid argo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com